Abstract
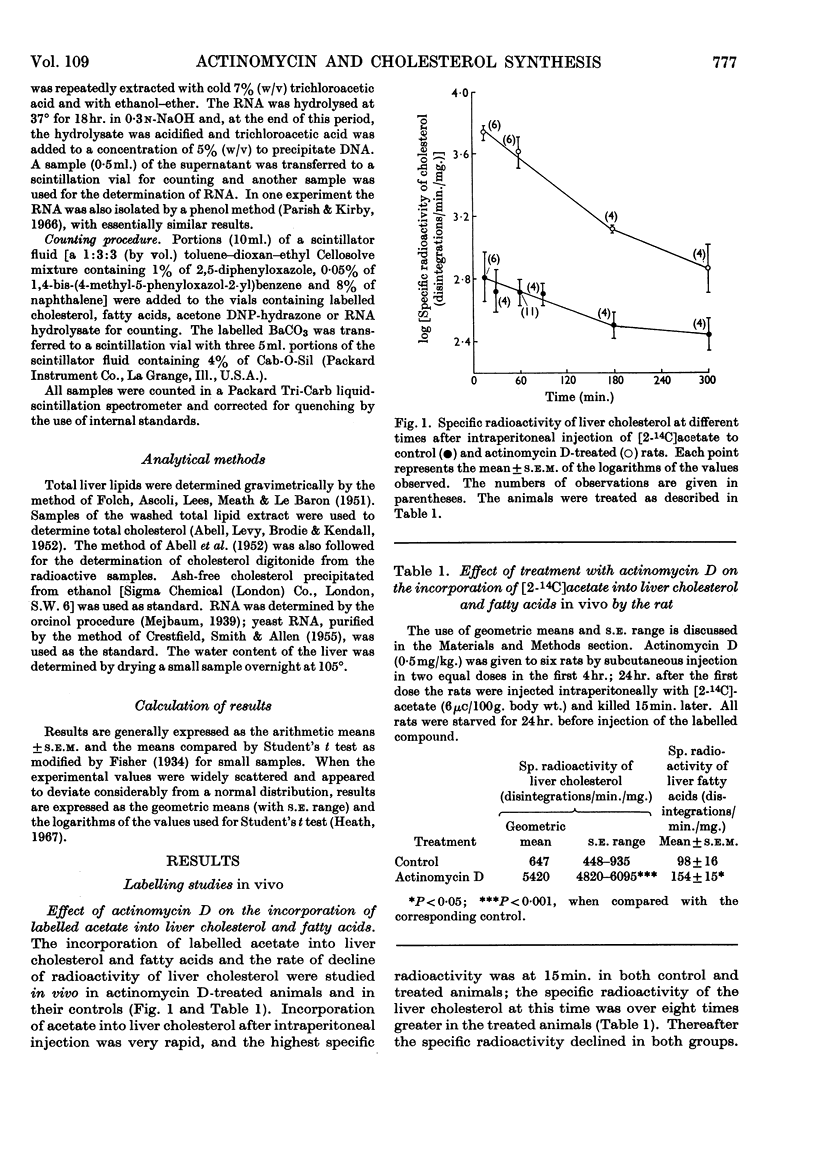
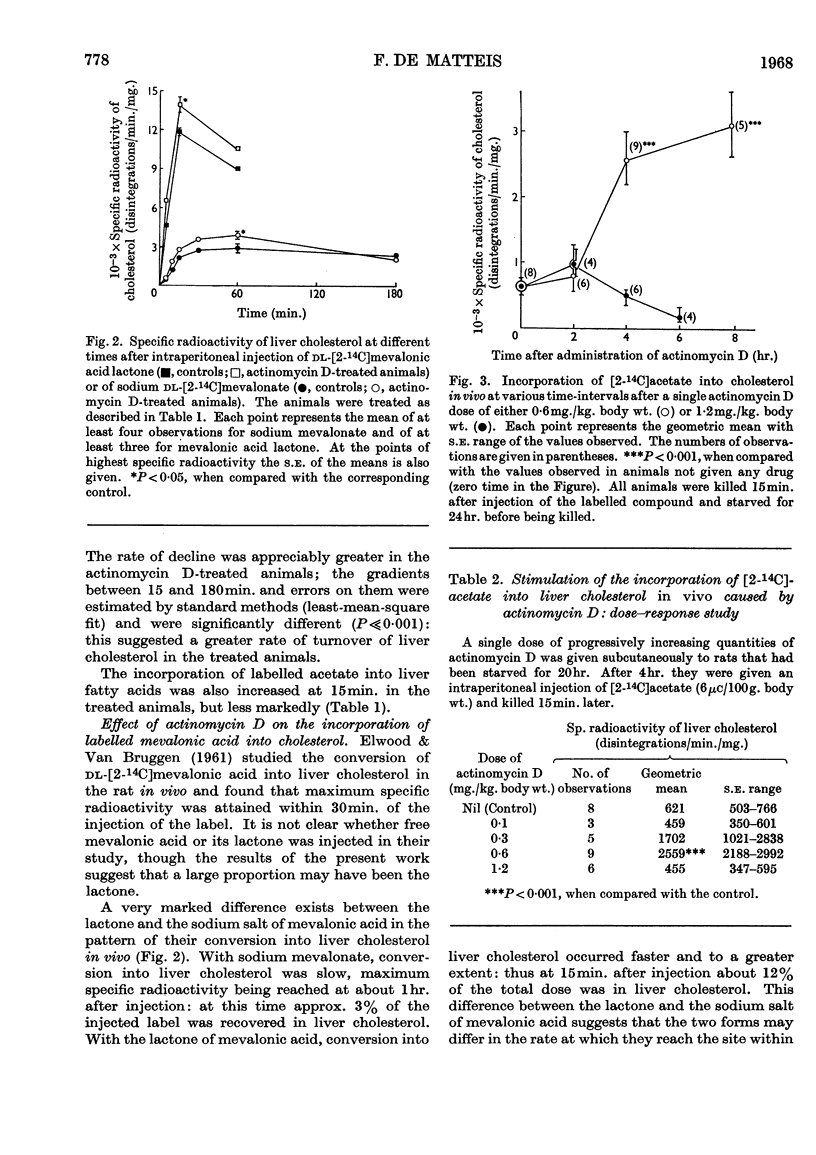
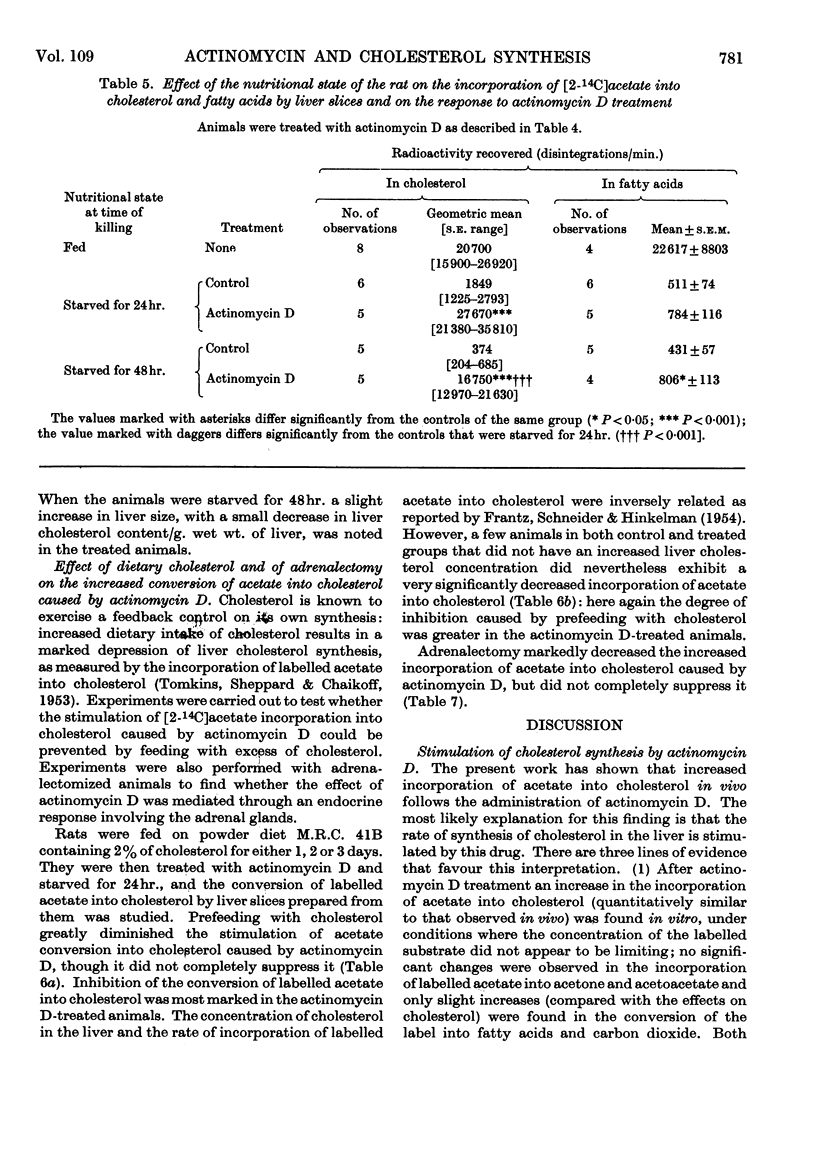
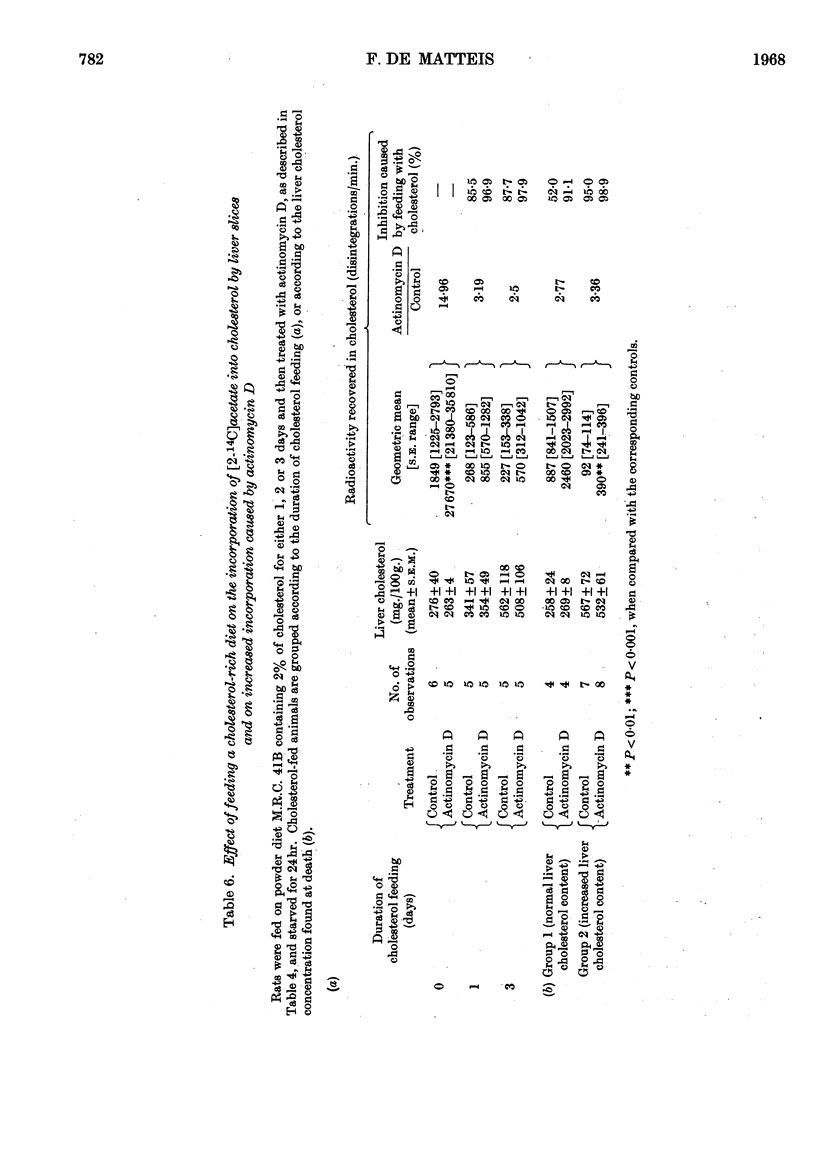
1. An eightfold increase in the incorporation of [2-14C]acetate into liver cholesterol in vivo was observed 24hr. after starved rats had been given actinomycin D (0·5mg./kg. of body wt.). Liver cholesterol radioactivity declined faster in the treated animals, suggesting a greater rate of cholesterol turnover. 2. Liver slices from treated animals showed a tenfold increase in the incorporation of [2-14C]acetate into cholesterol; conversion into CO2 and into fatty acids was less markedly increased, and conversion into ketone bodies was not significantly affected. 3. The patterns of conversion into liver cholesterol in vivo of the lactone and the sodium salt of mevalonic acid differed markedly. The former was converted at a faster rate and to a greater extent than the latter. Treatment with actinomycin D increased the conversion of both forms of mevalonic acid into liver cholesterol, but only to a small extent. 4. Stimulation of the incorporation of acetate into cholesterol occurred at 4hr. after the administration of actinomycin D but not at 2hr. The response was abolished by the simultaneous administration of dl-ethionine or puromycin. 5. Pre-feeding with a cholesterol-rich diet greatly diminished the stimulation of conversion of acetate into cholesterol caused by actinomycin D, though it did not completely suppress it. Adrenalectomized animals responded to the drug, but much less markedly. 6. It is concluded that actinomycin D stimulates the synthesis of cholesterol in the liver at a stage in the pathway before mevalonic acid, by a mechanism that probably requires protein synthesis. A likely site would be the β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis. Some possible mechanisms by which the drug may lead to increased activity of this enzyme are considered.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABEL L. L., LEVY B. B., BRODIE B. B., KENDALL F. E. A simplified method for the estimation of total cholesterol in serum and demonstration of its specificity. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):357–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCHER N. L., McGARRAHAN K., GOULD E., LOUD A. V. Cholesterol biosynthesis in preparations of liver from normal, fasting, x-irradiated, cholesterol-fed, triton, or delta 4-cholesten-3-one-treated rats. J Biol Chem. 1959 Feb;234(2):262–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., SMITH K. C., ALLEN F. W. The preparation and characterization of ribonucleic acids from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1955 Sep;216(1):185–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corte E. D., Stirpe F. Regulation of xanthine dehydrogenase in chick liver. Further experiments on the effects of inosine, actinomycin D and other factors. Biochem J. 1967 Feb;102(2):520–524. doi: 10.1042/bj1020520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRYSDALE J. W., MUNRO H. N. FAILURE OF ACTINOMYCIN D TO PREVENT INDUCTION OF LIVER APOFERRITIN AFTER IRON ADMINISTRATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 May 11;103:185–188. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90554-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., ASCOLI I., LEES M., MEATH J. A., LeBARON N. Preparation of lipide extracts from brain tissue. J Biol Chem. 1951 Aug;191(2):833–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANTZ I. D., Jr, HINKELMAN B. T. Acceleration of hepatic cholesterol synthesis by triton WR-1339. J Exp Med. 1955 Mar 1;101(3):225–232. doi: 10.1084/jem.101.3.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANTZ I. D., Jr, SCHNEIDER H. S., HINKELMAN B. T. Suppression of hepatic cholesterol synthesis in the rat by cholesterol feeding. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jan;206(1):465–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN M., BYERS S. O., GUNNING B. Observations concerning production and excretion of cholesterol in mammals. VIII. Fate of injected cholesterol in the animal body. Am J Physiol. 1953 Feb;172(2):309–316. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1953.172.2.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARREN L. D., HOWELL R. R., TOMKINS G. M., CROCCO R. M. A PARADOXICAL EFFECT OF ACTINOMYCIN D: THE MECHANISM OF REGULATION OF ENZYME SYNTHESIS BY HYDROCORTISONE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1121–1129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODWIN B. C., SIZER I. W. HISTONE REGULATION OF LACTIC DEHYDROGENASE IN EMBRYONIC CHICK BRAIN TISSUE. Science. 1965 Apr 9;148(3667):242–244. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3667.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOTTA S., CHAIKOFF I. L. The role of the liver in the turnover of plasma cholesterol. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 May;56(1):28–37. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90330-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilf R., Michel I., Silverstein G., Bell G. Effect of actinomycin D on estrogen-induced changes in enzymes and nucleic acids of R3230AC mammary tumors, uteri, and mammary glands. Cancer Res. 1965 Dec;25(11):1854–1859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNAPPE J., RINGELMANN E., LYNEN F. [On beta-hydroxy-beta-methylglutaryl reductase of yeast. On the biosynthesis of terpene. IX]. Biochem Z. 1959;332:195–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYNEN F., HENNING U., BUBLITZ C., SORBO B., KROPLIN-RUEFF L. Der chemische Mechanismus der Acetessigsäurebildung in der Leber. Biochem Z. 1958;330(4):269–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C. The effect of cholesterol feeding and fasting upon beta-hydroxy-beta-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):990–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippe B. M., Szego C. M. Participation of adrenocortical hyperactivity in the suppressive effect of systemic actinomycin D on uterine stimulation by oestrogen. Nature. 1965 Jul 17;207(994):272–274. doi: 10.1038/207272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEDES G., THOMAS A., WEINHOUSE S. Nutritional factors in fatty acid synthesis by tissue slices in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;197(1):181–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOOG F. INTESTINAL PHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY: ACCELERATION OF INCREASE BY PUROMYCIN AND ACTINOMYCIN. Science. 1964 Apr 24;144(3617):414–416. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3617.414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy E. E., Ebadi M. The paradoxical effect of hydrocortisone and actinomycin on the activity of rabbit leucocyte alkaline phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Feb 8;26(3):265–271. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish J. H., Kirby K. S. Reagents which reduce interactions between ribosomal RNA and rapidly labelled RNA from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 21;129(3):554–562. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN F., RAINA P. N., MILHOLLAND R. J., NICHOL C. A. INDUCTION OF SEVERAL ADAPTIVE ENZYMES BY ACTINOMYCIN D. Science. 1964 Oct 30;146(3644):661–663. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3644.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCARANO E., DEPETROCELLIS B., AUGUSTI-TOCCO G. STUDIES ON THE CONTROL OF ENZYME SYNTHESIS DURING THE EARLY EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT OF THE URCHINS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 18;87:174–176. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer F., Erfle J. D. On the mechanism of acetoacetate synthesis by guinea pig liver fractions. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 10;241(1):30–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siperstein M. D., Fagan V. M. Feedback control of mevalonate synthesis by dietary cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 10;241(3):602–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siperstein M. D., Fagan V. M. Studies on the feed-back regulation of cholesterol synthesis. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1964;2:249–264. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2571(64)80017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMKINS G. M., CHAIKOFF I. L. Cholesterol synthesis by liver. I. Influence of fasting and of diet. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;196(2):569–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMKINS G. M., SHEPPARD H., CHAIKOFF I. L. Cholesterol synthesis by liver. III. Its regulation by ingested cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1953 Mar;201(1):137–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing D. R., Robinson D. S. Clearing-factor lipase in adipose tissue. Studies with puromycin and actinomycin. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(3):667–676. doi: 10.1042/bj1060667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


