Abstract
Cathepsin B from calf liver was obtained by a method involving preparation of a lysosomal–mitochondrial pellet and treatment of this pellet with acetone. The material was extracted with an acid buffer, pH4·0, and then precipitated from the extract with acetone. The precipitate was dissolved in phosphate buffer, pH7·4, and subjected to gel filtration on Sephadex G-200 and G-100. The cathepsin B emerged in a range of molecular weight much lower than 50000 as a well-defined component. The purity of this material was checked by electrophoresis. To obtain maximum activity the enzyme had to be activated with a chelating agent and a reducing agent (i.e. EDTA and cysteine). A number of different substrates were used. The enzyme was active for the hydrolysis of both peptide bonds and ester bonds and had approximately equal reactivity in the two cases. The pH-dependence of the hydrolysis was the same with both substrates. The binding of the substrates was half-maximal at pH4·5 and at pH6·8. A thiol group occurred in the active centre but this group ought to have a much higher pK than that found in this enzyme.
Full text
PDF

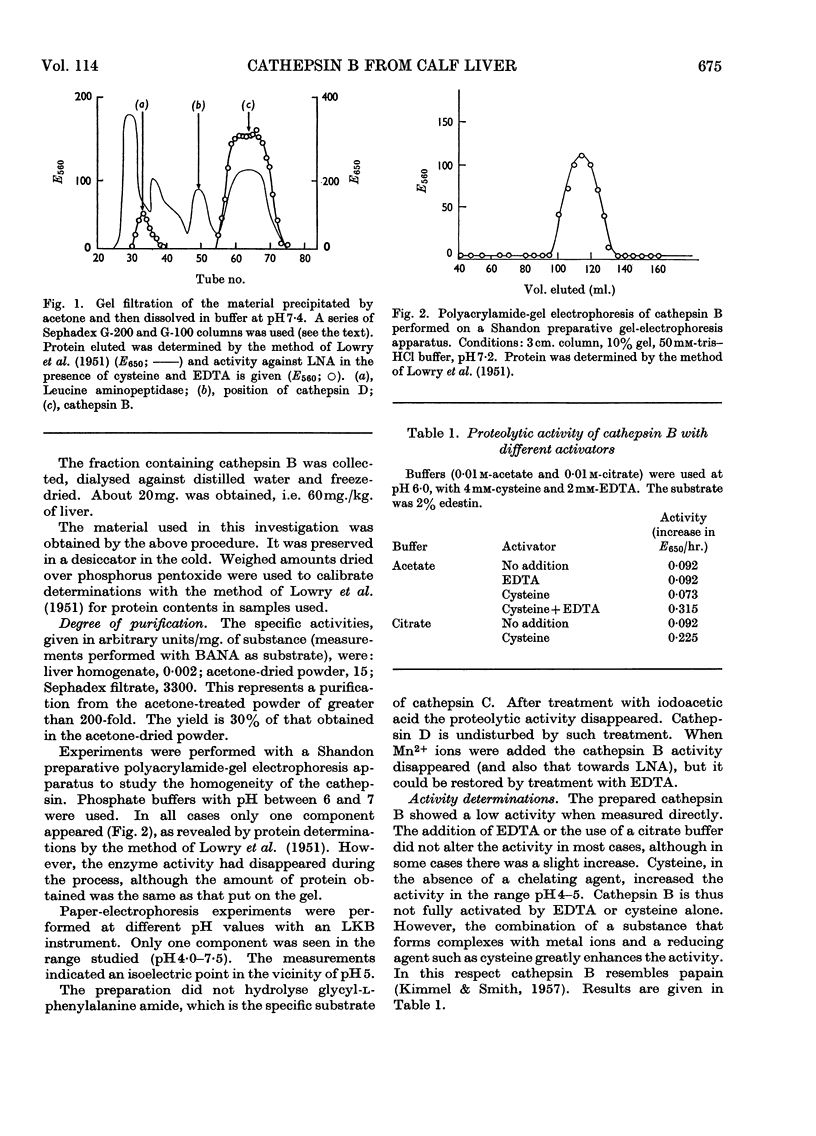
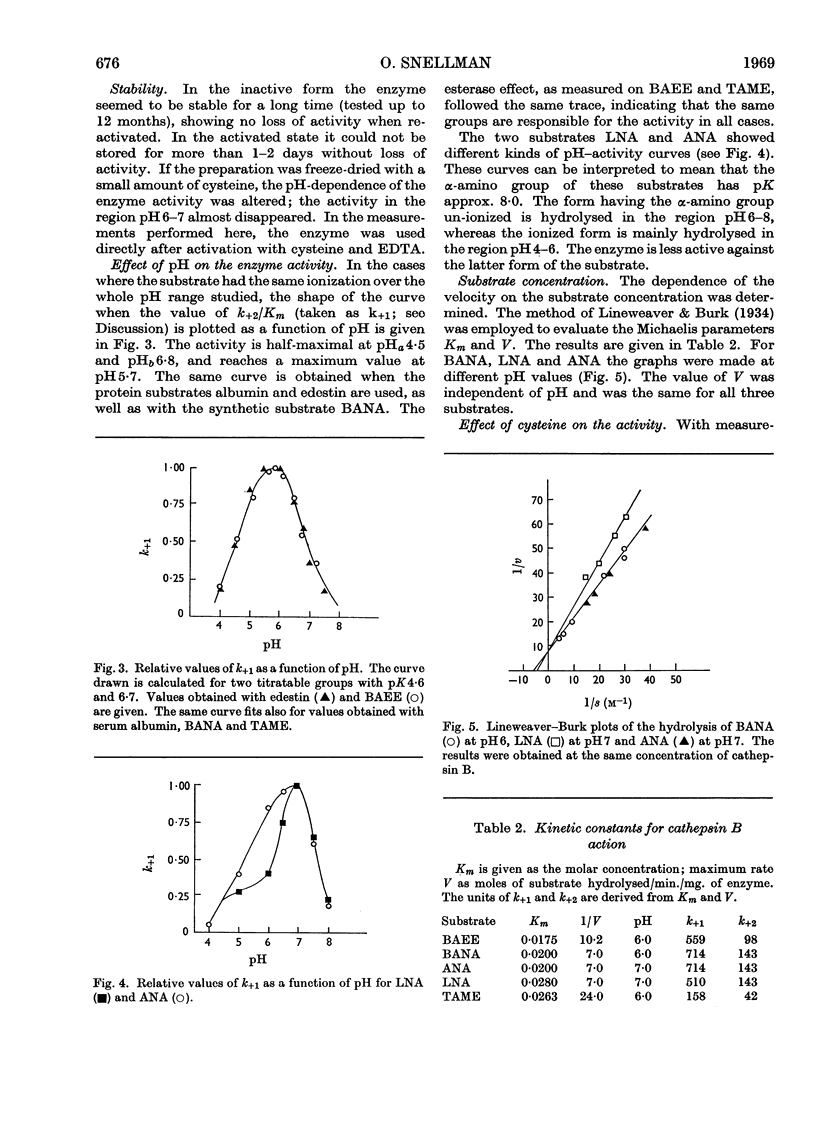


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERTY R. A. Enzyme kinetics. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1956;17:1–64. doi: 10.1002/9780470122624.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Lysosomal acid proteinase of rabbit liver. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):601–608. doi: 10.1042/bj1040601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., WATTIAUX R., BAUDHUIN P. Distribution of enzymes between subcellular fractions in animal tissues. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1962;24:291–358. doi: 10.1002/9780470124888.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBARG J. A., RUTENBURG A. M. The colorimetric determination of leucine aminopeptidase in urine and serum of normal subjects and patients with cancer and other diseases. Cancer. 1958 Mar-Apr;11(2):283–291. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195803/04)11:2<283::aid-cncr2820110209>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBAUM L. M., FRUTON J. S. Purification and properties of beef spleen cathepsin B. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):173–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain S. S., Lowe G. Evidence for histidine in the active site of papain. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;108(5):855–859. doi: 10.1042/bj1080855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain S. S., Lowe G. The location of the active-site histidine residue in the primary sequence of papain. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;108(5):861–866. doi: 10.1042/bj1080861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIMMEL J. R., SMITH E. L. The properties of papain. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1957;19:267–334. doi: 10.1002/9780470122648.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALLAN H. H., JONES M. E., FRUTON J. S. On the proteolytic enzymes of animal tissues. X. Beef spleen cathepsin C. J Biol Chem. 1952 Feb;194(2):793–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


