Figure 3.
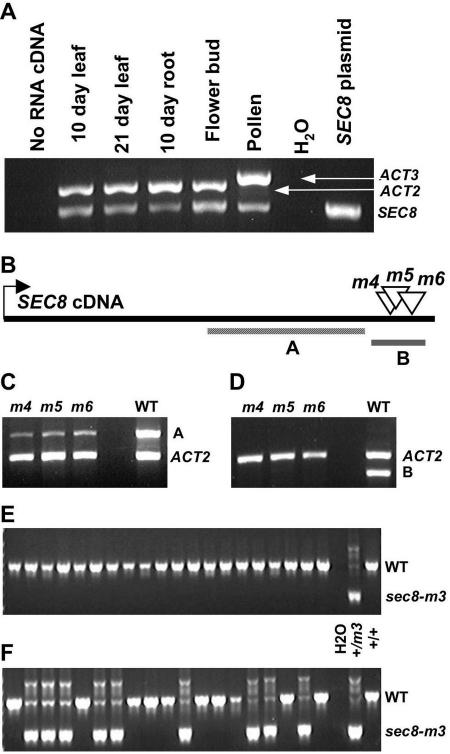
Insertional mutations affect the SEC8 transcript and transmission through the male gametophyte. A, The SEC8 transcript is detectable in several wild-type tissues, including mature pollen, by RT-PCR. Primers against ACTIN2 (sporophyte) and ACTIN3 (gametophyte) were included as internal controls. B, Schematic of the SEC8 transcript and the strategy to test for aberrant transcripts generated by the -m4, -m5, and -m6 alleles. RT-PCR product A is located 5′ to the insertion sites, whereas product B spans all three insertion sites. C and D, In RNA made from immature floral tissue, product A is detectable in the wild type and all three mutant homozygotes (C), whereas product B is only detectable in the wild type (D). E and F, Twenty outcross progeny were genotyped by PCR using a set of three primers (see “Materials and Methods”) to produce distinct wild-type (WT) and sec8-m3 heterozygote banding patterns. E, No heterozygous progeny were produced in an outcross to a wild-type homozygote using pollen from a sec8-m3 heterozygote. F, Heterozygous progeny were produced in an outcross using pollen from a sec8-m3 heterozygote also carrying a LAT52::SEC8 construct, demonstrating male transmission of the mutant allele, and complementation.