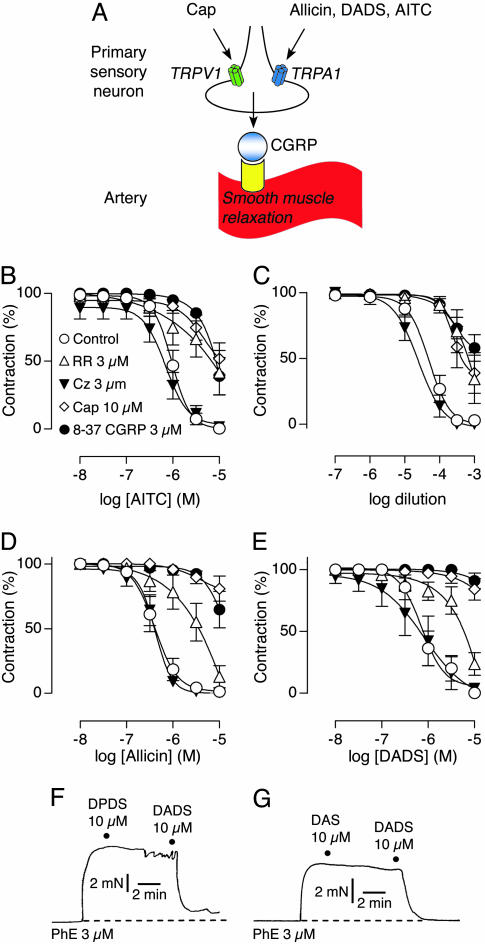
Fig. 4.
Vascular relaxation induced by AITC, garlic extract, allicin, and DADS. (A) Schematic diagram of vascular relaxation mediated by activation of sensory neurons. Inflammatory mediators, such as capsaicin and allicin, activate TRP channels (TRPV1 and TRPA1, respectively), on sensory neurons in blood vessels. TRP channel activation triggers local release of neuropeptides, such as the potent vasodilator CGRP. Concentration-response curves for AITC (B), garlic extracts (C), allicin (D), and DADS (E). Vasorelaxation was recorded in phenylephrine (PhE)-contracted mesenteric arterial segments in the presence of ruthenium red (3 μM, ▵), capsazepine (3 μM, ▾), 8-37 CGRP (3 μM, •), or vehicle (○), or after pretreatment with capsaicin (10 μM for 30 min; ⋄). Dipropyl disulfide (DPDS) (F) and DAS (G) failed to induce relaxation. DADS was applied as positive control. Force of vessel contraction is plotted as a function of time. Dashed line indicates basal tension before addition of drugs. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 6-8 in B and D, 5-6 in C, 5-8 in E, and 4-5 in F and G).