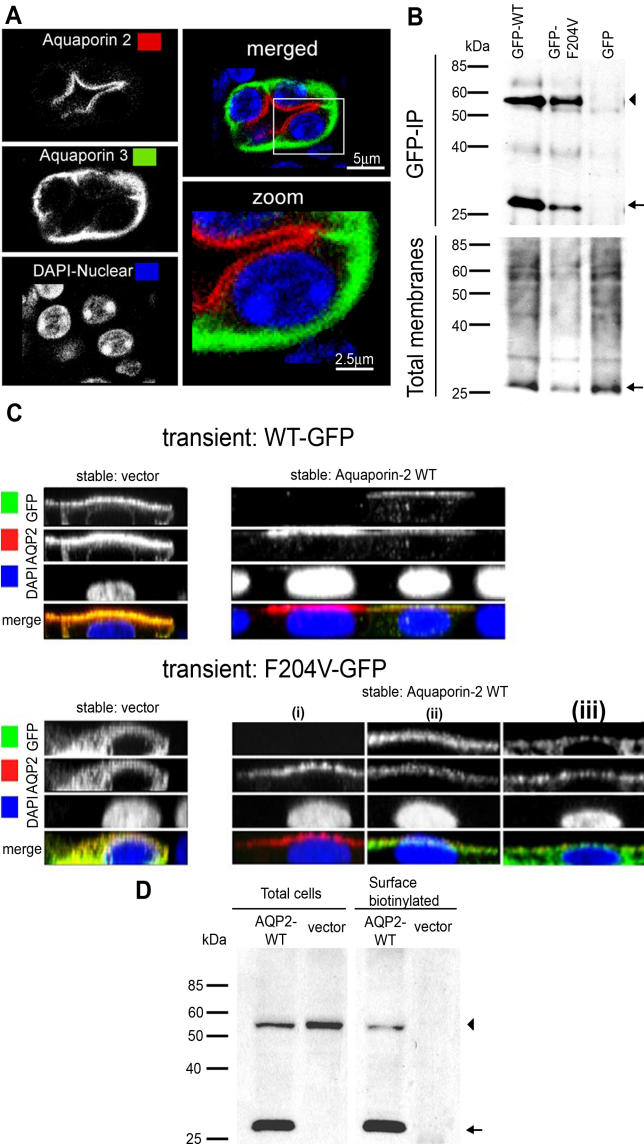
Figure 5. AQP2-F204V Rescue in Heterozygous Mouse Collecting Ducts and in Cotransfected MDCK Cells.
(A) In heterozygous animals, AQP2 localizes and responds to dDAVP normally. Immunohistochemistry was carried out on kidney sections from an Aqp2F204V/+ mouse, after injection with dDAVP. Kidney sections were sequentially immunostained for AQP2 (red) and the basolateral marker AQP3 (green).
(B) Mutant and wild-type AQP2 physically interact. MDCK cells stably expressing wild-type AQP2 were transiently transfected with GFP tagged wild-type AQP2, AQP2-F204V, or GFP alone. Solubilized membranes were immunoprecipitated with a GFP antibody. Total membranes and immunoprecipitates (GFP-IP) were Western blotted using an antibody against AQP2 (arrow) or AQP2-GFP fusions (arrowhead).
(C) Wild-type AQP2 rescues the localization defect of mutant AQP2. GFP fusions of either wild-type AQP2 (WT-GFP, top photomicrographs) or F204V AQP2 (F204V-GFP, bottom photomicrographs) were expressed in polarized MDCK stable cell lines expressing vector alone (vector, left photomicrographs) or AQP2-WT (right photomicrographs). Cells were stimulated with forskolin, processed for immunocytochemistry, and used to generate z-sectional images.
(D) Mutant AQP2 is present at the cell surface in cells coexpressing wild-type AQP2 (AQP2-WT). GFP fused to AQP2-F204V was expressed in MDCK cells expressing wild-type AQP2 or vector alone. Cells were stimulated with forskolin, and cell surface biotinylated proteins were precipitated then analyzed for the presence of wild-type AQP2 (arrow) and AQP2-F204V (arrowhead) by Western blot.