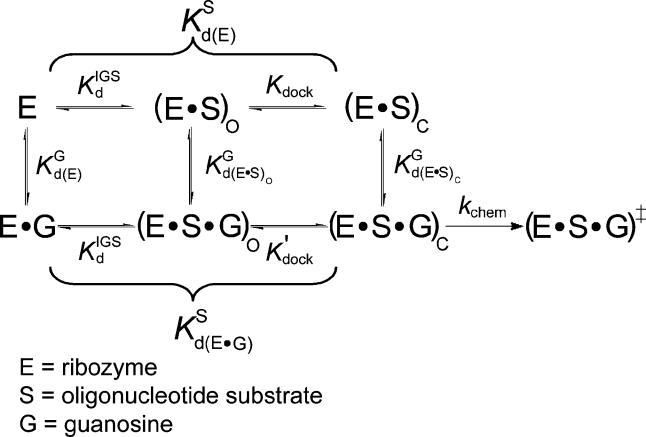
Figure 3. The Tetrahymena Ribozyme Reaction Pathway.
The ribozyme binds the oligonucleotide substrate (in two steps) and the exogenous G that serves as the nucleophile in the ribozyme reaction as described in the text ([33,56,57] and references therein). K G d(E), K G d(E·S)O, and K G d(E·S)c are G dissociation constants from free E, (E·S)O, and (E·S)C, respectively. K IGS d is the dissociation constant for the oligonucleotide substrate from the internal guide sequence, and K dock and K′dock are the docking equilibria for the E·S and E·S·G complexes, respectively. K S d(E) and K S d(E·G) are the observed dissociation constants for the oligonucleotide substrate from free E and the E·G complex, respectively, and k chem is the observed rate of oligonucleotide substrate cleavage.