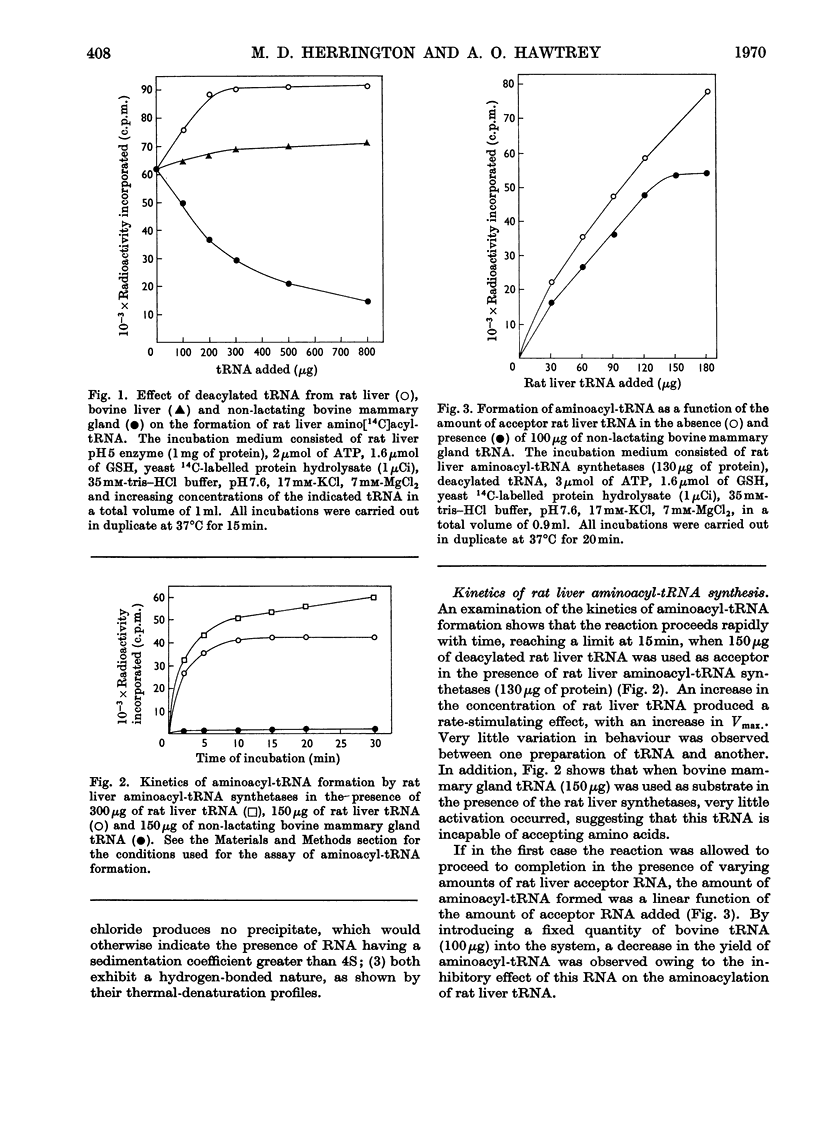
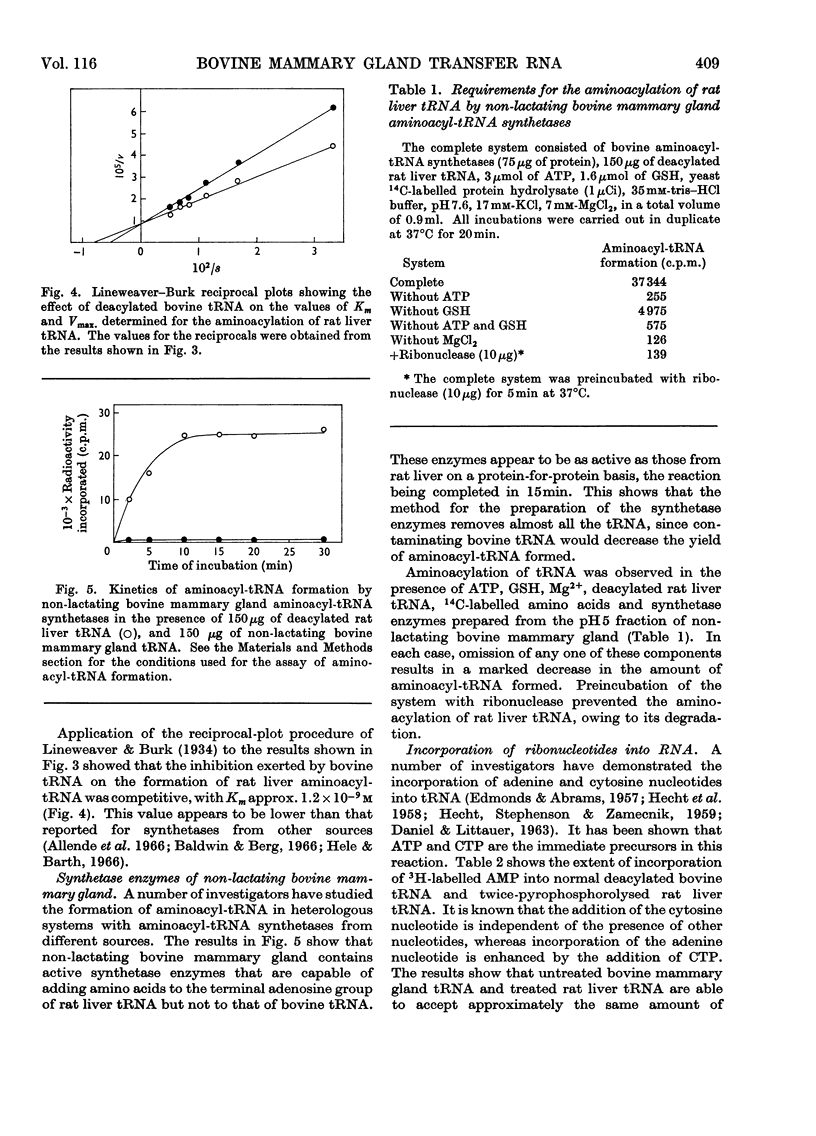
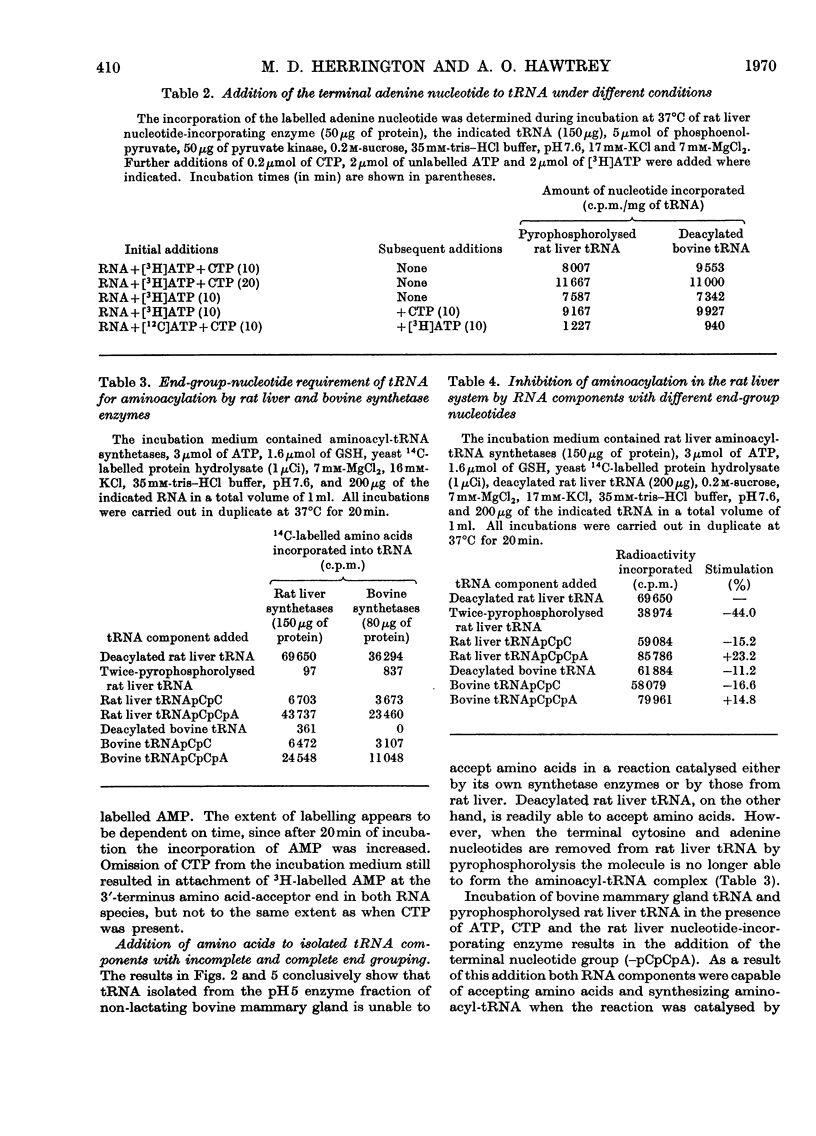
Abstract
1. tRNA isolated from non-lactating bovine mammary gland competitively inhibits the formation of aminoacyl-tRNA in the rat liver system. 2. Non-lactating bovine mammary gland tRNA and twice-pyrophosphorolysed rat liver tRNA are unable to accept amino acids in a reaction catalysed by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases from either rat liver or bovine mammary gland. Deacylated rat liver tRNA can however be aminoacylated in the presence of either enzyme. 3. Bovine mammary gland tRNA lacks the terminal adenine nucleotide at the 3′-terminus amino acid acceptor end, which can be replaced by incubation in the presence of rat liver nucleotide-incorporating enzyme, ATP and CTP. 4. The enzymically modified bovine tRNA (tRNApCpCpA) can bind labelled amino acids to form aminoacyl-tRNA, which can then transfer its labelled amino acids to growing polypeptide chains on ribosomes. 5. Molecules of rat liver tRNA or bovine mammary gland tRNA that lack the terminal adenine nucleotide or the terminal cytosine and adenine nucleotides inhibit the aminoacylation of normal rat liver tRNA to varying degrees. tRNA molecules lacking the terminal −pCpCpA nucleotide sequence exhibit the major inhibitory effect. 6. The enzyme fraction from bovine mammary gland corresponding to that containing the nucleotide-incorporating enzyme in rat liver is unable to catalyse the incorporation of cytosine and adenine nucleotides in pyrophosphorolysed rat liver tRNA and deacylated bovine tRNA. This fraction also markedly inhibits the action of the rat liver nucleotide-incorporating enzyme.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Korner A., Munro A. J. Inhibition by soluble ribonucleic acid of stimulatory effect of liver template ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):448–453. doi: 10.1042/bj1010448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allende C. C., Allende J. E., Gatica M., Celis J., Mora G., Matamala M. The aminoacyl ribonucleic acid synthetases. I. Properties of the threonyladenylate-enzyme complex. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2245–2251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. N., Berg P. Transfer ribonucleic acid-induced hydrolysis of valyladenylate bound to isoleucyl ribonucleic acid synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 25;241(4):839–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzer S., Weisblum B. ON THE SPECIES SPECIFICITY OF ACCEPTOR RNA AND ATTACHMENT ENZYMES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Aug;47(8):1149–1154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.8.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANELLAKIS E. S. On the mechanism of incorporation of adenylic acid form adenosine triphosphate into ribonucleic acid by soluble mammalian enzyme systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jul;25(1):217–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIEL V., LITTAUER U. Z. Incorporation of terminal ribonucleotides into soluble ribonucleic acid by a purified rat liver enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jun;238:2102–2112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDMONDS M., ABRAMS R. Incorporation of ATP into polynucleotide in extracts of Ehrlich ascites cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Oct;26(1):226–227. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER M. J., SHIMIZU H., GUTFREUND H. The reactions of amino acids with soluble ribonucleic acid from guinea-pig mammary cells. Biochem J. 1959 May;72(1):141–147. doi: 10.1042/bj0720141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECHT L. I., STEPHENSON M. L., ZAMECNIK P. C. Dependence of amino acid binding to soluble ribonucleic acid on cytidine triphosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Aug;29(2):460–461. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90225-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECHT L. I., ZAMECNIK P. C., STEPHENSON M. L., SCOTT J. F. Nucleoside tri-phosphates as precursors of ribonucleic acid end groups in a mammalian system. J Biol Chem. 1958 Oct;233(4):954–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELE P. The interaction of 'soluble' ribonucleic acid, magnesium ions and sulphydryl groups in the control of amino acid-dependent pyrophosphate-exchange reactions. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:329–339. doi: 10.1042/bj0810329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOAGLAND M. B., KELLER E. B., ZAMECNIK P. C. Enzymatic carboxyl activation of amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):345–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOAGLAND M. B., ZAMECNIK P. C., STEPHENSON M. L. Intermediate reactions in protein biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Apr;24(1):215–216. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawtrey A. O., Nourse L. D., King H. W. Binding of s-RNA to rat-liver polysomes during protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 21;114(2):409–412. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawtrey A. O., Nourse L. D. The effect of 4-dimethylamino-3'-methylazobenzene on 14-C-labelled amino acid incorporation by rat-liver polysome preparations. Biochem J. 1966 Mar;98(3):682–688. doi: 10.1042/bj0980682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawtrey A. O., Schirren V., Dijkstra J. Studies on azo-dye carcinogenesis in rat liver. The effect of 4-dimethylamino-3'-methylazobenzene on the incorporation of [C]leucine into rat-liver microsomal protein. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88(1):106–114. doi: 10.1042/bj0880106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawtrey A. O. The effect of diisopropylfluorophosphate on [14C]-leucine incorporation by rat-liver ribosomes. S Afr J Med Sci. 1965 Dec;30(4):100–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht L. I., Stephenson M. L., Zamecnik P. C. BINDING OF AMINO ACIDS TO THE END GROUP OF A SOLUBLE RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Apr;45(4):505–518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.4.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hele P., Barth P. T. Possible "allosteric" effects controlling the kinetic behavior of amino acid-dependent pyrophosphate exchange reactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 18;114(1):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90262-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington M. D., Hawtrey A. O. Inhibitory effects of pH5 enzyme from non-lactating bovine mammary gland on various stages of protein synthesis in the rat liver amino acid-incorporating system. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(4):671–678. doi: 10.1042/bj1150671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington M. D., Hawtrey A. O. Studies on subcellular fractions of non-lactating bovine mamm- ary gland. S Afr J Med Sci. 1969 Jul;34(2):49–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makman M. H., Cantoni G. L. Studies concerning the interaction of serine soluble ribonucleic acid with seryl soluble ribonucleic acid synthetase from baker's yeast. Biochemistry. 1966 Jul;5(7):2246–2254. doi: 10.1021/bi00871a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATERSON A. R., LEPAGE G. A. Ribonucleic acid synthesis in tumor homogenates. Cancer Res. 1957 Jun;17(5):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Berg P., Ofengand E. J., Bergmann F. H., Dieckmann M. THE CHEMICAL NATURE OF THE RNA-AMINO ACID COMPOUND FORMED BY AMINO ACID-ACTIVATING ENZYMES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Mar;45(3):319–328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARIN P. S., ZAMECNIK P. C. ON THE STABILITY OF AMINOACYL-S-RNA TO NUCLEOPHILIC CATALYSIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Dec 16;91:653–655. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WETTSTEIN F. O., STAEHELIN T., NOLL H. Ribosomal aggregate engaged in protein synthesis: characterization of the ergosome. Nature. 1963 Feb 2;197:430–435. doi: 10.1038/197430a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMANE T., SUEOKA N. CONSERVATION OF SPECIFICITY BETWEEN AMINO ACID ACCEPTOR RNA AND AMINO ACYL-SRNA SYNTHETASE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1093–1100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachau H. G., Acs G., Lipmann F. ISOLATION OF ADENOSINE AMINO ACID ESTERS FROM A RIBONUCLEASE DIGEST OF SOLUBLE, LIVER RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Sep 15;44(9):885–889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.9.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


