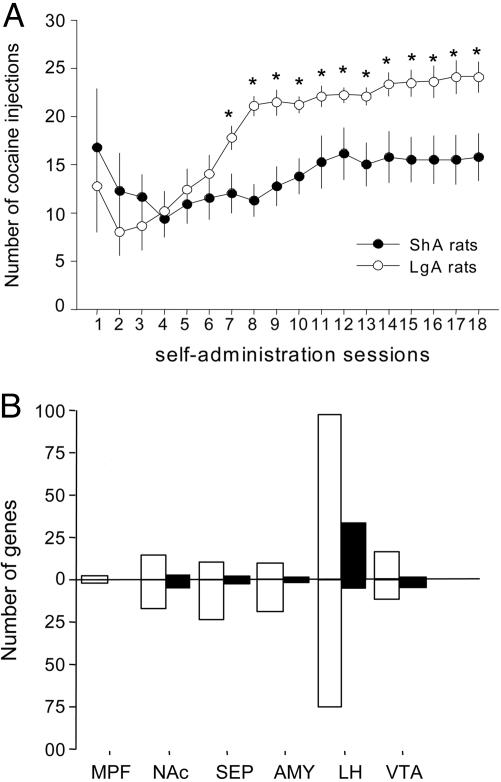
Fig. 1.
Effects of access time to cocaine self-administration on drug intake and brain gene expression levels. (A) Escalation of i.v. cocaine consumption in rats. Rats had access to cocaine for either 1 h (ShA rats, n = 8) or 6 h per day (LgA rats, n = 8). Data represent the mean (±SEM) number of cocaine injections obtained during the first hour of each daily self-administration session. *, Different from ShA rats; P < 0.05, tests of simple main effects after appropriate two-way analyses of variance. (B) Total number of probe sets per brain region that significantly changed in LgA and ShA rats compared with drug-naive control rats (CSA genes, white bars) and probe sets that significantly changed in LgA rats from ShA and drug-naive rats (ESC genes, black bars). AMY, amygaloid complex; MPF, medial prefrontal cortex.