Abstract
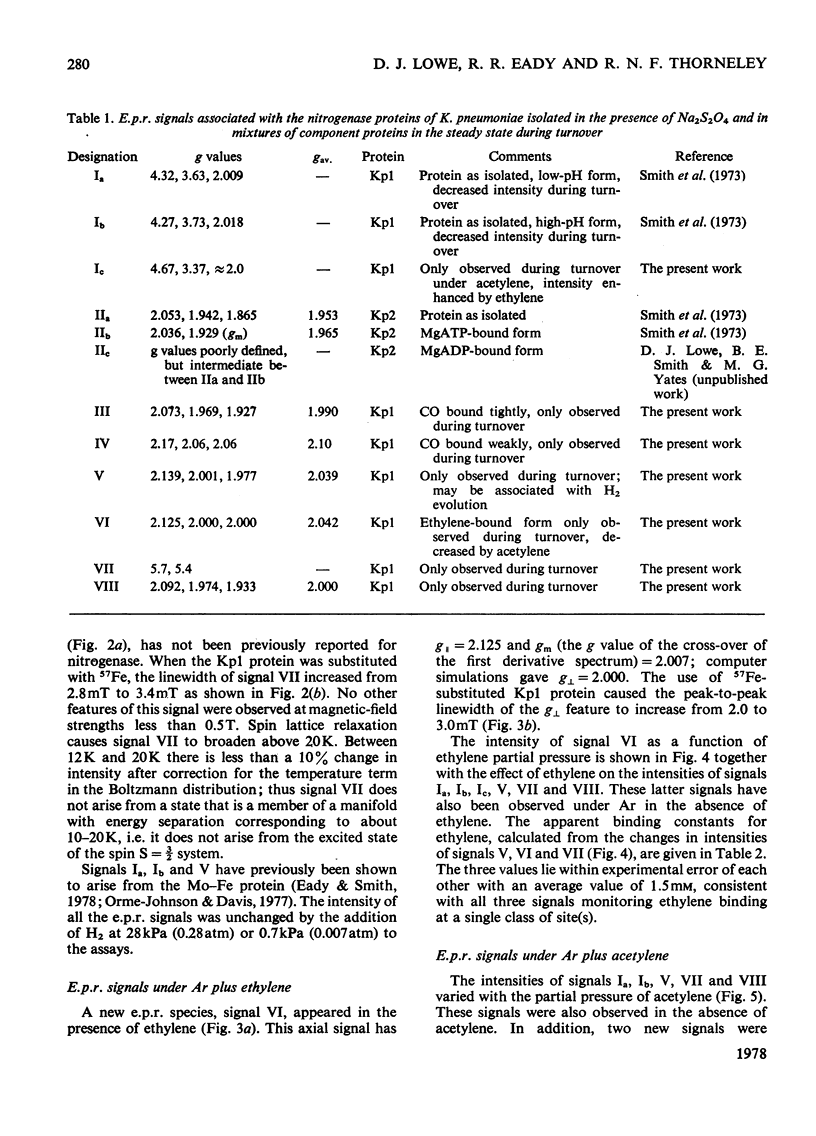
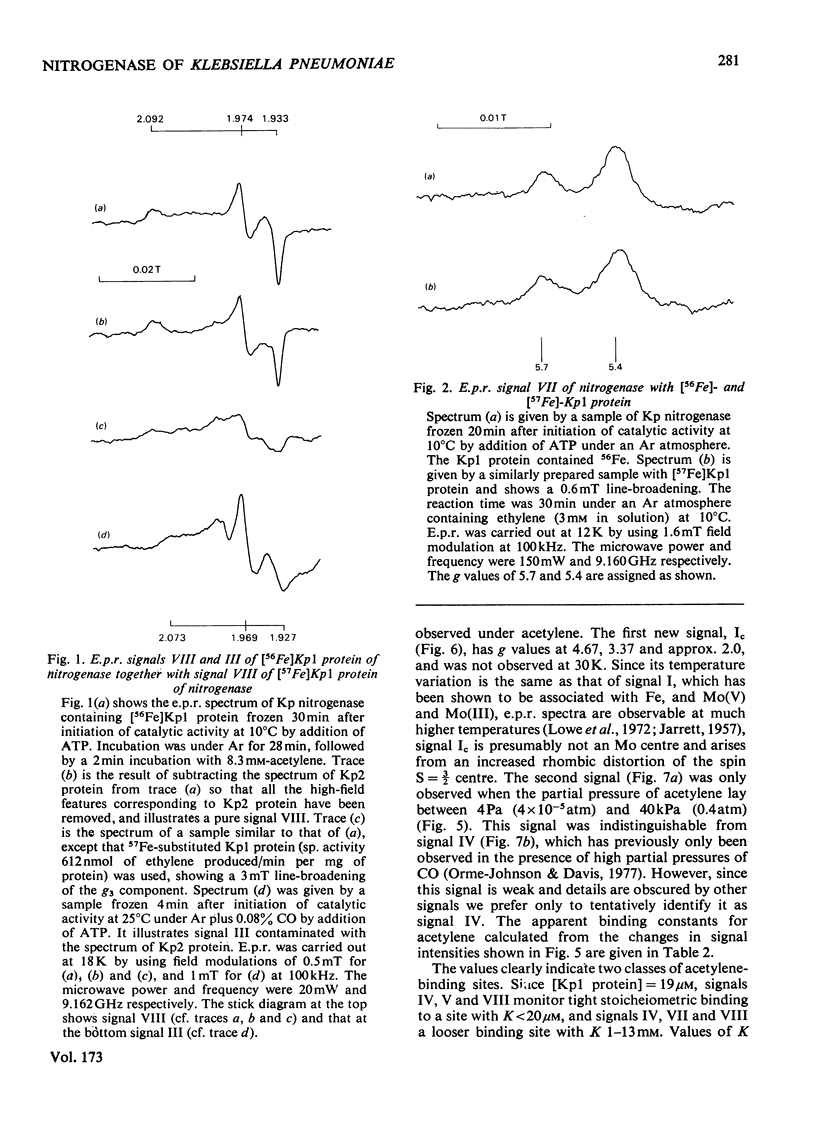
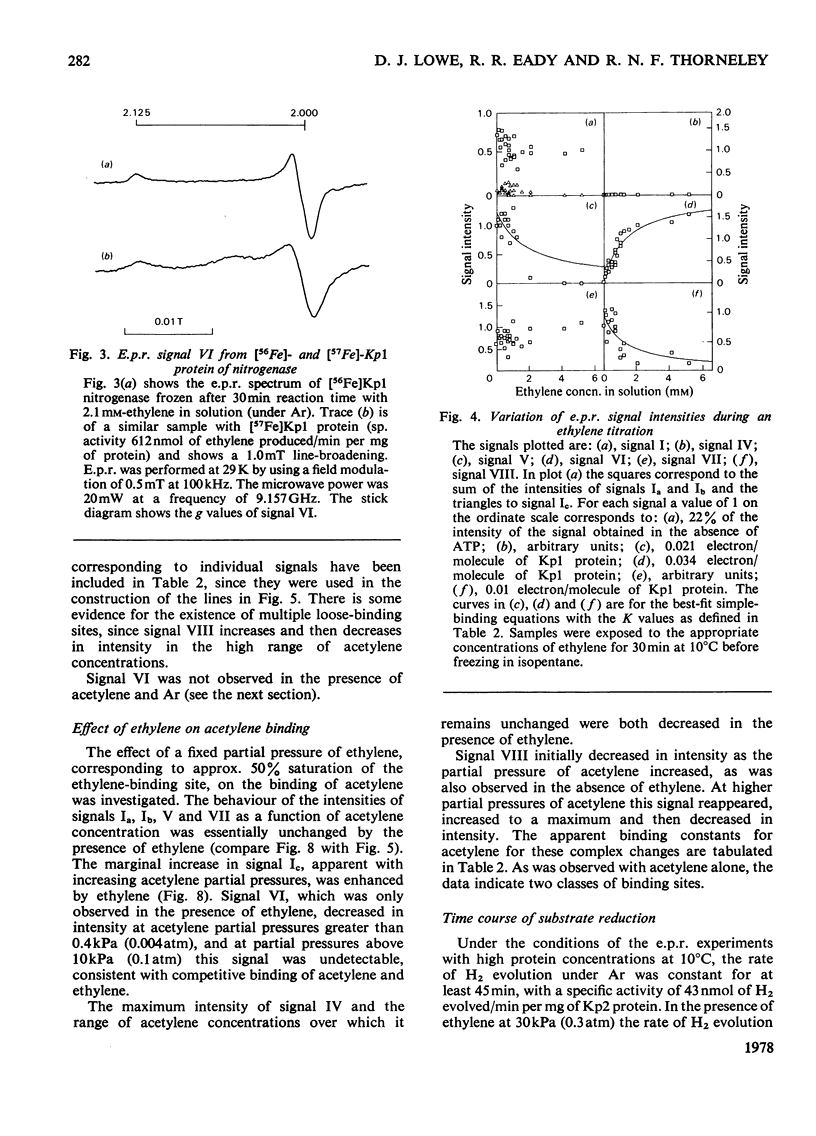
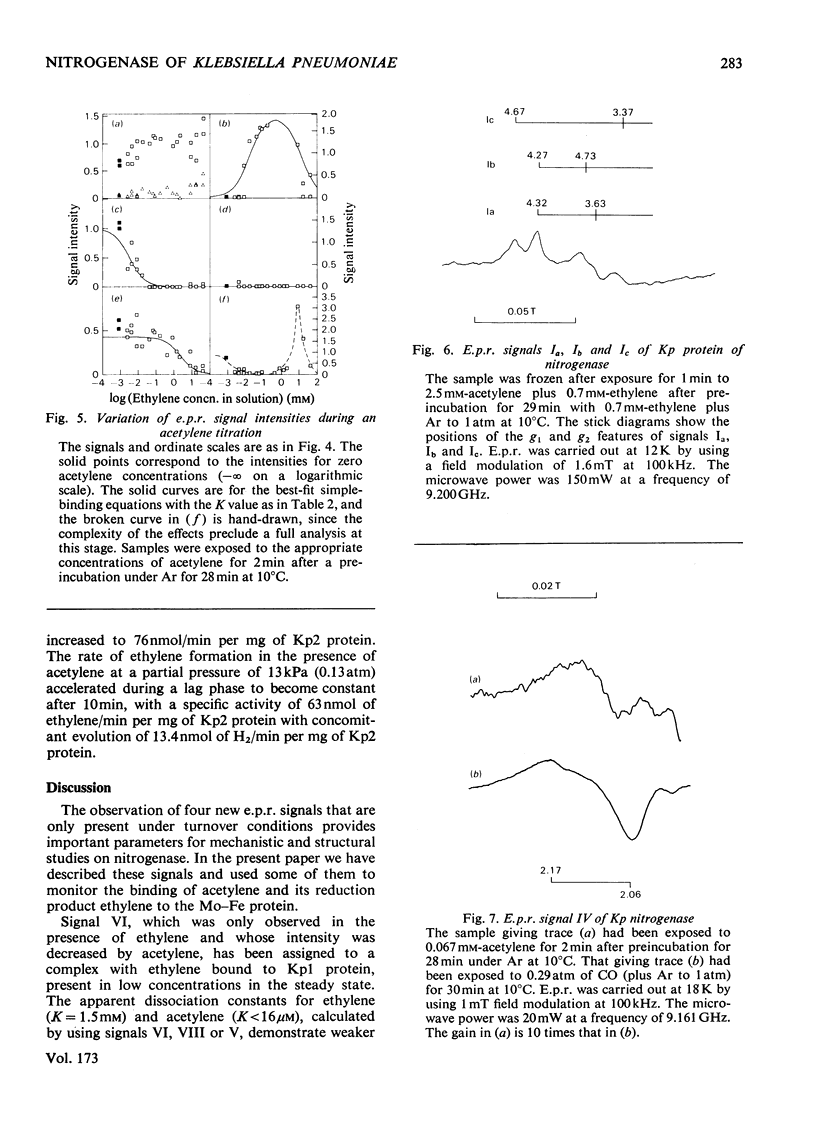
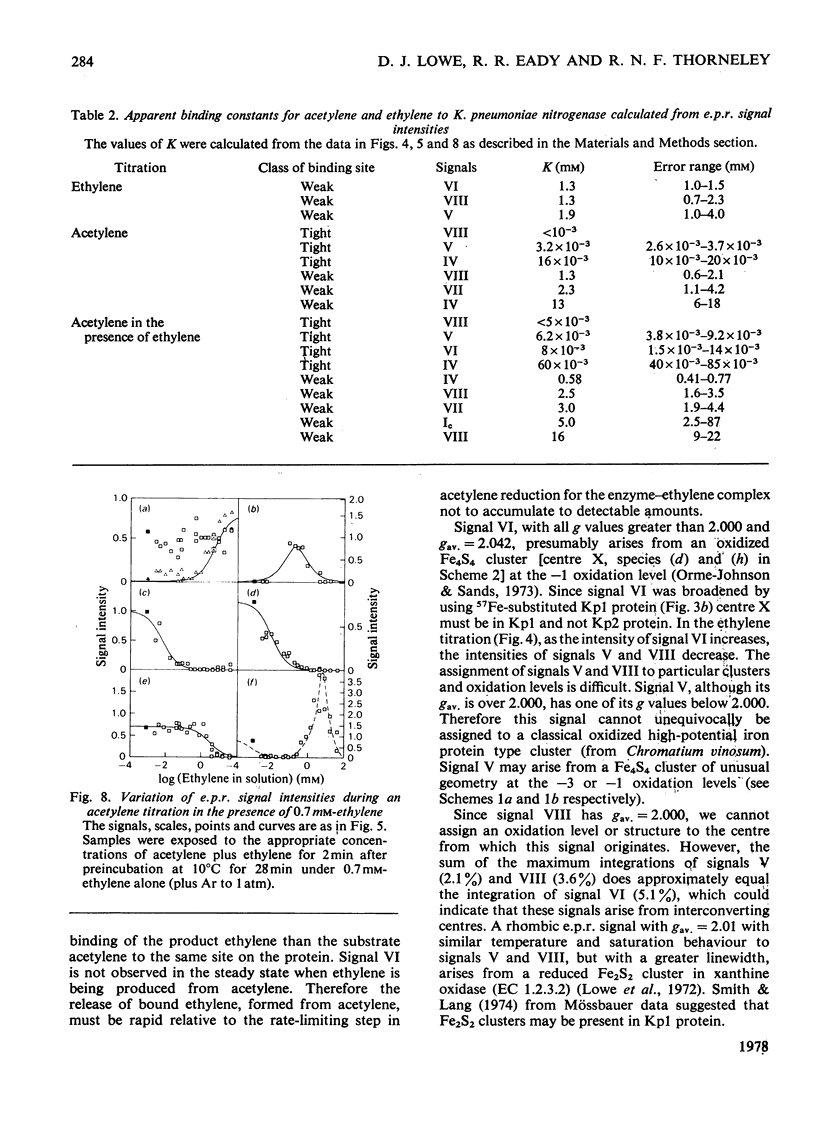
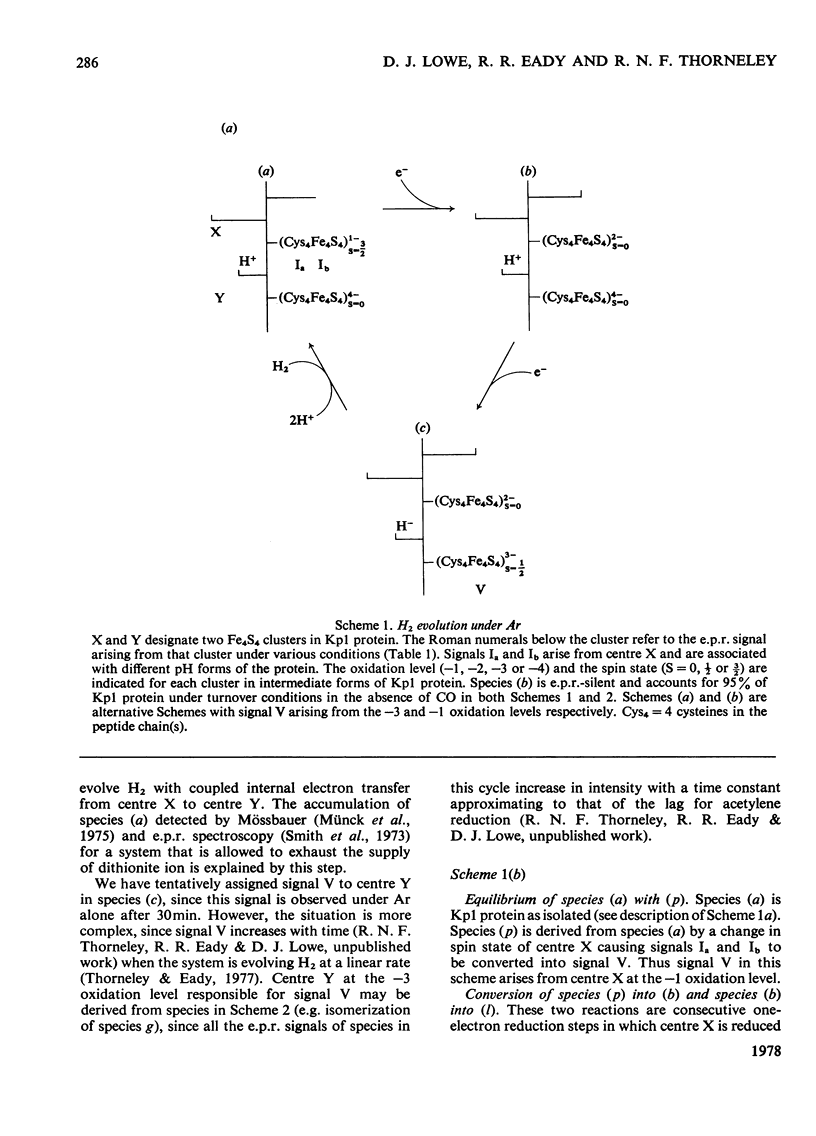
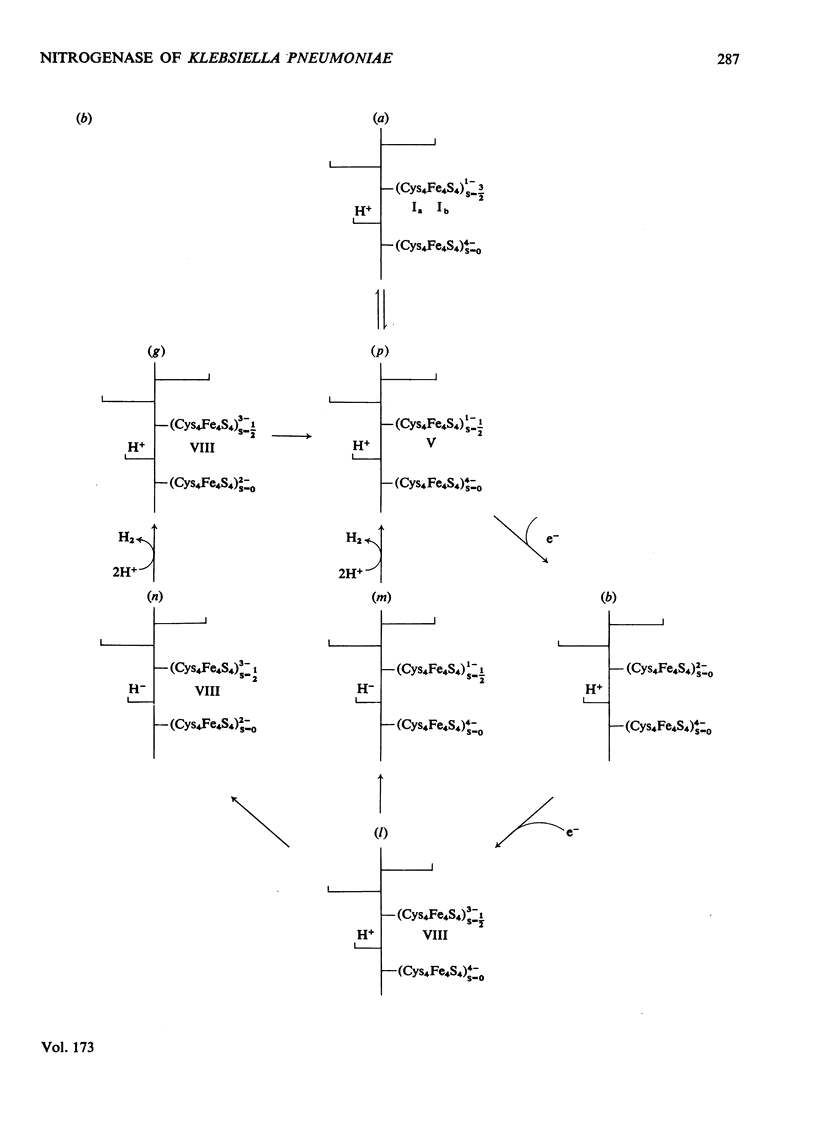
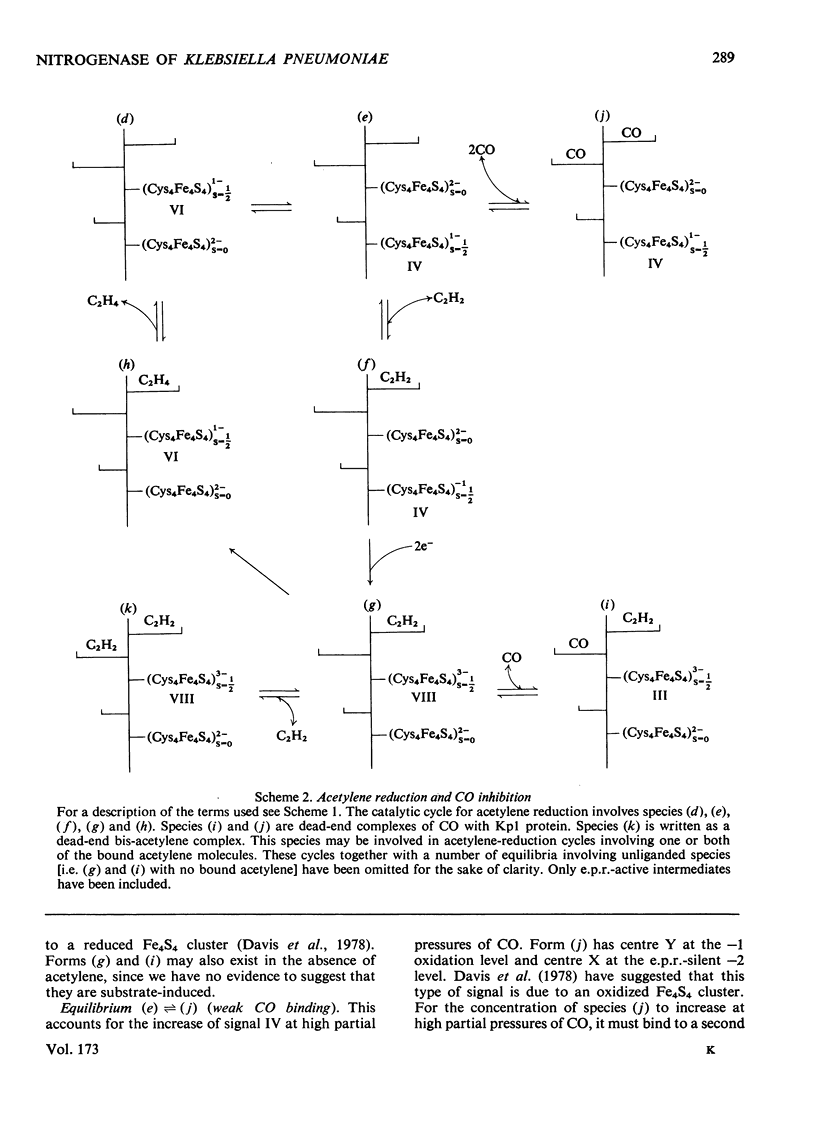
Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase exhibited four new electron-paramagnetic-resonance signals during turnover at 10 degrees C, pH7.4, which were assigned to intermediates present in low concentrations in the steady state. 57Fe-substituted Mo--Fe protein showed that they arose from Fe--S clusters in the Mo--Fe protein of nitrogenase. The new signals are designated: Ic, g values at 4.67, 3.37 and approx. 2.0; VI, g values at 2.125, 2.000 and 2.000; VII, g values at 5.7 and 5.4; VIII, g values at 2.092, 1.974 and 1.933. The sharp axial signal VI arises from a Fe4S4 cluster at the --1 oxidation level. This signal was only detected in the presence of ethylene and provides the first evidence of an enzyme--product complex for nitrogenase. [13C]Acetylene and [13C]ethylene provided no evidence for direct binding of this substrate and product to the Fe--S clusters giving rise to these signals. The dependence of signal intensities on acetylene concentration indicated two types of binding site, with apparent dissociation constants K less than 16 micron and K approximately 13mM. A single binding site for ethylene (K=1.5mM) was detected. A scheme is proposed for the mechanism of reduction of acetylene to ethylene and inhibition of this reaction by CO.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bray R. C., Barber M. J., Lowe D. J. Electron-paramagnetic-resonance spectroscopy of complexes of xanthine oxidase with xanthine and uric acid. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 1;171(3):653–658. doi: 10.1042/bj1710653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Smith B. E., Cook K. A., Postgate J. R. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Purification and properties of the component proteins. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):655–675. doi: 10.1042/bj1280655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erbes D. L., Burris R. H., Orme-Johnson W. H. On the iron-sulfur cluster in hydrogenase from Clostridium pasteurianum W5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4795–4799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum W. O., Mortenson L. E., Chen J. S., Holm R. H. Quantitative extrusions of the Fe4S4 cores of the active sites of ferredoxins and the hydrogenase of Clostridium pasteurianum. J Am Chem Soc. 1977 Jan 19;99(2):584–595. doi: 10.1021/ja00444a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J. C., Chen C. H., Burris R. H. Inhibition of nitrogenase-catalyzed reductions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 18;292(1):256–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. Comparisons and cross reactions of nitrogenase from Klebsiella pneumoniae, Azotobacter chroococcum and Bacillus polymyxa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;191(3):527–540. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90346-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C., Eady R. R., Kondorosi E., Rekosh D. K. The molybdenum--iron protein of Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase. Evidence for non-identical subunits from peptide 'mapping'. Biochem J. 1976 May 1;155(2):383–389. doi: 10.1042/bj1550383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. J., Bray R. C. Magnetic coupling of the molybdenum and iron-sulphur centres in xanthine oxidase and xanthine dehydrogenases. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 1;169(3):471–479. doi: 10.1042/bj1690471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. J. Electron paramagnetic resonance in biochemistry. Computer simulation of spectra from frozen aqueous samples. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 1;171(3):649–651. doi: 10.1042/bj1710649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. J., Lynden-Bell R. M., Bray R. C. Spin-spin interaction between molybdenum and one of the iron-sulphur systems of xanthine oxidase and its relevance to the enzymic mechanism. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(1):239–249. doi: 10.1042/bj1300239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münck E., Rhodes H., Orme-Johnson W. H., Davis L. C., Brill W. J., Shah V. K. Nitrogenase. VIII. Mössbauer and EPR spectroscopy. The MoFe protein component from Azotobacter vinelandii OP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 21;400(1):32–53. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer G., Multani J. S., Cretney W. C., Zumft W. G., Mortenson L. E. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies on nitrogenase. I. The properties of molybdoferredoxin and azoferredoxin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Nov;153(1):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90452-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Davis L. C., Brill W. J. Nitrogenase. VI. Acetylene reduction assay: Dependence of nitrogen fixation estimates on component ratio and acetylene concentration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 19;384(2):353–359. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Lang G. Mössbauer spectroscopy of the nitrogenase proteins from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Structural assignments and mechanistic conclusions. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):169–180. doi: 10.1042/bj1370169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Lowe D. J., Bray R. C. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae: electron-paramagnetic-resonance studies on the catalytic mechanism. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(2):641–643. doi: 10.1042/bj1300641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Lowe D. J., Bray R. C. Studies by electron paramagnetic resonance on the catalytic mechanism of nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;135(2):331–341. doi: 10.1042/bj1350331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Thorneley R. N., Eady R. R., Mortenson L. E. Nitrogenases from Klebsiella pneumoniae and Clostridium pasteurianum. Kinetic investigations of cross-reactions as a probe of the enzyme mechanism. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):439–447. doi: 10.1042/bj1570439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorneley R. N., Cornish-Bowden A. Kinetics of nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Heterotropic interactions between magnesium-adenosine 5'-diphosphate and magnesium-adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 1;165(2):255–262. doi: 10.1042/bj1650255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorneley R. N., Eady R. R. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Distinction between proton-reducing and acetylene-reducing forms of the enzyme: effect of temperature and component protein ratio on substrate-reduction kinetics. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 1;167(2):457–461. doi: 10.1042/bj1670457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorneley R. N. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. A stopped-flow study of magnesium-adenosine triphosphate-induce electron transfer between the compeonent proteins. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;145(2):391–396. doi: 10.1042/bj1450391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates M. G., Lowe D. J. Nitrogenase of Azotobacter chroococcum: a new electron-paramagnetic-resonance signal associated with a transient species of the Mo-Fe protein during catalysis. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 15;72(1):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80826-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


