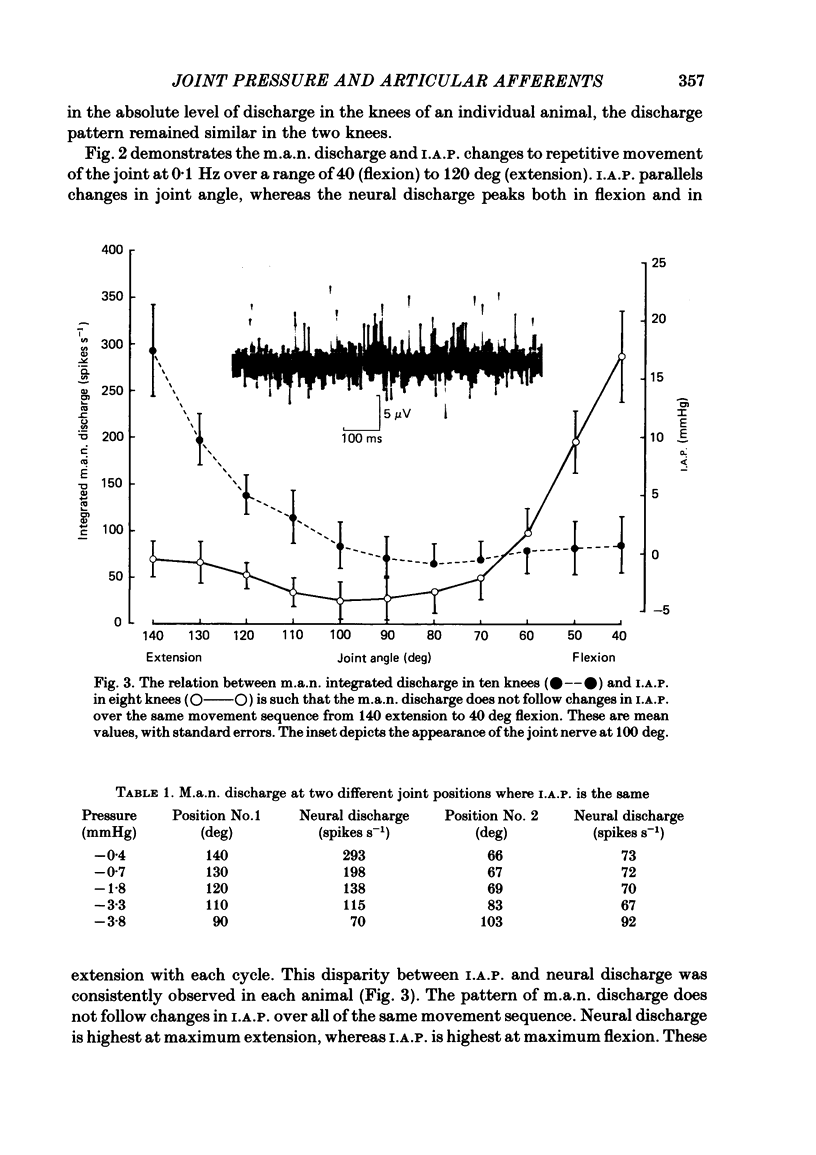
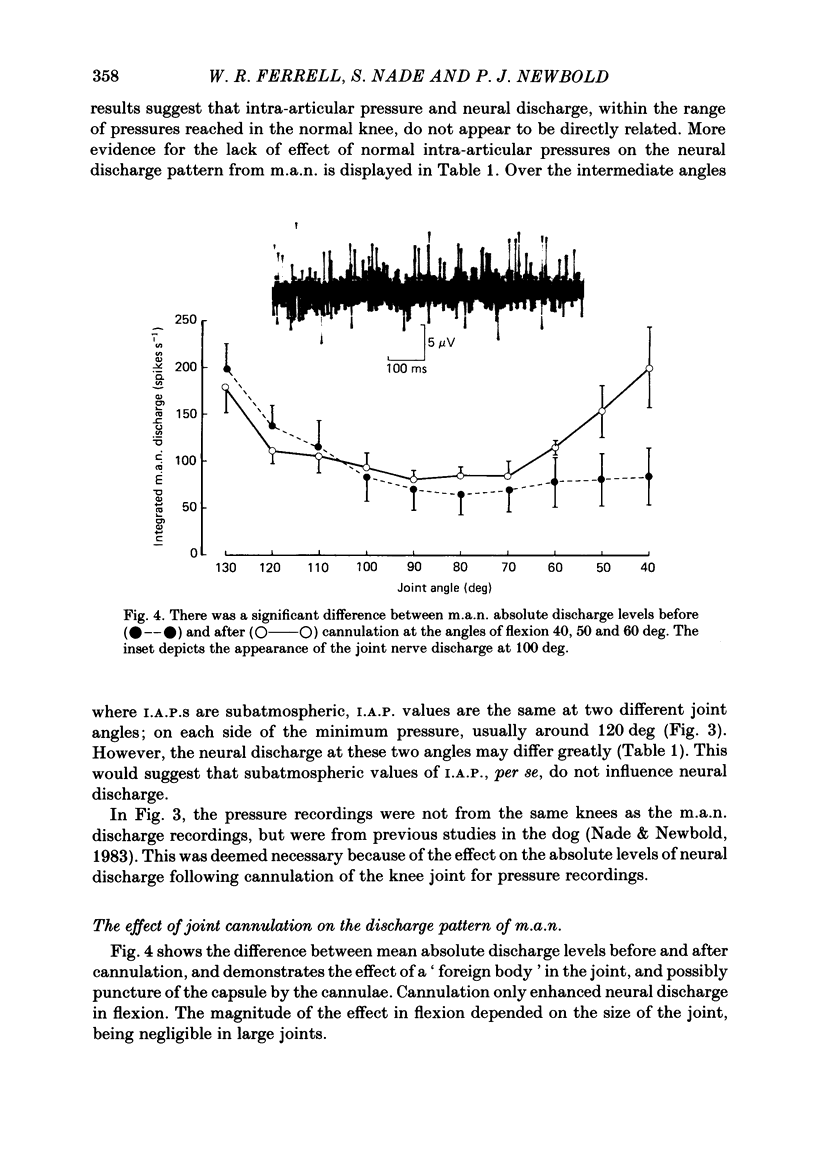
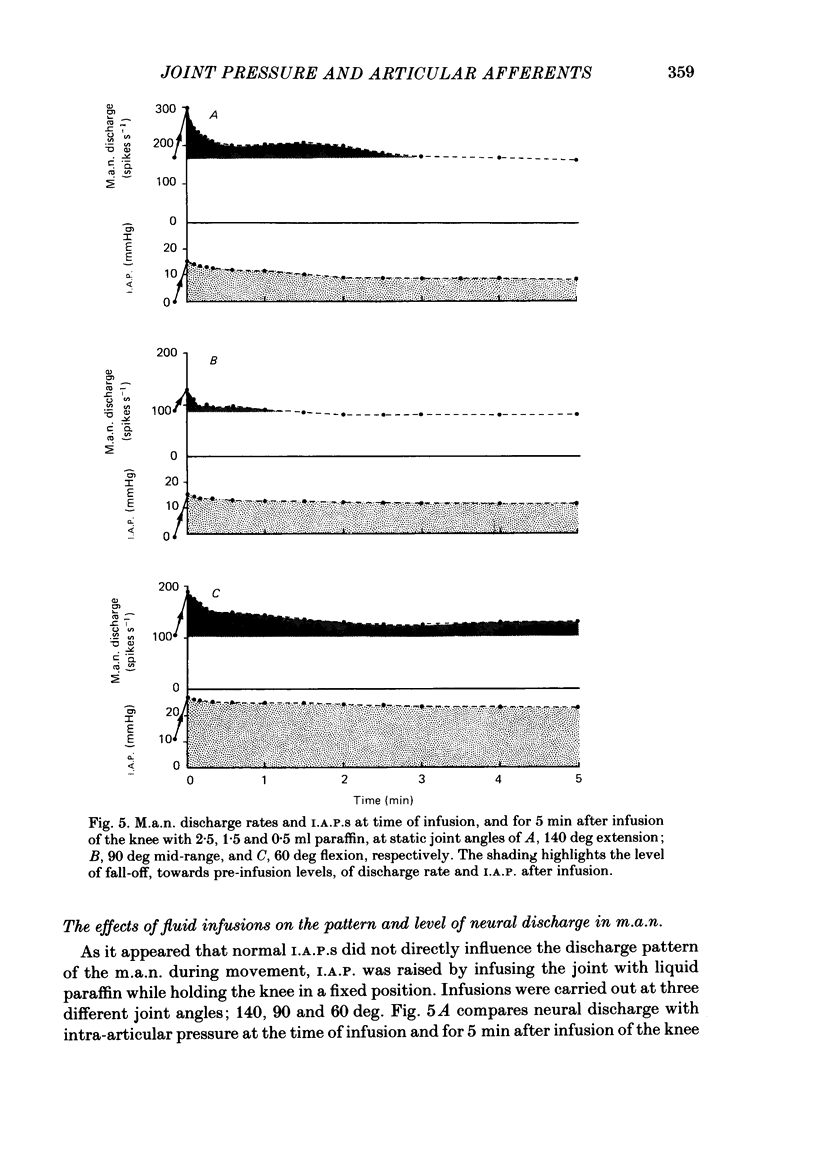
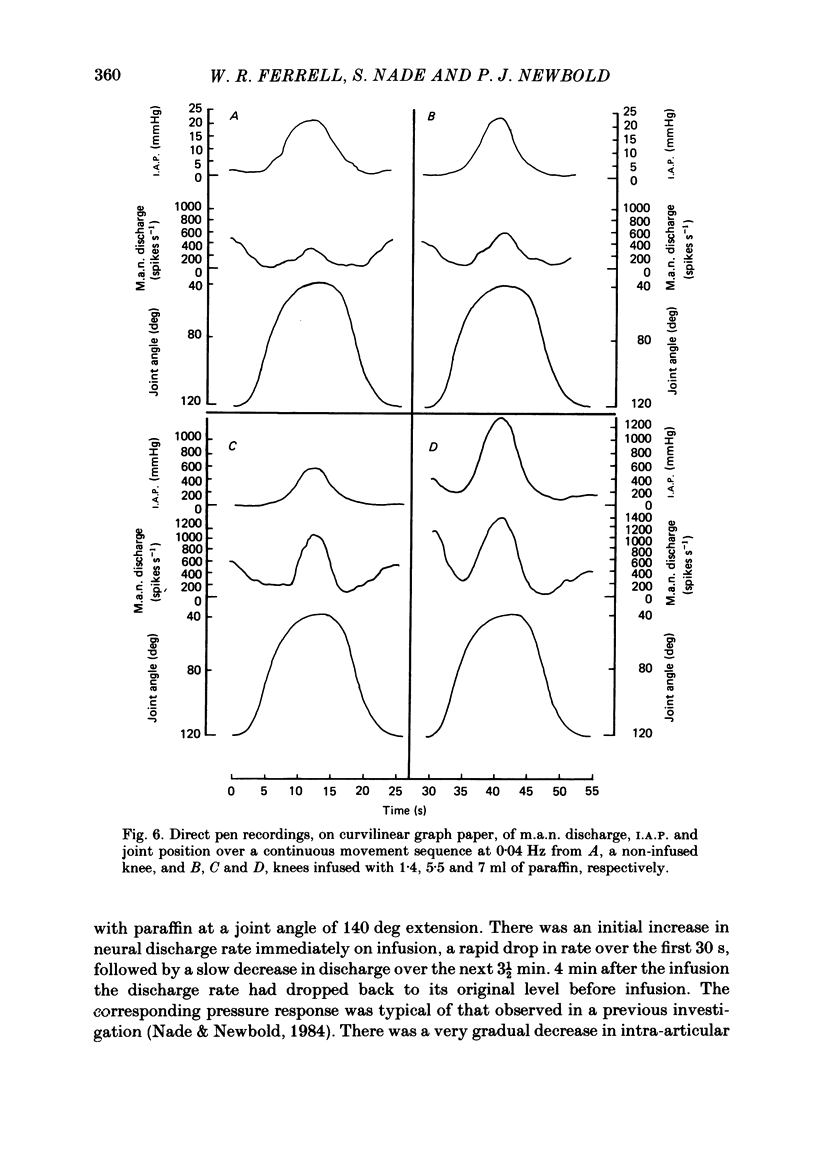
Abstract
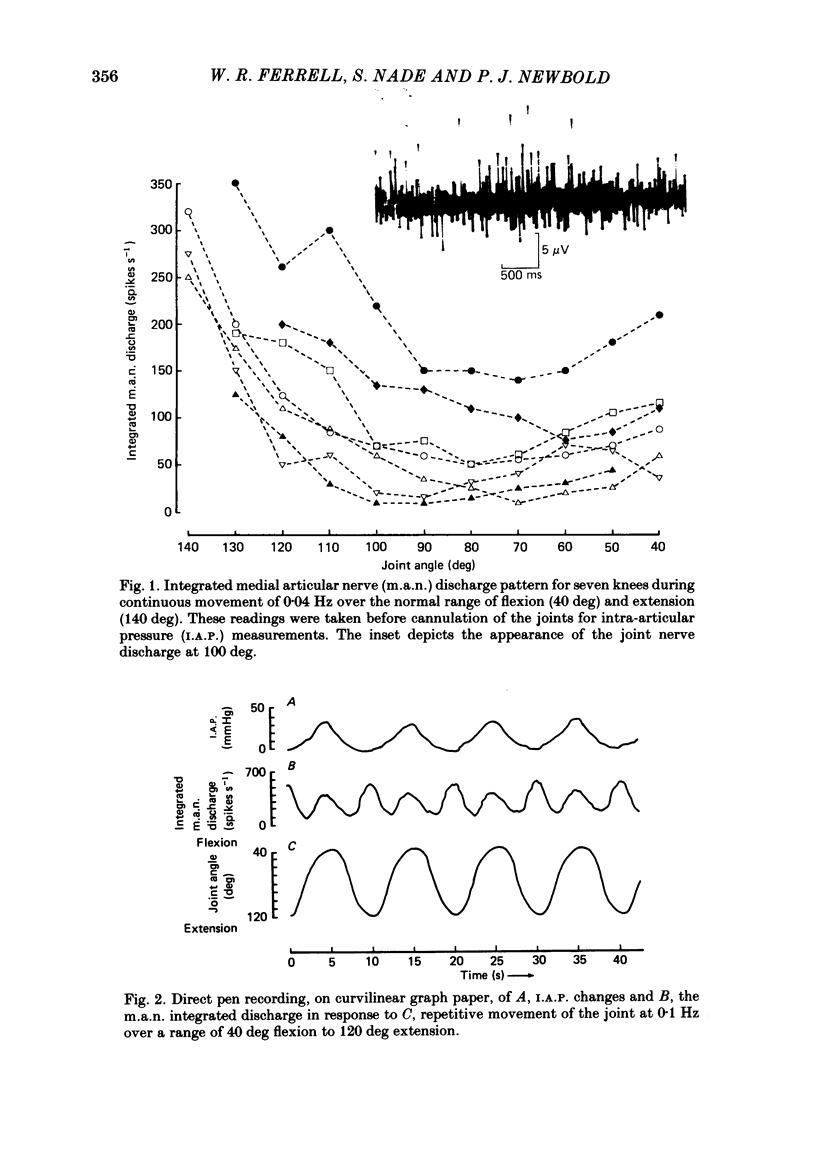
Single- and multi-unit recordings were obtained from the medial articular nerve (m.a.n.) of knee joints in the anaesthetized dog. The single-unit recordings were confined to low threshold (group I and II) articular mechanoreceptors. Multi-unit recordings revealed that the m.a.n. discharge was maximal in extension, submaximal in flexion, and minimal at intermediate angles, i.e. a U-shaped profile. Subatmospheric intra-articular pressures do not appear to influence the m.a.n. discharge. Intra-articular infusion of even small quantities of fluid, although not affecting the U-shaped profile, reversed the m.a.n. discharge pattern with maximum neural activity occurring in flexion and being submaximal in extension. Recordings from single units indicated that the enhanced discharge after fluid infusion was a result of increased discharge frequency and 'recruitment' of individual afferents.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYD I. A., ROBERTS T. D. Proprioceptive discharges from stretch-receptors in the knee-joint of the cat. J Physiol. 1953 Oct;122(1):38–58. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxendale R. H., Ferrell W. R. The effect of knee joint afferent discharge on transmission in flexion reflex pathways in decerebrate cats. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:231–242. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess P. R., Clark F. J. Characteristics of knee joint receptors in the cat. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):317–335. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark F. J., Burgess P. R. Slowly adapting receptors in cat knee joint: can they signal joint angle? J Neurophysiol. 1975 Nov;38(6):1448–1463. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.6.1448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark F. J. Information signaled by sensory fibers in medial articular nerve. J Neurophysiol. 1975 Nov;38(6):1464–1472. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.6.1464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEANDRADE J. R., GRANT C., DIXON A. S. JOINT DISTENSION AND REFLEX MUSCLE INHIBITION IN THE KNEE. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1965 Mar;47:313–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell W. R. The adequacy of stretch receptors in the cat knee joint for signalling joint angle throughout a full range of movement. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:85–99. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman M. A., Wyke B. Articular contributions to limb muscle reflexes. The effects of partial neurectomy of the knee-joint on postural reflexes. Br J Surg. 1966 Jan;53(1):61–68. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800530116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigg A., Hoffman A. H., Fogarty K. E. Properties of Golgi-Mazzoni afferents in cat knee joint capsule, as revealed by mechanical studies of isolated joint capsule. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Jan;47(1):31–40. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.47.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigg P. Mechanical factors influencing response of joint afferent neurons from cat knee. J Neurophysiol. 1975 Nov;38(6):1473–1484. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.6.1473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levick J. R. An investigation into the validity of subatmospheric pressure recordings from synovial fluid and their dependence on joint angle. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:55–67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Role of joint afferents in motor control exemplified by effects on reflex pathways from Ib afferents. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:327–343. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall W. D., Jr, Farias M. C., Williams W. J., BeMent S. L. Static and dynamic responses of slowly adapting joint receptors. Brain Res. 1974 Apr 19;70(2):221–243. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty D. J., Jr, Phelps P., Pyenson J. Crystal-induced inflammation in canine joints. I. An experimental model with quantification of the host response. J Exp Med. 1966 Jul 1;124(1):99–114. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nade S., Newbold P. J. Factors determining the level and changes in intra-articular pressure in the knee joint of the dog. J Physiol. 1983 May;338:21–36. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nade S., Newbold P. J. Pressure-volume relationships and elastance in the knee joint of the dog. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:417–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor B. L., Woodbury P. The primary articular nerves to the dog knee. J Anat. 1982 May;134(Pt 3):563–572. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOGLUND S. Anatomical and physiological studies of knee joint innervation in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1956;36(124):1–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible H. G., Schmidt R. F. Activation of groups III and IV sensory units in medial articular nerve by local mechanical stimulation of knee joint. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Jan;49(1):35–44. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.49.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible H. G., Schmidt R. F. Responses of fine medial articular nerve afferents to passive movements of knee joints. J Neurophysiol. 1983 May;49(5):1118–1126. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.49.5.1118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J. D., Hayes K. C., Alexander I. J. Knee joint effusion and quadriceps reflex inhibition in man. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1984 Apr;65(4):171–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood L., Ferrell W. R. Response of slowly adapting articular mechanoreceptors in the cat knee joint to alterations in intra-articular volume. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Apr;43(2):327–332. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]