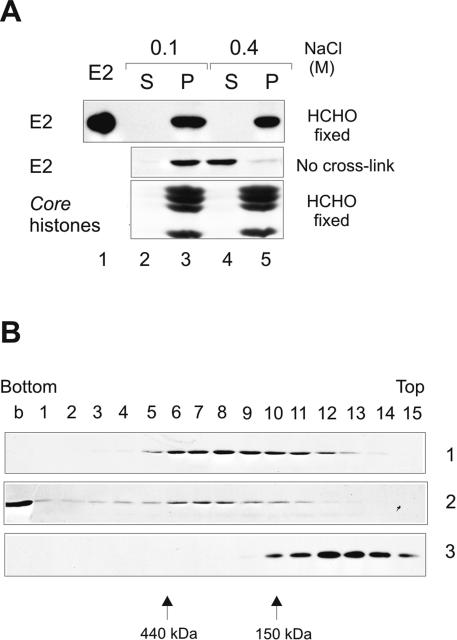
FIG. 4.
Biochemical analysis of localization of E2 after formaldehyde cross-link. CHOBgl40 cells were fractionated as depicted in Fig. 1B, and the CSK plus 0.5% Triton X-100 pellet fraction was cross-linked (upper panel) using 1% formaldehyde. After cross-linking, the pellet fraction was further incubated with buffer containing either 0.1 M (lanes 2 and 3) or 0.4 M (lanes 4 and 5) NaCl and separated by centrifugation into super (S) and pellet (P) fractions. The lower part of the gel was analyzed for the presence of histones (Coomassie blue staining). (B) Glycerol gradient centrifugation of the E2 protein released from chromatin by 0.4 M salt. Gel 1, a total of 1.5 × 107 CHOBgl40 cells were extracted as depicted in Fig. 1B, and the S fraction of 0.4 M salt treatment was centrifuged through glycerol as detailed in Materials and Methods. Gel 2, a total of 3 × 107 CHOBgl40 cells were extracted as depicted in Fig. 1B, and the S fraction of 0.4 M salt treatment was cross-linked with formaldehyde before loading onto the gradient. Glycerol gradient fractions were precipitated with trichloroacetic acid and subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with E2-specific antibodies. Gel 3, the E2 protein (2 μg) purified from Escherichia coli was run in parallel gradient.