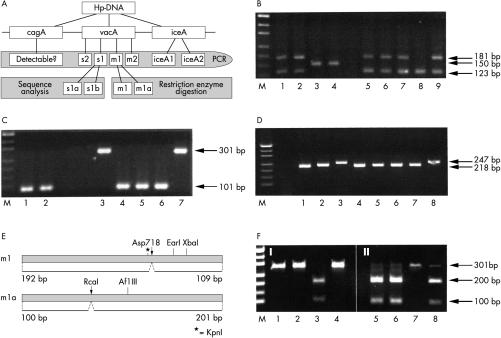
Figure 1.
Multiplex analyses of the genomic Helicobacter pylori virulence determinants cagA, vacA, and ice A. (A) A schematic overview of the virulence genes and the method for their simultaneous detection. The cagA, vacA s1 or s2, vacA m1 or m2, and iceA 1 or 2 domains were amplified by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and detected by electrophoresis. The vacA s1 and m1 alleles were further analysed by sequencing or restriction enzyme digests. (B) Multiplex PCR assay of vacA signal regions s1 (123 bp) and s2 (150 bp), in addition to the cagA gene (181 bp). Samples in lanes 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, and 9 are vacA s1/cagA positive; those in lanes 3 and 4 are vacA s2 positive/cagA negative, and the sample in lane 8 is vacA s1 positive/cagA negative. (C) Combined PCR detection of vacA midregion m1 (101 bp) and m2 (301 bp). Helicobacter pylori in lanes 1, 2, and 4–6 are of the vacA m1 subtype and those in lanes 3 and 7 are of the vacA m2 subtype. (D) Simultaneous PCR analysis of the iceA1 (218 bp) and iceA2 (247 bp) alleles. All samples except lanes 3 and 8, which contain the iceA2 subtype, are iceA1 positive. (E) Schematic illustration of restriction enzyme polymorphisms within the m1 and m1a sequences. (F) Restriction enzyme digestion of vacA m1 PCR products with Asp718 (I) and RcaI (II). Lane 3 shows a vacA m1 subtype whereas lanes 5, 6, and 8 show m1a subtypes.