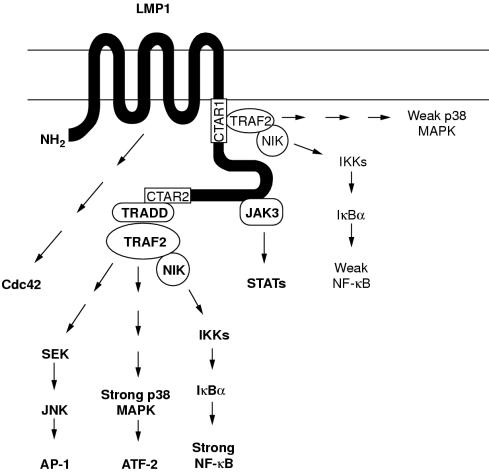
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of the known signalling pathways activated by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1). The LMP1 cytoplasmic tail contains two functional domains with respect to NF-κB activation (shown as white boxes). The extreme C-terminal domain (CTAR2, aa 352–386) binds TRADD and RIP and is the major mediator of NF-κB, JNK, and p38 signalling in most cell lines. TRAF2, a TRADD interacting protein, regulates CTAR2 induced NF-κB activation via a NIK→IKK→IκBα cascade, but the components of JNK and p38 signalling downstream of TRADD/TRAF2 remain largely unknown. The membrane proximal region (CTAR1, aa 187–231), which is crucial for B cell transformation, interacts weakly with TRAF2 and induces only low amounts of NF-κB and p38 activation. TRAF1 and TRAF3 also bind CTAR1 and might influence TRAF2 mediated signals. The intermediate region between CTAR1 and CTAR2 has been shown to bind JAK3 and activate STAT signalling, whereas the transmembrane domains of LMP1 mediate activation of the small GTPase, Cdc42, leading to cytoskeletal changes. CTAR, C-terminal activating region; IKK, IκB kinase; JAK, Janus kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; MAPK, mitogen activated protein kinase; NIK, MAPK kinase kinase; RIP, receptor interacting protein; SEK, extracellular signal related kinase (ERK) kinase; STAT, signal transducers and activators of transcription; TRADD, tumour necrosis factor receptor associated death domain; TRAF, tumour necrosis factor receptor associated factor.