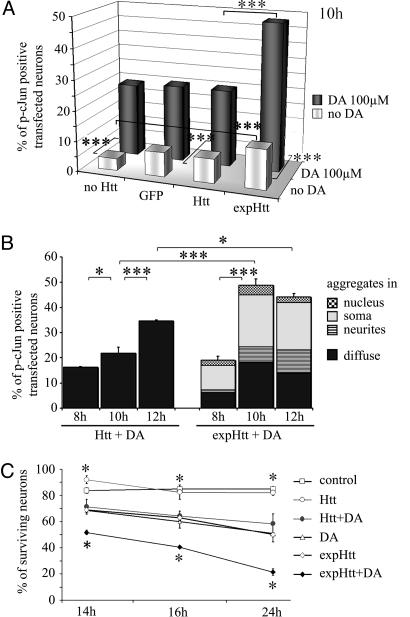
Fig. 3.
DA potentiates expHtt-induced c-Jun activation and neuronal death. (A) Comparative effects of 100 μM DA (at 10 h) on c-Jun activation in striatal neurons that were not transfected (no Htt) or transfected with GFP alone (GFP), normal Htt (Htt), or mutated Htt (expHtt). Gray bars, without DA; black bars, with DA. Data are representative of three independent experiments for each condition and each time point (100 cells counted per well; two wells per experiment; 600 transfected cells for each condition). Statistical analyses were performed using ANOVA followed by Fisher's analysis for post hoc comparisons: ***, P < 0.001. (B) Kinetics (at 8, 10, and 12 h) of c-Jun activation in Htt- or expHtt-transfected neurons in the presence of 100 μM DA. Different populations of P-c-Jun-positive neurons were separated on the basis of GFP-expHtt localization, i.e., diffuse or aggregated in the neurites, soma, or nucleus. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001. (C) Kinetics (at 14, 16, and 24 h) of DA effects on survival of striatal neurons in control conditions or after transfection (Htt or expHtt). The percentage of surviving neurons was determined by morphological criteria based on DNA labeling with Hoechst. Quantification and statistical analyses were performed as in A. *, P < 0.05 when compared with expHtt.