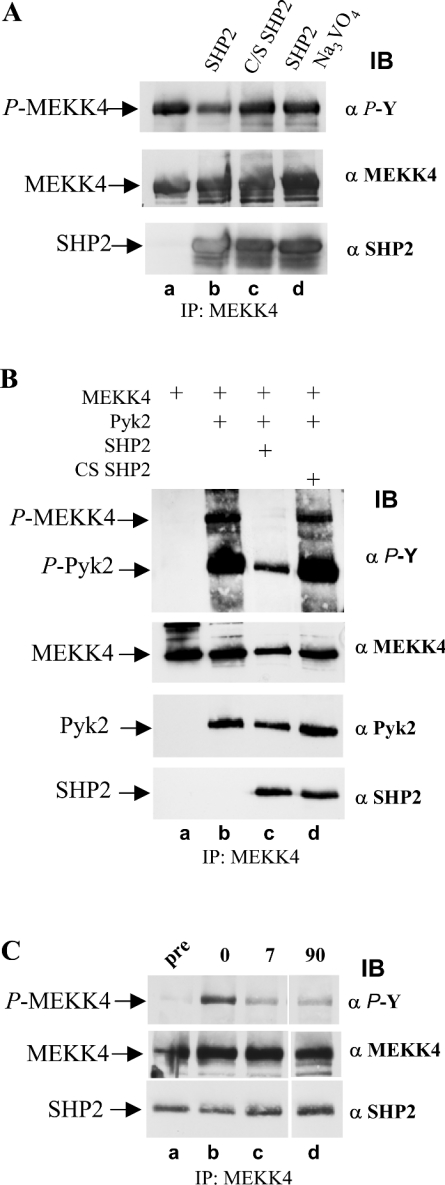
Figure 7. Co-expression of SHP2 in Sf9 cells results in loss of phosphotyrosine on MEKK4.
(A) In vitro phosphatase assay with SHP2 on tyrosine-phosphorylated MEKK4. MEKK4 and Pyk2 were co-expressed in Sf9 cells and tyrosine-phosphorylated MEKK4 was immunoprecipitated (IP) with antibodies against MEKK4 (α MEKK4). Equal amounts of immunoprecipitated MEKK4 were incubated with purified SHP2, phosphatase-inactive CS SHP2, and SHP2 in the presence of 2 mM Na3VO4 under phosphatase assay conditions (lanes b–d), and, subsequently, MEKK4 tyrosine phosphorylation was determined by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-phosphotyrosine antibody (α P-Y). Active SHP2 leads to loss of phosphotyrosine of MEKK4. (B) Co-expression of SHP2, but not CS SHP2, results in greatly decreased amounts of tyrosylphosphate on MEKK4 and Pyk2. Sf9 cells were co-infected with MEKK4 and Pyk2 without and with SHP2. Substitution with inactive CS SHP2 served as a control. MEKK4 was immunoprecipitated, and tyrosine phosphorylation was determined by immunoblotting with anti-phosphotyrosine antibody (α P-Y; top panel). Amounts of proteins were visualized by re-probing the membrane with antibodies against MEKK4 (α MEKK4; second panel), Pyk2 (α Pyk2; third panel) and SHP2 (α SHP2; bottom panel). (C) SHP2 dephosphorylates MEKK4 directly. Sf9 suspension cell culture co-expressing MEKK4, Pyk2 and SHP2 were supplemented with 2 mM Na3VO4 for 1 h, and subsequently washed out. MEKK4 was immunoprecipitated from aliquots taken before (pre), after treatment (0) and after Na3VO4 washout (7 and 90 min) and were analysed for phosphotyrosine (α P-Y; top panel). Amounts of proteins, MEKK4 and co-immunoprecipitating SHP2 were determined by re-probing the immunoblot with antibodies against MEKK4 (α MEKK4; middle panel) and monoclonal SHP2 (α SHP2; bottom panel). SHP2 dephosphorylates MEKK4 directly as well as its activating kinase Pyk2.