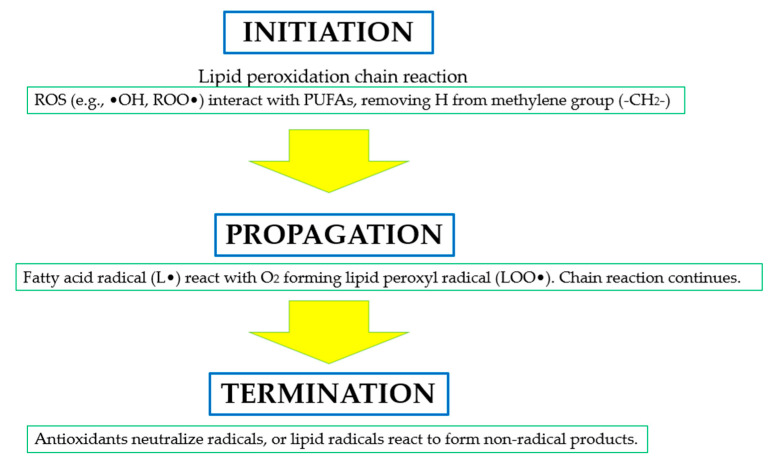
Figure 5.
The three stages of lipid peroxidation, a critical oxidative process affecting polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in biological membranes. During the initiation phase, reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as hydroxyl radicals (•OH) or peroxyl radicals (ROO•), abstract a hydrogen atom from the methylene group (-CH2-) in PUFAs, generating lipid radicals (L•). In the propagation phase, these lipid radicals react with molecular oxygen (O2), forming lipid peroxyl radicals (LOO•), propagating further chain reactions and amplifying oxidative damage. The termination phase involves neutralizing these radicals with antioxidants or forming non-radical products, halting the chain reaction [32,33,34].