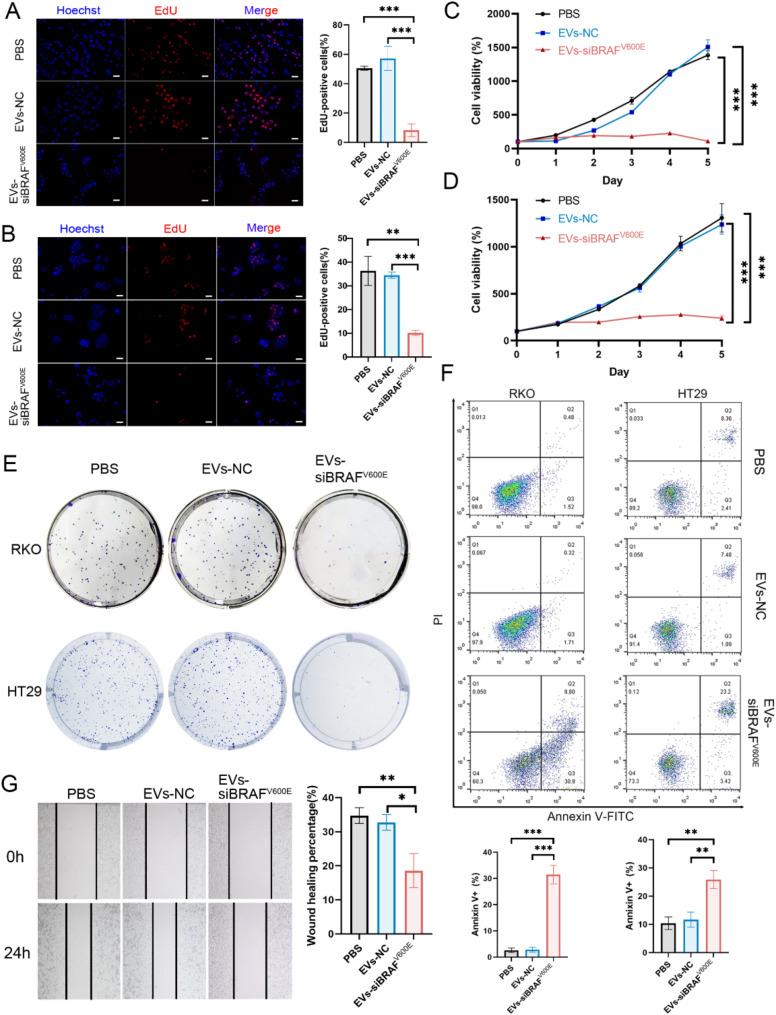
Fig. 4.
EVs-siBRAFV600E can inhibit BRAFV600E CRC cells. RKO (A) and HT29 (B) cells were treated with PBS, EVs-NC or EVs-siBRAFV600E for 48 h, followed by EdU assays to measure cell proliferation activity and imaging via fluorescence microscopy. Scale bar: 20 μm. RKO(C) and HT29 (D) cells were treated with PBS, EVs-NC or EVs-siBRAFV600E for 5 days, and cell viability was measured via CCK-8 assays. (E) Colony formation. Images of single-cell-derived colonies formed by RKO and HT29 cells after treatment with PBS, EVs-NC or EVs-siBRAFV600E for 2 weeks. (F) Flow cytometry analysis of cell apoptosis. RKO and HT29 cells were treated with PBS, EVs-NC or EVs-siBRAFV600E for 24 h, stained with Annexin V-FITC and PI, and apoptosis was detected via flow cytometry. (G) Cell migration was assessed by wound healing assays. RKO cells were treated with PBS, EVs-NC or EVs-siBRAFV600E for 24 h. The concentration of EVs-NC or EVs-siBRAFV600E in all the treatments was 50 µg/mL. The data are reported as the means ± SDs of the experiments (n = 3). Two-way ANOVA for (A) and (B), and one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test multiple comparisons for the others, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001