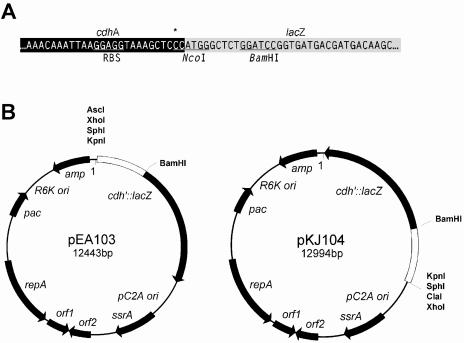
FIG. 1.
Archaeal reporter plasmids pEA103 and pKJ104. (A) Detailed map showing the sequence of the Methanosarcina thermophila TM-1 cdh promoter-lacZ translational fusion reporter. The cdhA promoter, which included the putative archaeal ribosomal binding site (RBS), was amplified with a 3′ NcoI restriction site by substituting a C for an A (shown with an asterisk) and ligated to the 5′ NcoI site of lacZ. The BamHI restriction site 9 bp downstream of the translational start site provides an alternative restriction site for constructing translational lacZ fusions. (B) The complete maps of the reporter plasmids pEA103 and pKJ104, constructed from the autonomously replicating shuttle vector pWM315 (9), which contain the native Methanosarcina acetivorans strain C2A plasmid with an archaeal origin of replication (pC2A ori), open reading frames with sequence similarity to a putative replication initiation protein (repA), site-specific recombinase (ssrA), and two open reading frames without significant sequence similarity to known proteins. The constructs also include a puromycin N-acetyltransferase gene (pac) under the control of an archaeal methyl coenzyme M reductase promoter and terminator for puromycin selection in Methanosarcina spp.; an origin of replication (R6K ori) and β-lactamase gene (bla) for replication and ampicillin selection, respectively, in E. coli.