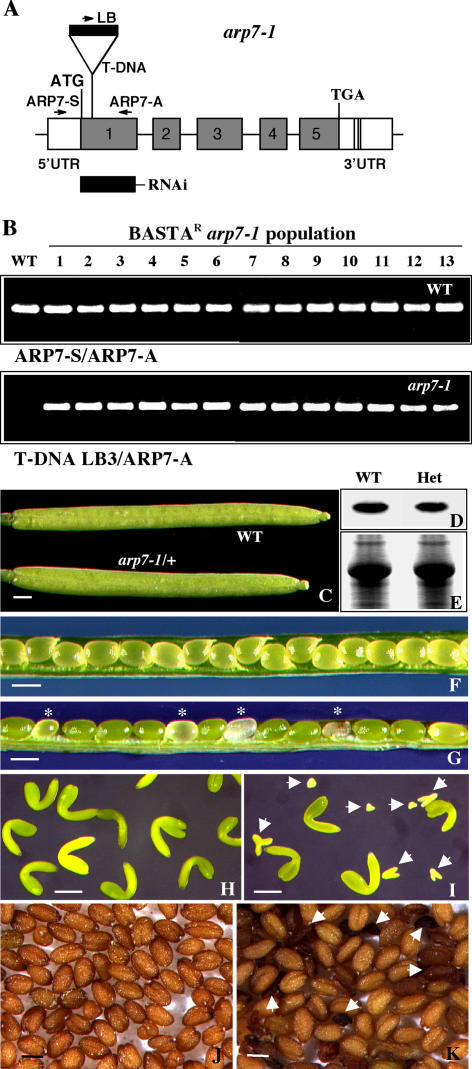
Figure 2.
Characterization of the arp7-1 mutant allele. A, Map of the Arabidopsis ARP7 gene indicating the location of T-DNA insertion in the arp7-1 mutant allele. The T-DNA is inserted into the first exon disrupting the sixth (Val) codon. The locations of primer sequences used for PCR genotyping of ARP7 (wild-type) and arp7-1 mutant alleles are marked with arrows. The solid rectangle (RNAi) indicates the location of the 300-bp target sequence used in a RNAi construct. B, PCR screening of the genotypes of wild-type (top) and mutant (bottom) alleles in a population of Basta-resistant arp7-1 T4 plants. The first lane represents wild-type control. C, Morphology of self-pollinated wild-type and mutant (arp7-1/+) siliques. D, Western-blot analysis of ARP7 protein in the wild-type and heterozygous mutant plants using mAbARP7a antibody. E, A duplicate gel stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue to reveal equal loading of total protein. F, Wild-type silique with seeds. G, Heterozygous arp7-1 mutant silique with seeds. The aborting seeds are marked with asterisks. H, Embryos isolated from a wild-type silique. I, Embryos isolated from a heterozygous arp7-1 silique. Four normal embryos at the bent-curled cotyledon stage are shown along with homozygous mutant embryos (arrows) arresting at different stages of development. J and K, Mature wild-type (J) and heterozygous arp7-1 (K) mutant seeds. The arrows in K point to the aborted abnormal seeds. Scale bars = 1 mm (C, F, and G); 100 μm (H and I); and 500 μm (J and K). WT, Wild type; Het, heterozygous.