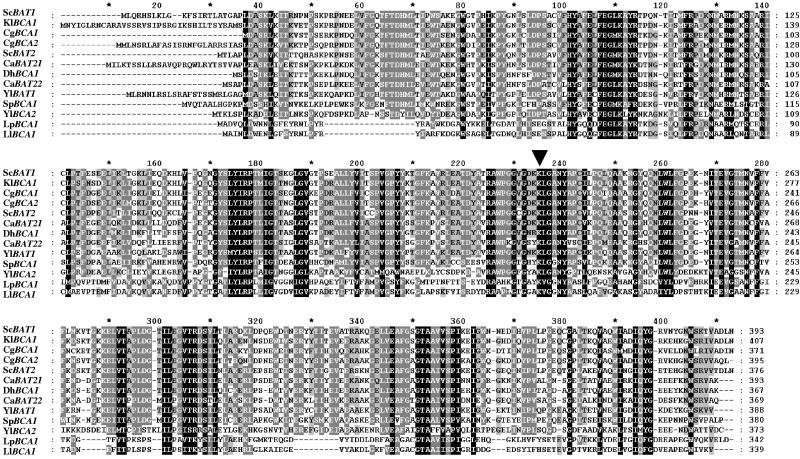
FIG. 1.
Alignment of yeast branched-chain amino acid aminotransferases. The alignment was constructed using the Clustal X v1.8 software. The N-terminal extensions observed in several aminotransferases, such as the products ofYlBCA1 and ScBAT1, correspond to mitochondrial presequences. The following sequences were used: Candida albicans CaBAT21 (GenBank accession no. EAL02229) and CaBAT22 (GenBank accession no. EAK95653), Candida glabrata CgBCA1 (GenBank accession no. XP_446368) and CgBCA2 (GenBank accession no. XP_449352), Debaryomyces hansenii DhBCA1 (GenBank accession no. CAG86908), Lactococcus lactis LlBCA1 (GenBank accession no. NP_267444), Lactobacillus plantarum LpBCA1 (GenBank accession no. NP_785849), Kluyveromyces lactis KlBCA1 (GenBank accession no. XP_451451), Saccharomyces cerevisiae ScBAT1 (Swiss-Prot accession no. P38891), ScBAT2 (Swiss-Prot accession no. P47176), Schizosaccharomyces pombe SpBCA1 (GenBank accession no. NP_595180), and Yarrowia lipolytica YlBCA1 (GenBank accession no. XP_502278) and YlBCA2 (GenBank accession no. XP_505642). The arrowhead indicates the lysine residue of the active site of PLP-dependent enzymes.