Abstract
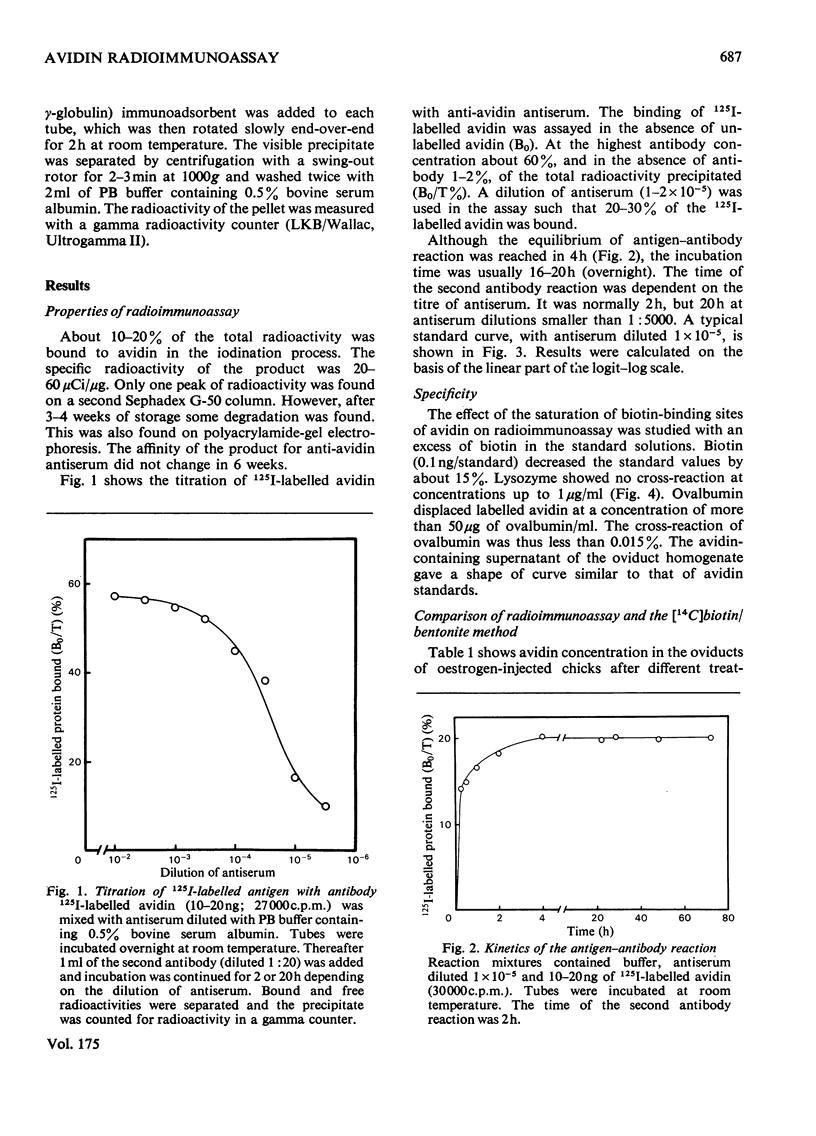
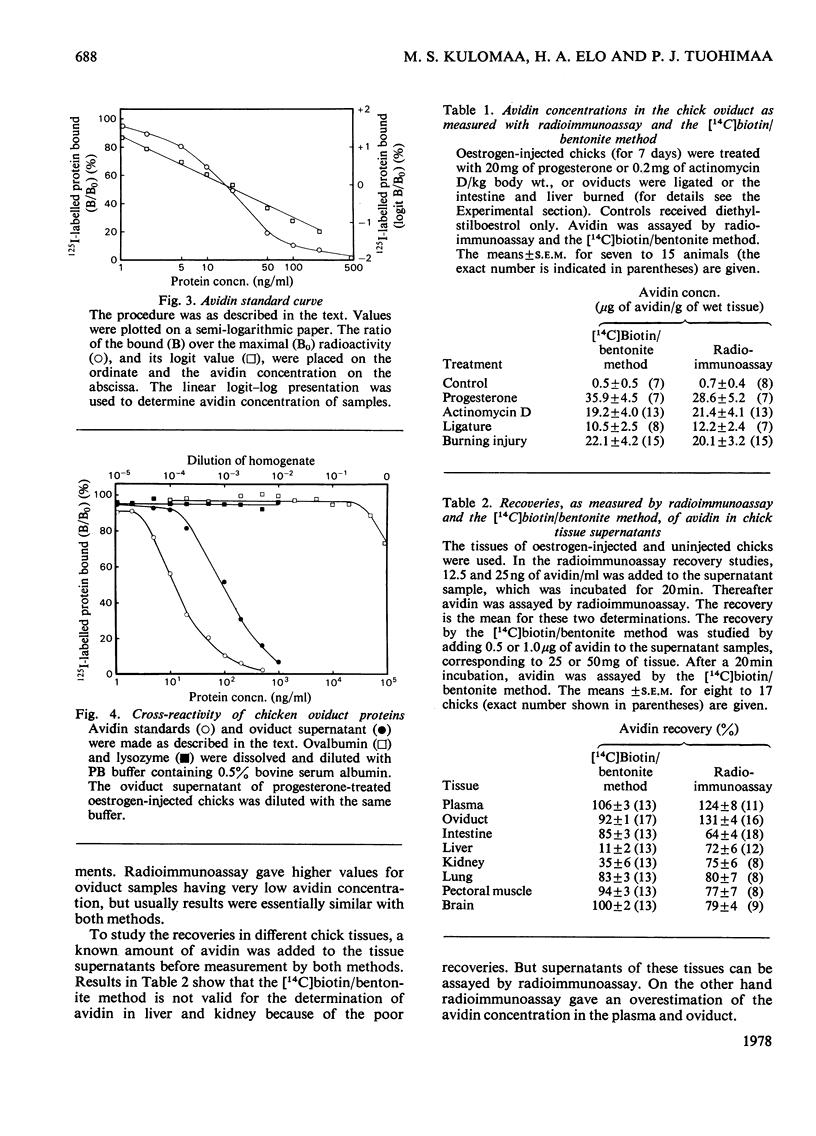
A double-antibody solid-phase radioimmunoassay for chicken avidin is reported. Avidin was labelled with 125I by the chloramine-T method. The bound and free avidin were separated with a second antibody bound to a solid matrix. In the logit-log scale the standard curve was linear from 1-2 to 100-200ng of avidin/ml. Cross-reaction of ovalbumin was less than 0.015%. Saturation of biotin-binding sites of avidin with an excess of biotin decreased radioimmunoassay values by about 15%. Recovery studies indicated that avidin can be assayed from all chicken tissues studied with radioimmunoassay, whereas the [14C]biotin/bentonite method gave poor recoveries for avidin in the liver and kidney. Radioimmunoassay and the [14C]biotin/bentonite method gave similar concentrations for oviduct avidin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Elo H., Tuohimaa P. An improved micro-method for avidin assay. Biochem J. 1974 Apr;140(1):115–116. doi: 10.1042/bj1400115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elo H., Tuohimaa P., Jänne O. Cumulative superinduction of avidin in the chick oviduct by tissue damage and actinomycin D. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1975 Mar;2(3):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(75)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN N. M. AVIDIN. 1. THE USE OF (14-C)BIOTIN FOR KINETIC STUDIES AND FOR ASSAY. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:585–591. doi: 10.1042/bj0890585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Avidin. Adv Protein Chem. 1975;29:85–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60411-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Evidence for a genetic relationship between avidins and lysozymes. Nature. 1968 Jan 20;217(5125):254–256. doi: 10.1038/217254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. W., Korenman S. G. Studies on the mechanism of hormone induction of a specific protein. Immunological identity and kinetic studies of avidin synthesized in vitro by the chick oviduct. Life Sci. 1967 Sep 15;6(18):1953–1959. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. W., McGuire W. L., Kohler P. O., Korenman S. G. Studies on the mechanism of steroid hormone regulation of synthesis of specific proteins. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1969;25:105–160. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571125-8.50006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIVA SANKAR D. V., COSSANO B. J., THEIS H. W., MARKS C. R. Antigenicity of avidin. Nature. 1958 Mar 1;181(4609):619–620. doi: 10.1038/181619b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEI R., WRIGHT L. D. DETERMINATION OF AVIDIN BY USE OF RADIOACTIVE BIOTIN AND SEPHADEX CHROMATOGRAPHY. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Oct;117:17–20. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. B., 3rd, Dennison B. A., Della Fera M. A., Whitney C. J., McGuire J. C., Meslar H. W., Sammelwitz P. H. Biotin-binding protein from chicken egg yolk. Assay and relationship to egg-white avidin. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):395–400. doi: 10.1042/bj1570395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


