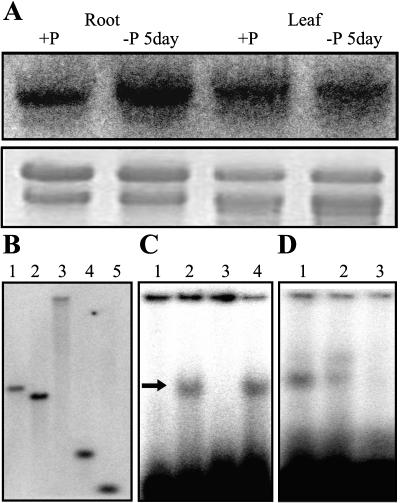
Figure 1.
A, RNA gel-blot analysis for the expression of OsPTF1 in roots and leaves of 15-d-old seedlings under P-sufficient (10 mg Pi L−1) and Pi-deficient (0.5 mg Pi L−1) hydroponic solutions. Twenty milligrams of total RNA from each sample were electrophoresed. A 32P-labeled cDNA fragment of OsPTF1 was used as probe for hybridization. An ethidium bromide-stained gel is shown at the bottom. B, Southern-blot analysis of rice genomic DNA from the Kasalath genotype. DNA samples were digested with DraI (1), EcoRI (2), EcoRV (3), HindIII (4), and XbaI (5). The blot was hybridized with a 32P-labeled cDNA fragment of OsPTF1. C, E-box (G-box)-specific DNA binding properties of OsPTF1. Arrow shows OsPTF1-bound DNA. Lane 1, 32P-labeled E-box probe without OsPTF1 protein; lane 2, 32P-labeled E-box probe with OsPTF1 protein; lane 3, 32P-labeled mutated G-box probe with OsPTF1 protein; and lane 4, 32P-labeled G-box probe with OsPTF1 protein. D, Sequence-specific DNA-binding properties of OsPTF1. Lane 1, 32P-labeled G-box probe with OsPTF1 protein; lane 2, 5-fold excess of no labeled G-box DNA added to the reaction mixture of lane1; and lane 3, 100-fold excess of no labeled G-box DNA added to the reaction mixture of lane1.