Figure 8.
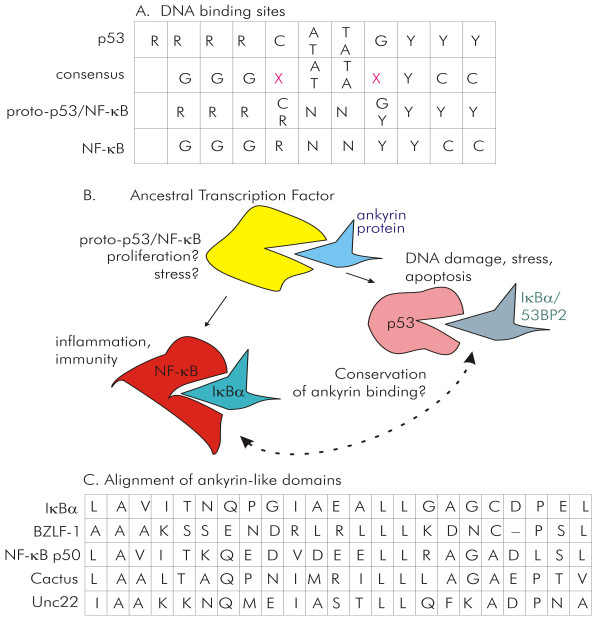
A model for molecular evolution of p53 and NF-κB from a common ancestral transcription factor, proto-p53/ NF-κB. A. P53 (first row) and NF-κB (fourth row) DNA binding sites share eight out of ten nucleotides as shown by the sequence depicted in the second row (consensus). R represents purine, A or G; Y represents pyrimidine, C or T. The red X denotes nucleotides where there is no match. The predicted DNA binding site sequence of the ancestral proto-p53/NF-κB is shown in the third row. B. An ancestral transcription factor proto-p53/ NF-κB, also regulated by an ankyrin protein, with a DNA binding site shown in A, above, could have been the precursor to both p53 and NF-κB. C. An ankyrin-like region in EBV protein BZLF-1 (ZEBRA) is shown in alignment with ankyrin motifs in IκBα, NF-κB p50, as well as invertebrate ankyrin like regulatory repeats from Drosophila Cactus and C. elegans Unc22.
