Abstract
By using metabolically altered mutants and acrylate, novel putative intermediates of alpha-pinene metabolism by Pseudomonas putida PIN11 were detected. They were characterized as 3-isopropylbut-3-enoic acid and (zeta)-2-methyl-5-isopropylhexa-2,5-dienoic acid.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson B. A., Holman R. T. Pyrrolidides for mass spectrometric determination of the position of the double bond in monounsaturated fatty acids. Lipids. 1974 Mar;9(3):185–190. doi: 10.1007/BF02532690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
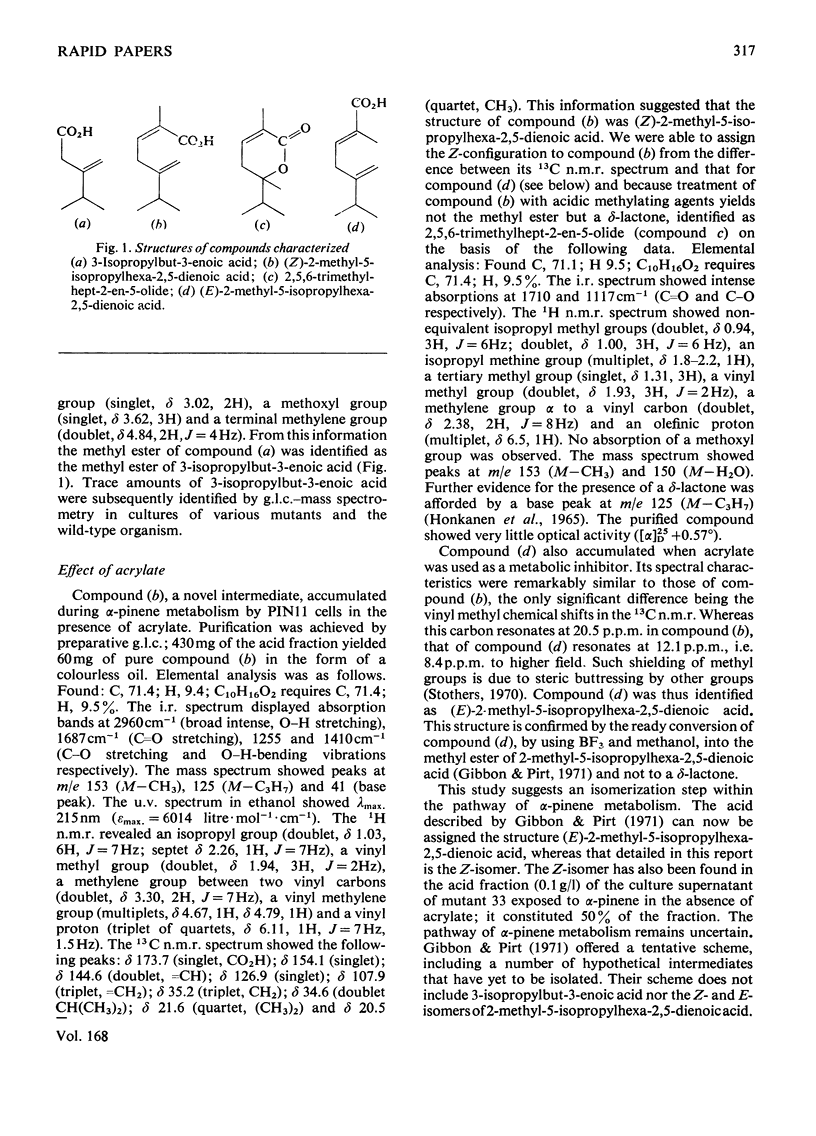
- Gibbon G. H., Pirt S. J. The degradation of alpha-pinene by Pseudomonas PX1. FEBS Lett. 1971 Oct 15;18(1):103–105. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80418-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris L. J. Separations of lipids by silver ion chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1966 Nov;7(6):717–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIJSSE G. J. FATTY-ACID ACCUMULATION BY ACRYLATE INHIBITION OF BETA-OXIDATION IN ALKANE-OXIDIZING PSEUDOMONAS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 20;84:195–197. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


