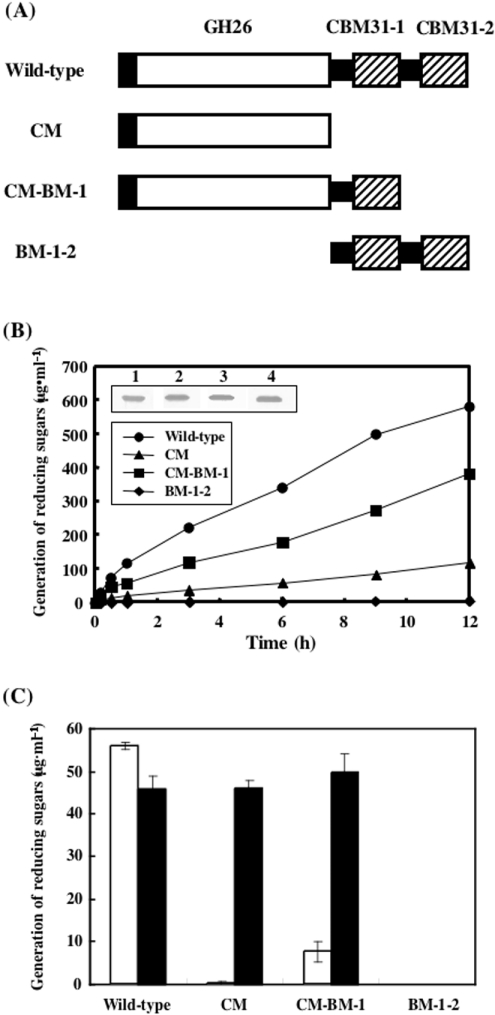
Figure 6. Construction of rXYL4 deletion mutants and examination of their activities with insoluble and soluble substrates.
(A) Modular architectures of rXYL4 deletion mutants. Open and closed boxes indicate catalytic modules and signal peptides respectively. Putative CBMs are shown by hatched boxes. Putative CBMs at the N- and C-termini are designated CBM31-1 and CBM31-2 respectively. Black bars indicate linkers that connect modules. CM has a catalytic module, but lacks putative CBMs. CM-BM-1 and BM-1-2 lack CBM31-2 and the catalytic module respectively. (B) Time courses for hydrolysis of β-1,3-xylan with wild-type and mutant enzymes. The reaction mixtures containing 0.5% β-1,3-xylan and 0.01 unit of wild-type or mutant enzyme in 300 μl of 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.5, were incubated at 37 °C for the periods indicated. After incubation, the reaction mixtures were centrifuged, and the reducing sugars generated in the supernatants were quantified by the Somogyi–Nelson method [24]. Expression of wild-type and mutant enzymes was analysed by Western blotting (inset). Lane 1, wild type; lane 2, CM; lane 3, CM-BM-1; lane 4, BM-1-2. (C) Effect of CBMs on hydrolysis of soluble substrate. The reaction mixtures containing 0.5% β-1,3-xylan (□) or glycol-β-1,3-xylan (■) and 0.01 unit of wild-type or mutant enzyme in 300 μl of 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer containing 50 mM NaCl, pH 7.5, were incubated at 37 °C for 30 min.