Fig. 6.
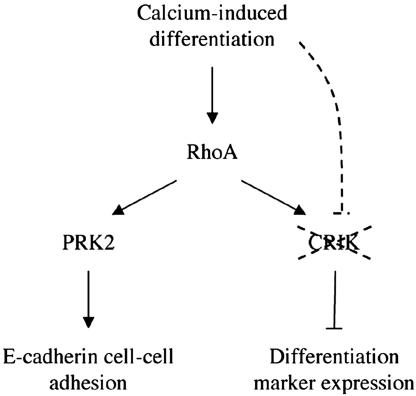
Diagrammatic illustration of the dual mode of Rho function in keratinocyte differentiation. As discussed in the text, available data are consistent with a model whereby activation of the RhoA pathway plays a positive role at early times of keratinocyte differentiation, promoting establishment of cell–cell adhesion through activation of a specific effector, the PKN/PRK2 kinase. Rho signaling can have a second suppressive function on downstream gene expression events associated with differentiation. Such inhibitory function is mediated by a specific Rho effector, CRIK (Citron kinase), which is selectively down-modulated with differentiation, through an as yet uncharacterized mechanism, thereby allowing the normal process to occur.