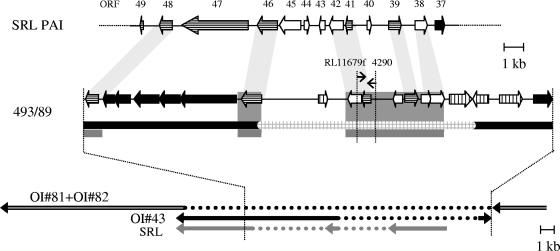
FIG. 1.
Genetic organization of the mosaic genomic island in the SF EHEC O157:H− strain 493/89 in comparison to E. coli O157:H7 strain EDL933 and to the SRL PAI of Shigella flexneri 2a. At the top the SRL PAI sequence is shown, which contains the respective homologue ORFs. In the middle, the mosaic genomic island of strain 493/89 is demonstrated. Black ORFs demonstrate homologues to the EDL933 sequence, vertically striped ORFs are associated with transposase sequences, and horizontally striped ORFs are homologous to bacteriophage P4 sequences. White ORFs do not have any similarities in data banks. The black line represents homology to EDL933, whereas the square gray line represents the specific 493/89 sequence. Areas with similarities to the SRL PAI sequence are shown in dark gray. At the bottom the putative surrounding of the fragment as determined by cosmid shotgun sequencing is depicted. Both ends of the cosmid insert are homologous to three different O islands of the strain EDL933 (OI-41, OI-81, and OI-82). The sequence of contig 3 of 3, sections 44 to 46 of 290 of EDL933 (GenBank accession numbers AE005425 to AE005427, part of O islands 81 and 82) is inserted by contig 1 of 3, sections 100 and 101 of 155 of EDL933 (GenBank accession numbers AE005276 and AE005277, part of O island 43). Similarities to the SRL PAI sequence are indicated by gray arrows. The dotted lines mark the parts of the respective sequences of EDL933 and of SRL PAI, which are absent from strain 493/89. In addition, positions of PCR primers RL11679f and 4290 used to target the SRL-related sequence of SF EHEC O157:H− strains are shown.