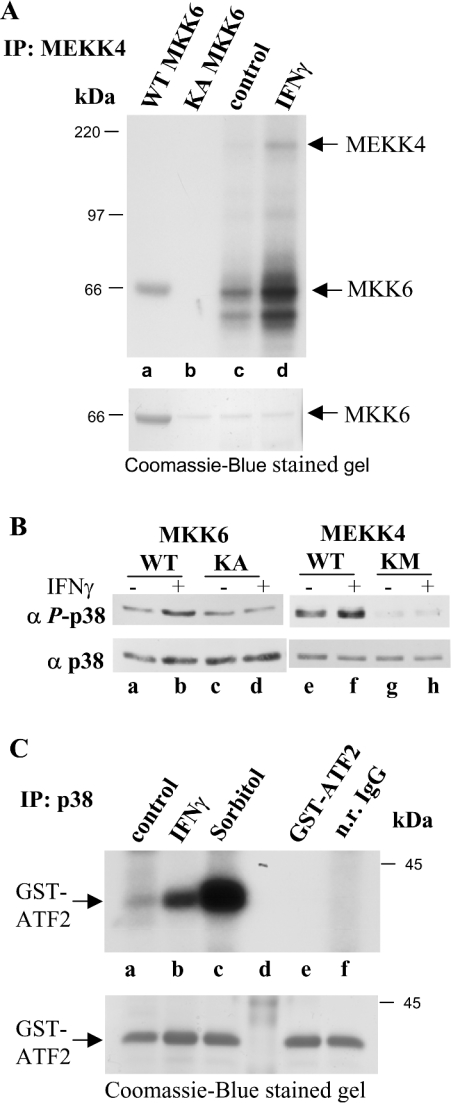
Figure 5. IFNγ regulates MEKK4 activity towards MKK6, the activating kinase for p38 MAPK.
(A) MEKK4 was immunoprecipitated (IP) from HaCaT cells untreated and treated for 25 min with IFNγ, and subjected to in vitro kinase assay conditions in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP with recombinant KA MKK6 as substrate (lanes c and d). Note, in lanes c and d, the band below the indicated MKK6 signal is probably a breakdown product of KA MKK6. As controls, MKK6 and kinase-inactive KA MKK6 were also incubated under kinase assay conditions (lanes a and b). The amount of MKK6 used in each assay was visualized by Coomassie-Blue-staining the same gel before autoradiography. (B) p38 MAPK activation is dependent on MKK6 and MEKK4 activity. HEK-293 cells were transfected with MKK6 and KA MKK6 or with MEKK4 and KM MEKK4, and were stimulated with IFNγ as indicated. Cell lysates were probed for p38 activation with a monoclonal phospho-specific anti-p38 antibody (α P-p38; upper panel). The membrane was reprobed with a monoclonal p38 antibody (α p38; lower panel) to show total p38 protein amounts. (C) p38 is activated by IFNγ. p38 was immunoprecipitated from HaCaT cells, untreated or treated for 15 min with IFNγ and subjected to in vitro kinase assay conditions in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP with a recombinant GST–ATF2 fragment. Incubation with 0.3 M sorbitol for 20 min was used as control, while GST–ATF2 alone and normal rabbit (n.r.) IgG served as negative controls. Shown is an autoradiograph, while the amounts of GST–ATF2 was visualized by Coomassie-Blue-staining the same gel.