Abstract
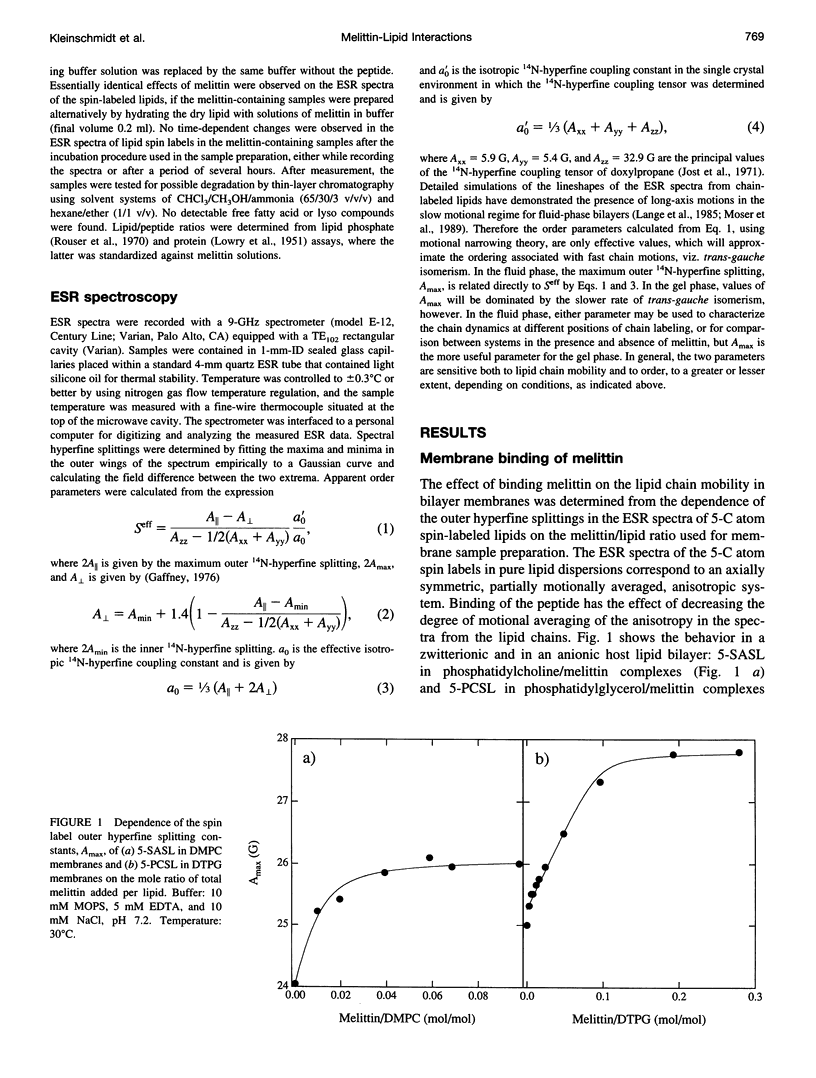
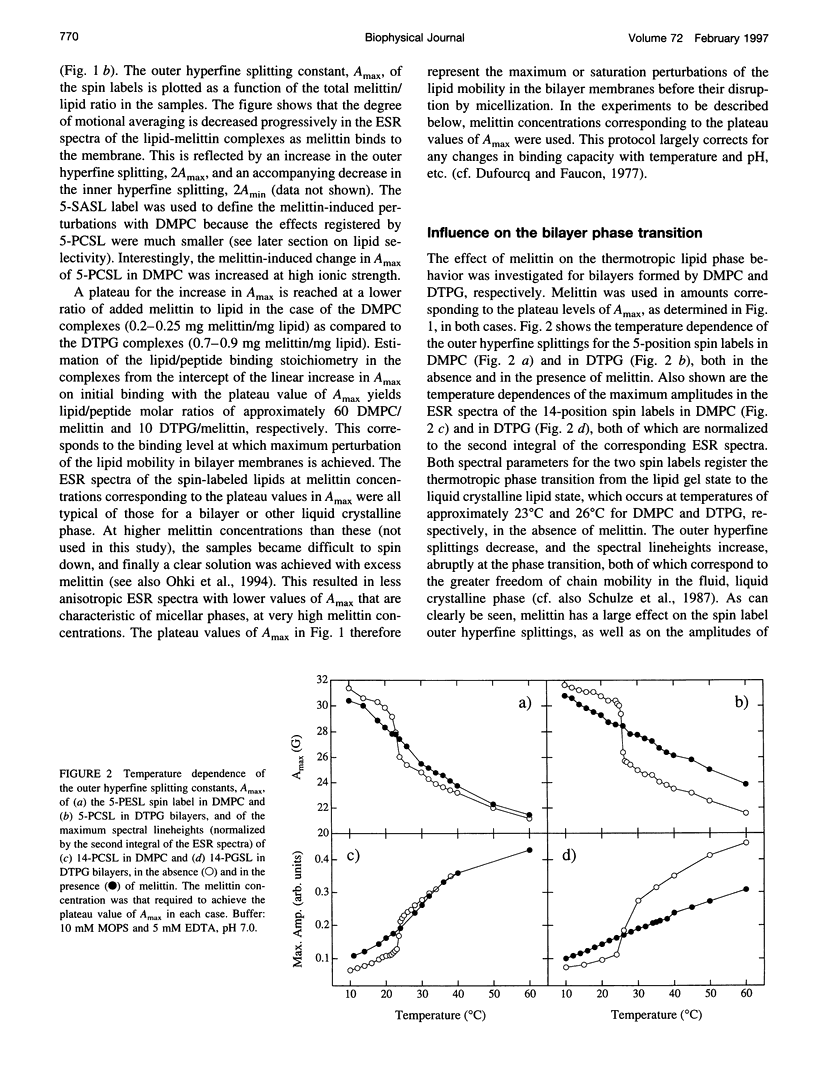
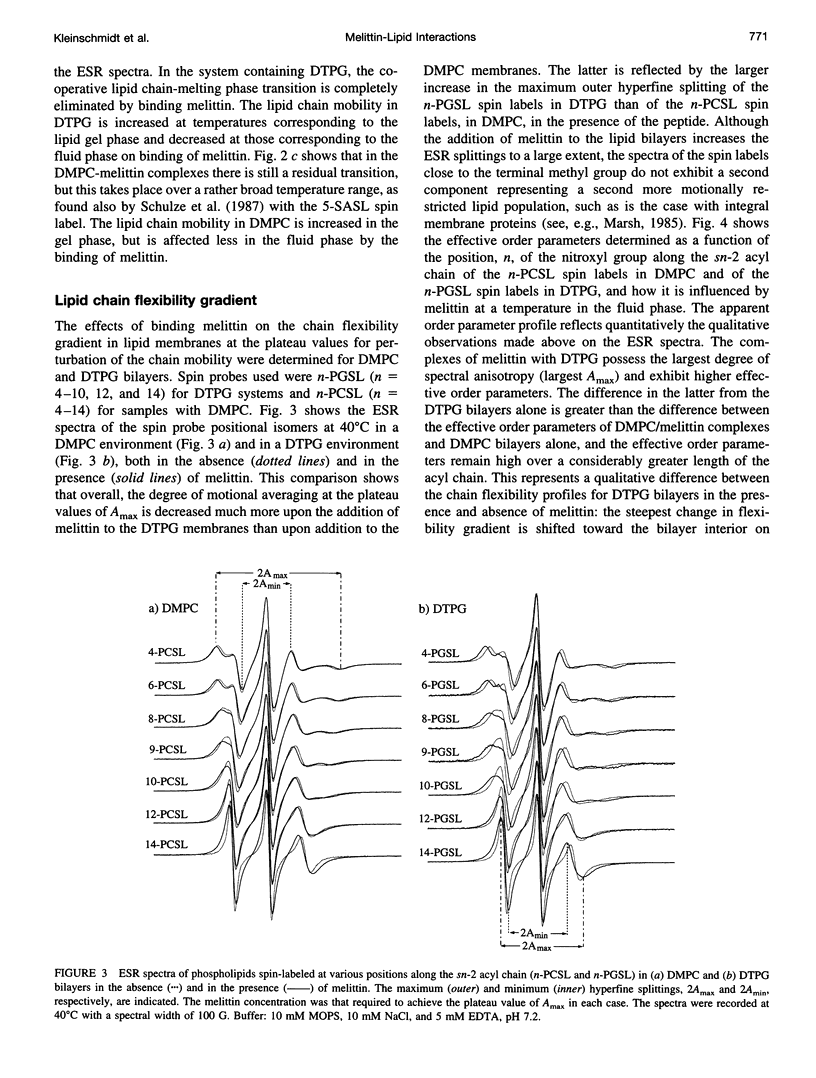
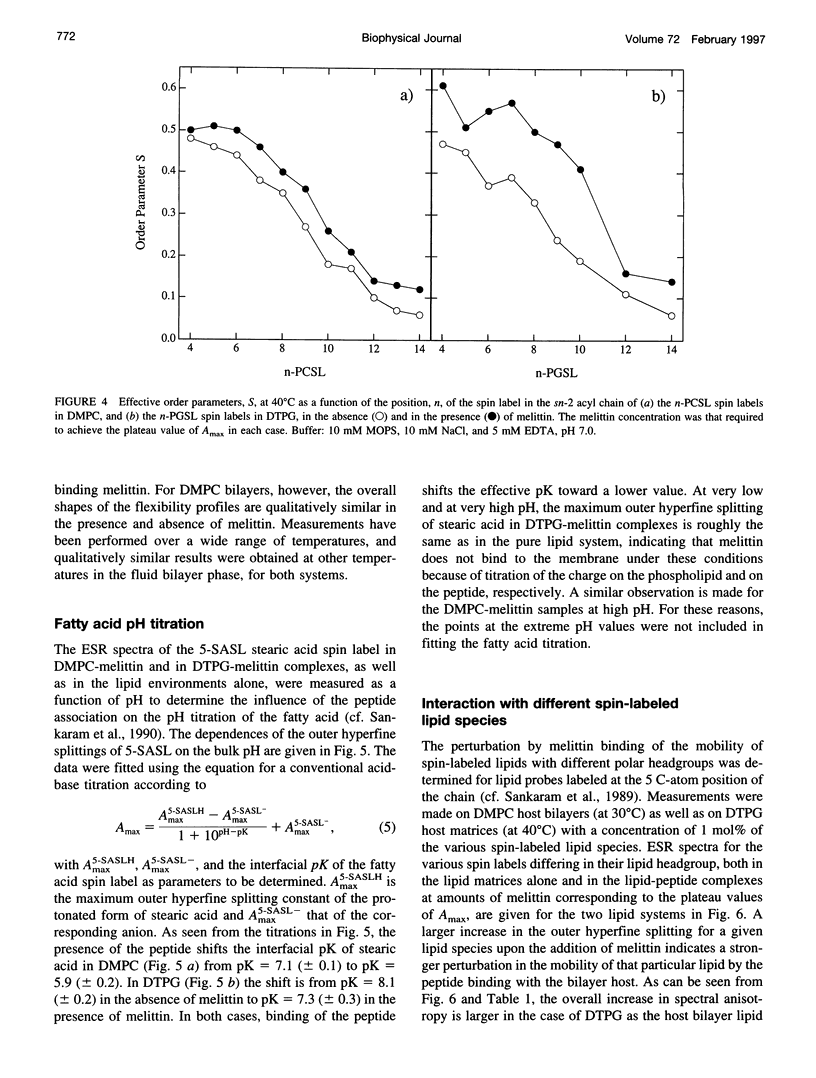
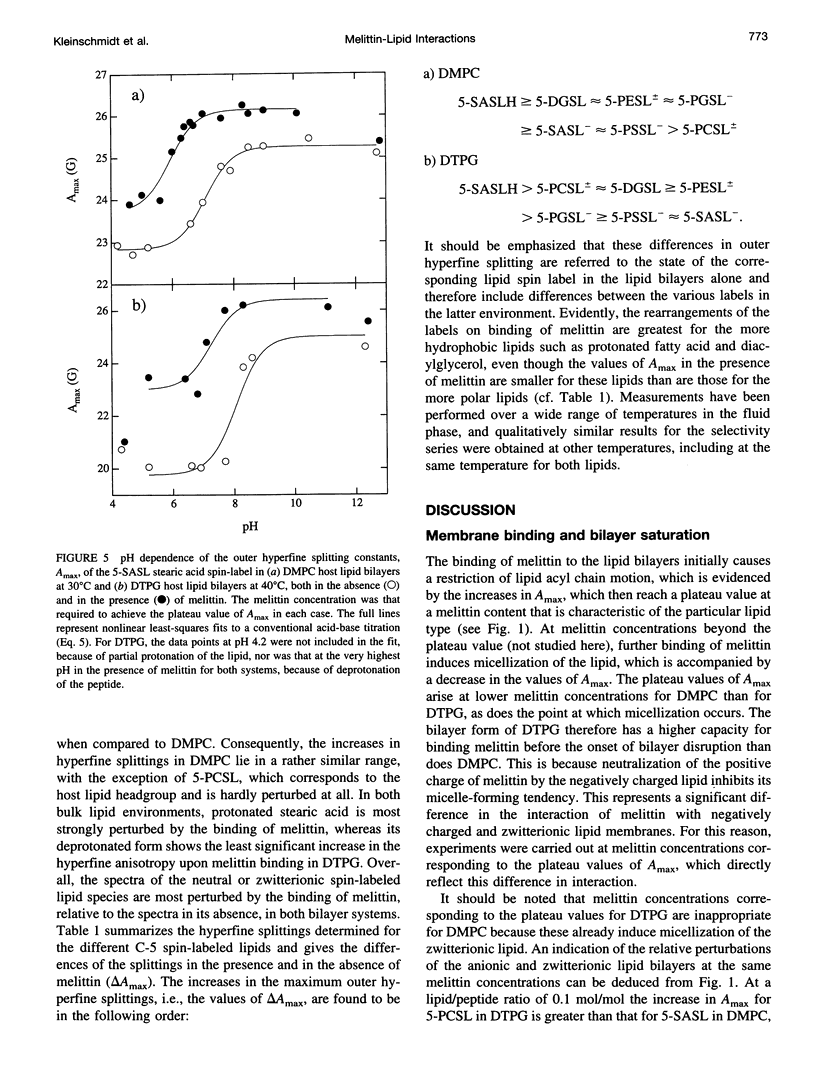
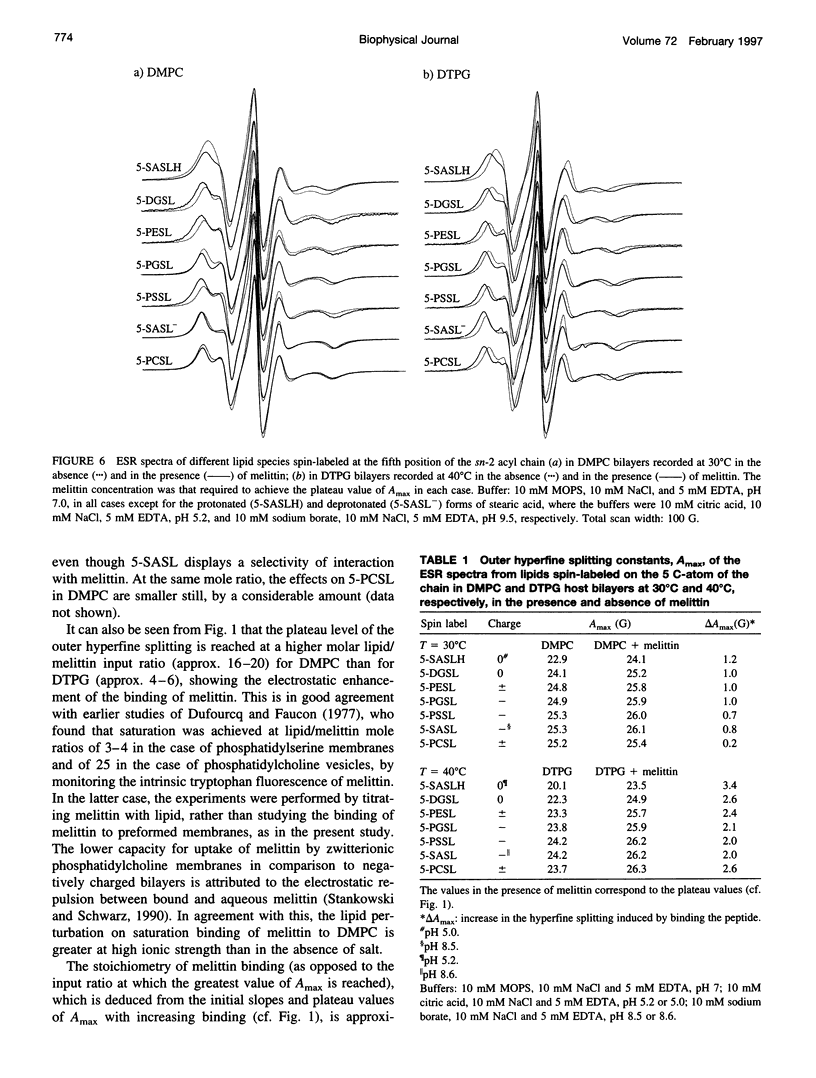
Electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy was used to study the penetration and interaction of bee venom melittin with dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC) and ditetradecylphosphatidylglycerol (DTPG) bilayer membranes. Melittin is a surface-active, amphipathic peptide and serves as a useful model for a variety of membrane interactions, including those of presequences and signal peptides, as well as the charged subdomain of the cardiac regulatory protein phospholamban. Derivatives of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylglycerol spin-labeled at various positions along the sn-2 acyl chain were used to establish the chain flexibility gradient for the two membranes in the presence and absence of melittin. Negatively charged DTPG bilayer membranes showed a higher capacity for binding melittin without bilayer disruption than did membranes formed by the zwitterionic DMPC, demonstrating the electrostatic neutralization of bound melittin by DTPG. The temperature dependence of the ESR spectra showed that the gel-to-liquid crystalline phase transition is eliminated by binding melittin to DTPG bilayers, whereas a very broad transition remains in the case of DMPC bilayers. None of the spin labels used showed a two-component spectrum characteristic of a specific restriction of their chain motion by melittin, but the outer hyperfine splittings and effective chain order parameters were increased for all labels upon binding melittin. This indicates a reduced flexibility of the lipid chains induced by a surface orientation of the bound melittin. Whereas the characteristic shape of the chain flexibility gradient was maintained upon melittin addition to DMPC bilayers, the chain flexibility profile in DTPG bilayers was much more strongly perturbed. It was found that the steepest change in segmental flexibility was shifted toward the bilayer interior when melittin was bound to DTPG membranes, indicating a greater depth of penetration than in DMPC membranes. pH titration of stearic acid labeled at the C-5 position, used as a probe of interfacial interactions, showed net downward shifts in interfacial pK of 0.8 and 1.2 pH units contributed from the positive charge of melittin, outweighing upward shifts from interfacial dehydration, when melittin was bound to DTPG and DMPC, respectively. The perturbation of the outer hyperfine splitting was used to determine the interactions of melittin with spin-labeled lipids of different polar headgroups in DTPG and DMPC. Anionic lipids (phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylglycerol, and stearic acid) and zwitterionic lipids (phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine) had the largest outer splittings in the presence of melittin. Neutral lipids (protonated stearic acid and diacylglycerol) displayed the largest increase in outer splitting on binding melittin, which was attributed to a change in the vertical location of these lipids in the bilayer. Both effects were more pronounced in DTPG than in DMPC.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenbach C., Froncisz W., Hyde J. S., Hubbell W. L. Conformation of spin-labeled melittin at membrane surfaces investigated by pulse saturation recovery and continuous wave power saturation electron paramagnetic resonance. Biophys J. 1989 Dec;56(6):1183–1191. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82765-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altenbach C., Hubbell W. L. The aggregation state of spin-labeled melittin in solution and bound to phospholipid membranes: evidence that membrane-bound melittin is monomeric. Proteins. 1988;3(4):230–242. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batenburg A. M., Hibbeln J. C., Verkleij A. J., de Kruijff B. Melittin induces HII phase formation in cardiolipin model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 18;903(1):142–154. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90164-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batenburg A. M., van Esch J. H., Leunissen-Bijvelt J., Verkleij A. J., de Kruijff B. Interaction of melittin with negatively charged phospholipids: consequences for lipid organization. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 19;223(1):148–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80526-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brauner J. W., Mendelsohn R., Prendergast F. G. Attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared studies of the interaction of melittin, two fragments of melittin, and delta-hemolysin with phosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8151–8158. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiesi M., Vorherr T., Falchetto R., Waelchli C., Carafoli E. Phospholamban is related to the autoinhibitory domain of the plasma membrane Ca(2+)-pumping ATPase. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 13;30(32):7978–7983. doi: 10.1021/bi00246a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson C. R., Drake A. F., Helliwell J., Hider R. C. The interaction of bee melittin with lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 16;510(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempsey C. E., Butler G. S. Helical structure and orientation of melittin in dispersed phospholipid membranes from amide exchange analysis in situ. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 8;31(48):11973–11977. doi: 10.1021/bi00163a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempsey C. E. The actions of melittin on membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 7;1031(2):143–161. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufourcq J., Faucon J. F., Fourche G., Dasseux J. L., Le Maire M., Gulik-Krzywicki T. Morphological changes of phosphatidylcholine bilayers induced by melittin: vesicularization, fusion, discoidal particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 10;859(1):33–48. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufourcq J., Faucon J. F. Intrinsic fluorescence study of lipid-protein interactions in membrane models. Binding of melittin, an amphipathic peptide, to phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 16;467(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90236-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A. The spontaneous insertion of proteins into and across membranes: the helical hairpin hypothesis. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faucon J. F., Dufourcq J., Lussan C. The self-association of melittin and its binding to lipids: an intrinsic fluorescence polarization study. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 1;102(1):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80956-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey S., Tamm L. K. Orientation of melittin in phospholipid bilayers. A polarized attenuated total reflection infrared study. Biophys J. 1991 Oct;60(4):922–930. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82126-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E. Bee and wasp venoms. Science. 1972 Jul 28;177(4046):314–322. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4046.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Jentsch J. Sequenzanalyse des Melittins aus den tryptischen und peptischen Spaltstücken. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Jan;348(1):37–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlos K., Eibl H. Influence of calcium on phosphatidylglycerol. Two separate lamellar structures. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):895–899. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimburg T., Marsh D. Protein surface-distribution and protein-protein interactions in the binding of peripheral proteins to charged lipid membranes. Biophys J. 1995 Feb;68(2):536–546. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80215-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimburg T., Würz U., Marsh D. Binary phase diagram of hydrated dimyristoylglycerol-dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine mixtures. Biophys J. 1992 Nov;63(5):1369–1378. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81714-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holak T. A., Prestegard J. H., Forman J. D. NMR-pseudoenergy approach to the solution structure of acyl carrier protein. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 28;26(15):4652–4660. doi: 10.1021/bi00389a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikura T., Go N., Inagaki F. Refined structure of melittin bound to perdeuterated dodecylphosphocholine micelles as studied by 2D-NMR and distance geometry calculation. Proteins. 1991;9(2):81–89. doi: 10.1002/prot.340090202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P., Libertini L. J., Hebert V. C., Griffith O. H. Lipid spin labels in lecithin multilayers. A study of motion along fatty acid chains. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):77–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90414-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange A., Marsh D., Wassmer K. H., Meier P., Kothe G. Electron spin resonance study of phospholipid membranes employing a comprehensive line-shape model. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 30;24(16):4383–4392. doi: 10.1021/bi00337a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauterwein J., Brown L. R., Wüthrich K. High-resolution 1H-NMR studies of monomeric melittin in aqueous solution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 25;622(2):219–230. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahaney J. E., Kleinschmidt J., Marsh D., Thomas D. D. Effects of melittin on lipid-protein interactions in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biophys J. 1992 Dec;63(6):1513–1522. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81736-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahaney J. E., Thomas D. D. Effects of melittin on molecular dynamics and Ca-ATPase activity in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes: electron paramagnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 23;30(29):7171–7180. doi: 10.1021/bi00243a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser M., Marsh D., Meier P., Wassmer K. H., Kothe G. Chain configuration and flexibility gradient in phospholipid membranes. Comparison between spin-label electron spin resonance and deuteron nuclear magnetic resonance, and identification of new conformations. Biophys J. 1989 Jan;55(1):111–123. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82784-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohki S., Marcus E., Sukumaran D. K., Arnold K. Interaction of melittin with lipid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Sep 14;1194(2):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Fkeischer S., Yamamoto A. Two dimensional then layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1970 May;5(5):494–496. doi: 10.1007/BF02531316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom M. S. The biophysics of peptide models of ion channels. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1991;55(3):139–235. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(91)90004-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze J., Mischeck U., Wigand S., Galla H. J. Incorporation of highly purified melittin into phosphatidylcholine bilayer vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 10;901(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90261-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sessa G., Freer J. H., Colacicco G., Weissmann G. Interaction of alytic polypeptide, melittin, with lipid membrane systems. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3575–3582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stankowski S., Pawlak M., Kaisheva E., Robert C. H., Schwarz G. A combined study of aggregation, membrane affinity and pore activity of natural and modified melittin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Oct 14;1069(1):77–86. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90106-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stankowski S., Schwarz G. Electrostatics of a peptide at a membrane/water interface. The pH dependence of melittin association with lipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 27;1025(2):164–172. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot J. C., Dufourcq J., de Bony J., Faucon J. F., Lussan C. Conformational change and self association of monomeric melittin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 1;102(1):191–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80957-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger T. C., Eisenberg D. The structure of melittin. II. Interpretation of the structure. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6016–6022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger T. C., Weissman L., Eisenberg D. The structure of melittin in the form I crystals and its implication for melittin's lytic and surface activities. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):353–361. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84683-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson M. T., Tosteson D. C. The sting. Melittin forms channels in lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1981 Oct;36(1):109–116. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84719-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H., Jähnig F., Hoffmann V., Stümpel J. The orientation of melittin in lipid membranes. A polarized infrared spectroscopy study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 7;733(2):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90523-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H., Jähnig F. The structure of melittin in membranes. Biophys J. 1986 Oct;50(4):573–582. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83497-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss J. C., Mahaney J. E., Thomas D. D. Mechanism of Ca-ATPase inhibition by melittin in skeletal sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry. 1995 Jan 24;34(3):930–939. doi: 10.1021/bi00003a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss J., Birmachu W., Hussey D. M., Thomas D. D. Effects of melittin on molecular dynamics and Ca-ATPase activity in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes: time-resolved optical anisotropy. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 30;30(30):7498–7506. doi: 10.1021/bi00244a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wille B. A preparation of melittin depleted of phospholipase A2 by ion exchange chromatography in denaturing solvents. Anal Biochem. 1989 Apr;178(1):118–120. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90365-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


