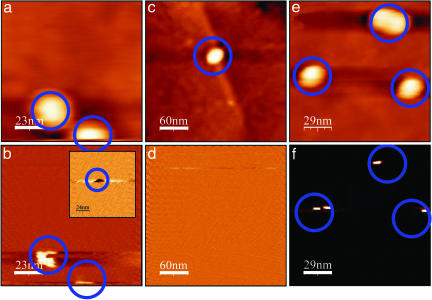
Fig. 2.
Simultaneously acquired topography and current maps. Shown are measurements on a sample with GNPs connected to dsDNA (a and b; 115 × 115 nm2), on a sample with GNPs connected to noncomplementary strands (the same strand as on the surface) (c and d; 300 × 300 nm2), and immediately after on a sample with GNPs connected to a dsDNA (to prove that the tip is still conductive) (e and f; 170 × 170 nm2). a, c, and e show topography images. No current is observed for current maps recorded simultaneously with a, c, and e with zero bias voltage on the tip (V = 0). b, d, and f present current maps measured simultaneously with the next topography images (not shown), for which 4 V were applied to the tip. A current signal is clearly observed at the positions corresponding to the positions of GNPs connected to dsDNA (blue circles), and no current is observed for the noncomplementary ones. An opposite signal is measured for –4V (b Inset). No current is measured in any other position on the ssDNA in all cases.