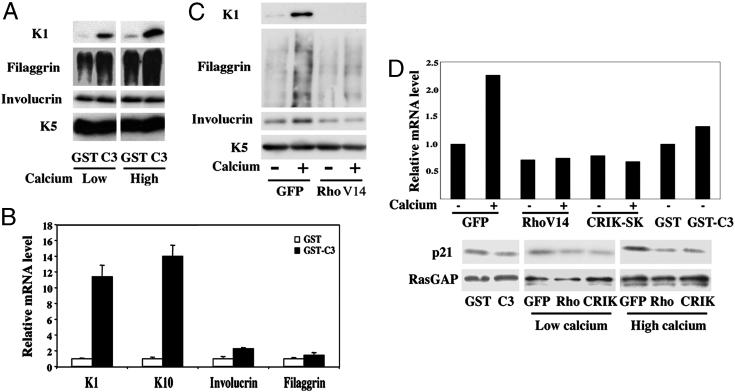
Fig. 1.
Rho signaling negatively regulates keratinocyte differentiation marker expression. (A) Mouse primary keratinocytes under growing conditions were treated with the C3 toxin as a GST-fusion product or GST control as described (14), and further incubated in growth medium or induced to differentiate by the addition of CaCl2 (2 mM) for 7 h. Total protein extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against the indicated proteins. Filaggrin is produced as a high molecular precursor, profilaggrin, which is converted into multiple products migrating as a diffuse set of bands on a gel. Keratin 5 is constitutively expressed in cultured keratinocytes irrespective of their growing or differentiating conditions and was used as equal loading control. (B) Mouse primary keratinocytes were treated with the C3 toxin or GST control proteins as in A, followed by total RNA preparation and real-time RT-PCR analysis for the indicated markers. Values are expressed as relative mRNA levels after normalization for GAPDH mRNA expression. (C) Mouse primary keratinocytes were infected with an adenovirus expressing an activated form of RhoA (RhoV14) or GFP control (GFP) as described (14), and either kept under growing conditions or induced to differentiate by high calcium concentrations for 9 h, followed by immunoblot analysis for the indicated markers. (D) Keratinocytes were treated with the C3 and GST proteins, or infected with the adenoviruses indicated above in parallel with an adenovirus expressing CRIK-SK (8), plus/minus calcium treatment for the last 9 h of the experiment. Levels of p21WAF1/Cip1 expression were determined at the RNA level, by real-time PCR analysis with p21WAF1/Cip1 specific primers and normalization for GAPDH expression (Upper). Alternatively, total protein extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against p21 and RasGAP as an equal loading control (Lower).