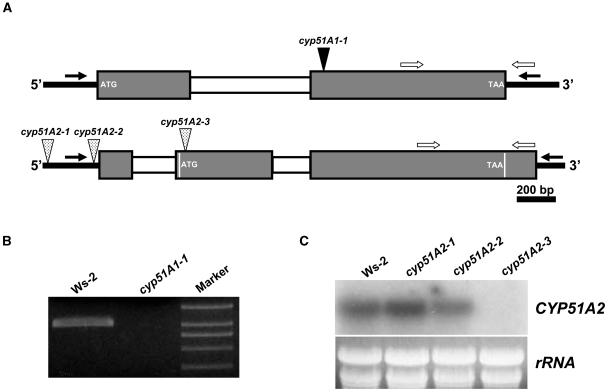
Figure 1.
Isolation of loss-of-function mutants for CYP51A1 and CYP51A2. A, Schematic representation of T-DNA insertions in CYP51A1 and CYP51A2 genes. Mutant lines were isolated by PCR-based reverse genetics using a gene-specific primer and a T-DNA border primer on DNA from lines containing 120,000 T-DNA insertions. Gray and white boxes indicate exons and introns, respectively. The second exon of the CYP51A2 gene contains 10 bp between the 5′-UTR intron and the ATG start codon. The size of the first exon of 5′-UTR of CYP51A2 gene is based on a full-length cDNA clone (AY050860). Black and white arrows indicate gene-specific primers to isolate T-DNA insertion mutants and primers for RT-PCR, respectively. B, RT-PCR analysis to confirm knockout mutation in the cyp51A1 mutant. Total RNA was isolated from 10-d-old seedlings of wild-type and cyp51A1 mutants. C, RNA gel-blot analysis to confirm knockout and/or knockdown mutations in the cyp51A2 mutants. Total RNA was isolated from 10-d-old seedlings of wild-type and cyp51A2 mutants.