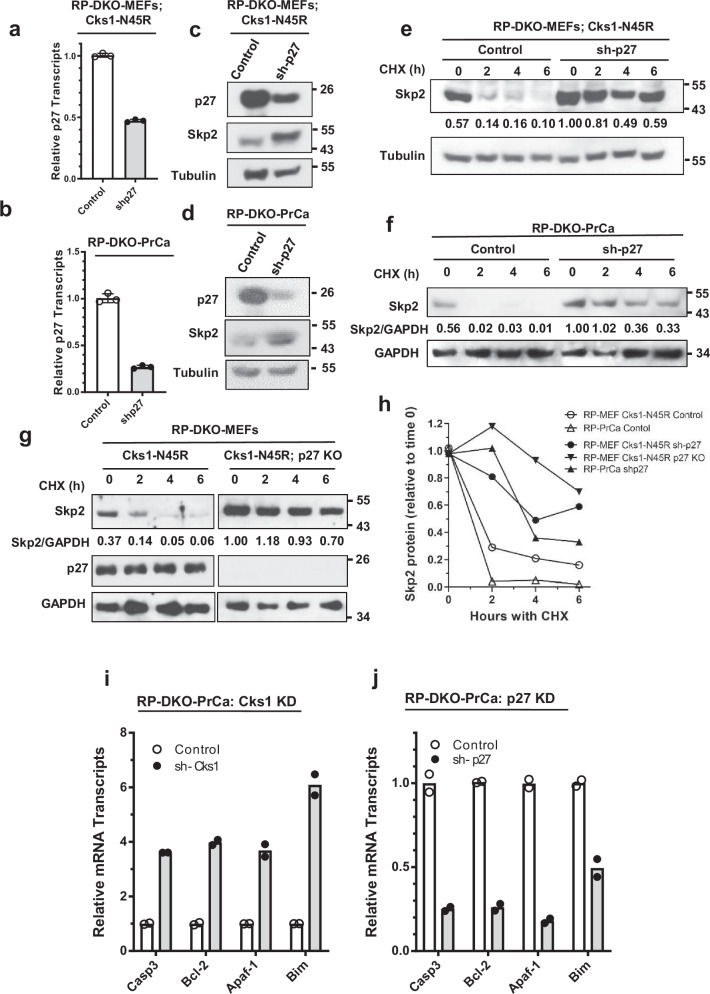
Fig. 6. Knockdown of p27 causes increased Skp2 protein due to a reduction in Skp2 proteasomal degradation.
a, b p27 was knocked down in RP-DKO-Cks1N45R MEFs (a) and RP-DKO-PrCa cells (b), and p27 mRNA levels determined by RT-qPCR. Mean ± SEM, n = 3 biologically independent samples. c, d Western blots of Skp2 and p27 from cells in (a, b). e, f Cells treated with cycloheximide (CHX) to determine the degradation rates of Skp2. Effect of p27 knockdown in Cks1N45R RP-DKO-MEFs (e) and RP-DKO-PrCa (f). g Skp2 protein levels in Cks1N45R RP-DKO-MEFs with and without p27 knockout, and with CHX. h Quantification of Skp2 degradation from (e–g). i, j Effect of Cks1 knock down (i) and Skp2 knock down (j) in RP-DKO-PrCa cells on mRNA levels of the indicated E2F1-regulated apoptotic genes, relative to GAPDH mRNA. Mean of two biologically independent samples.