Abstract
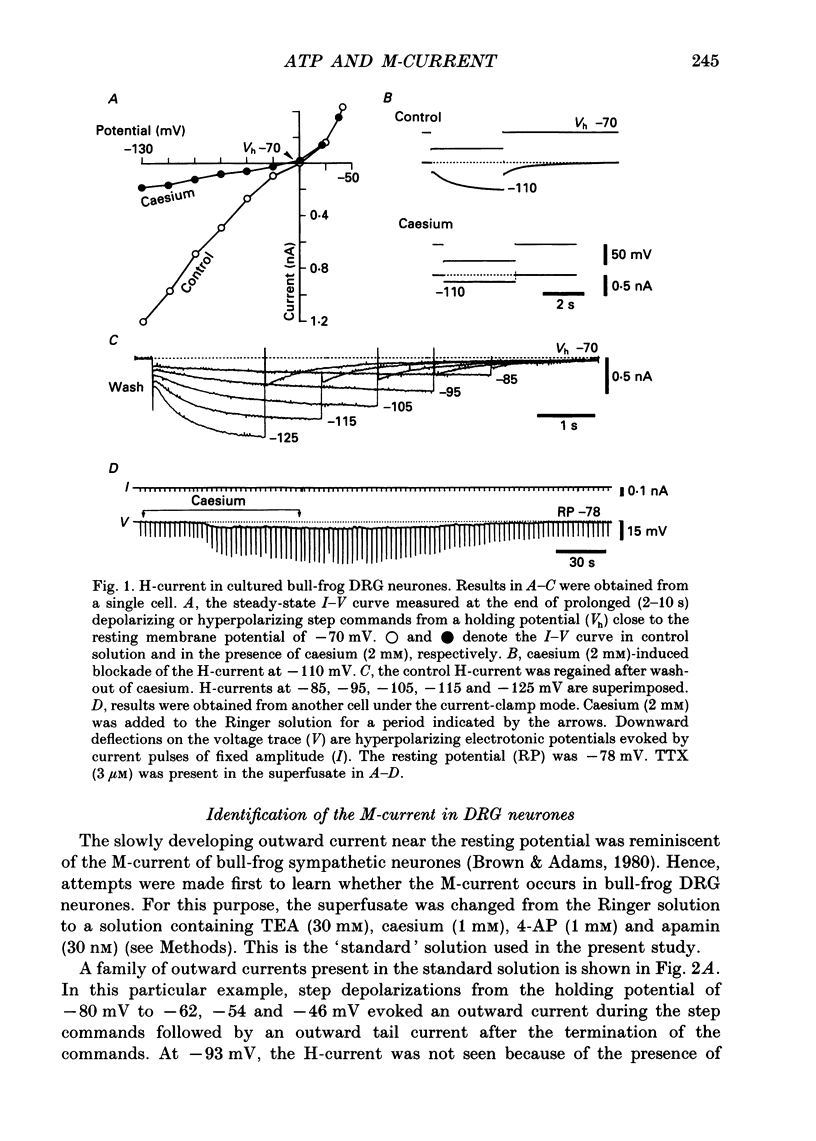
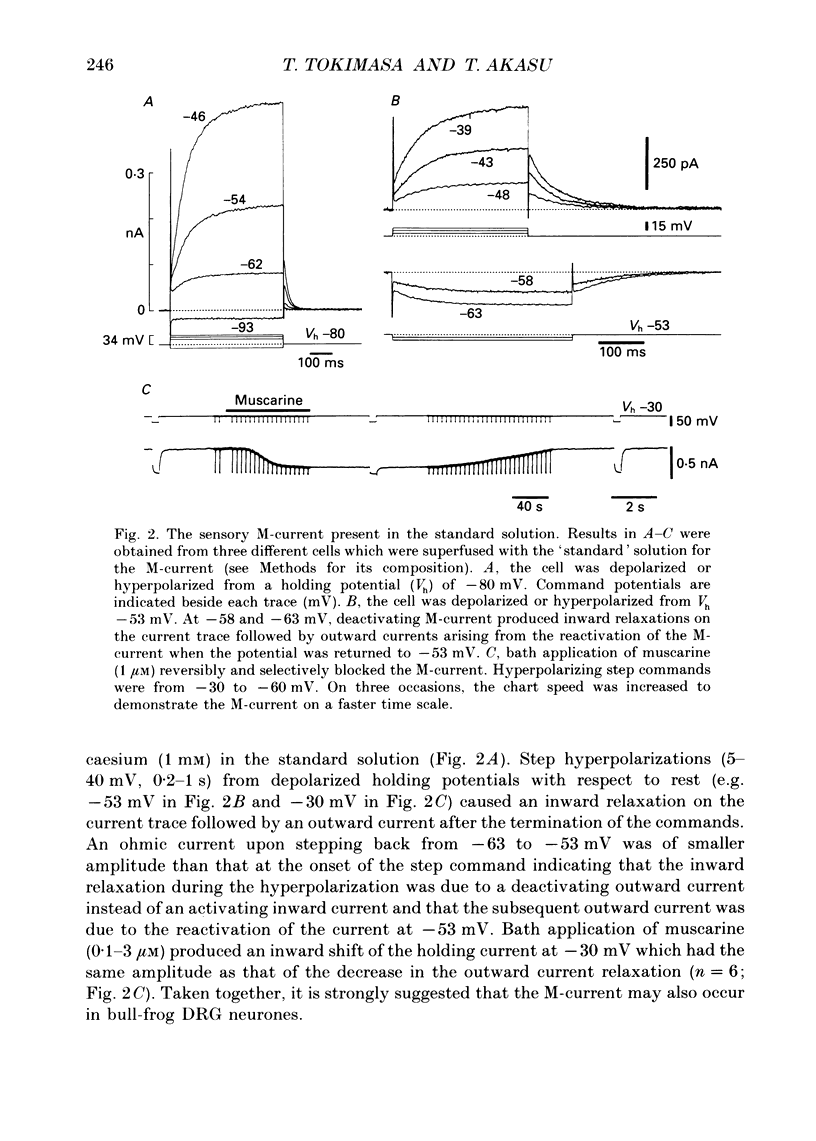
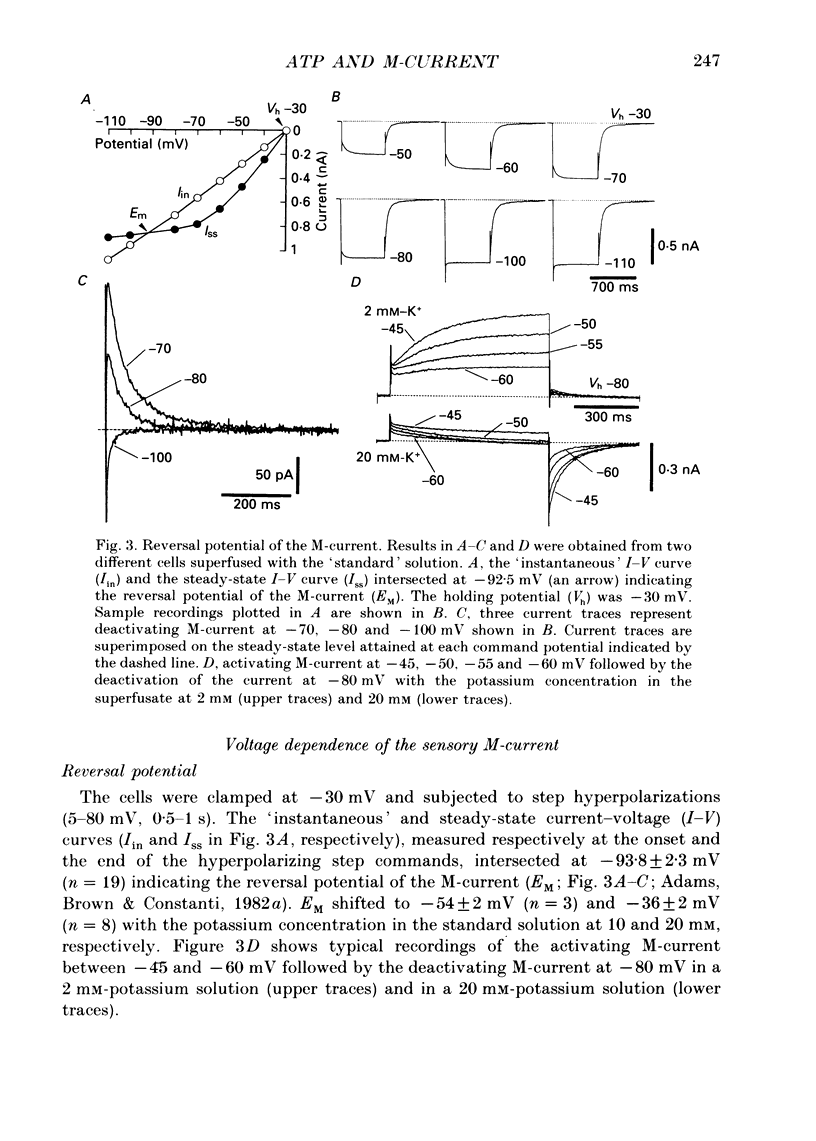
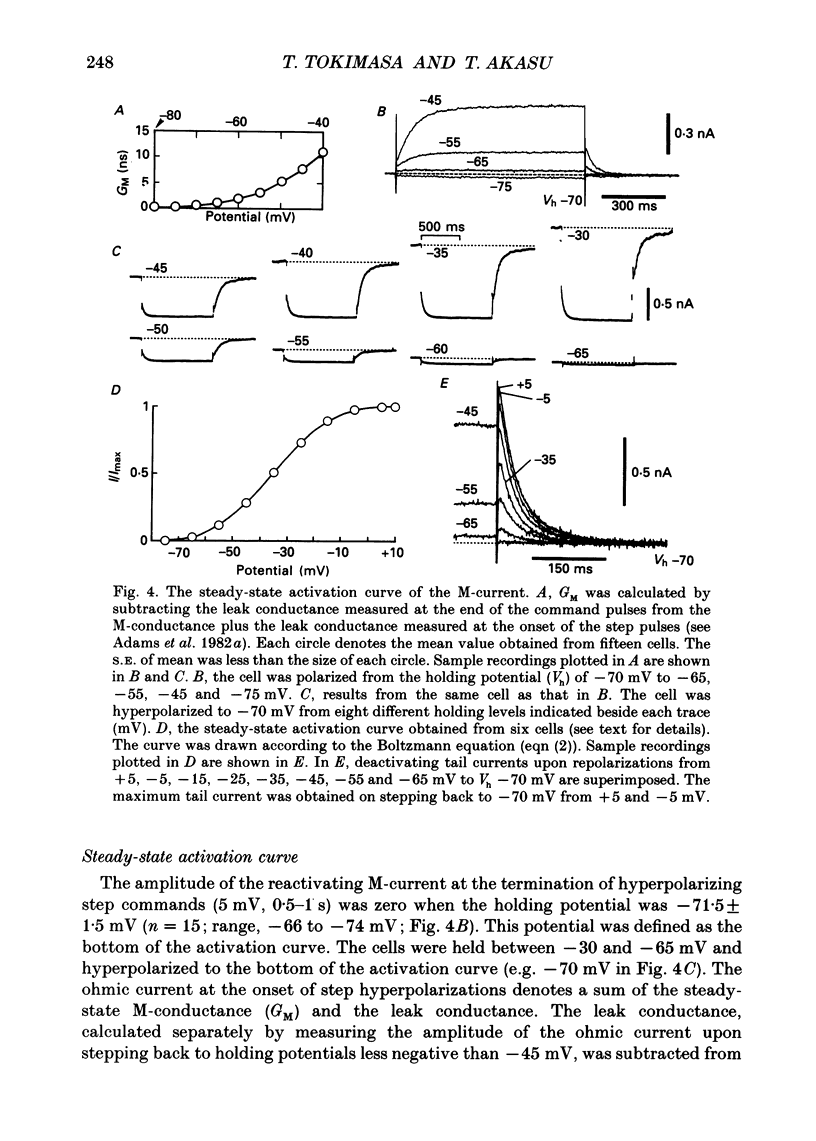
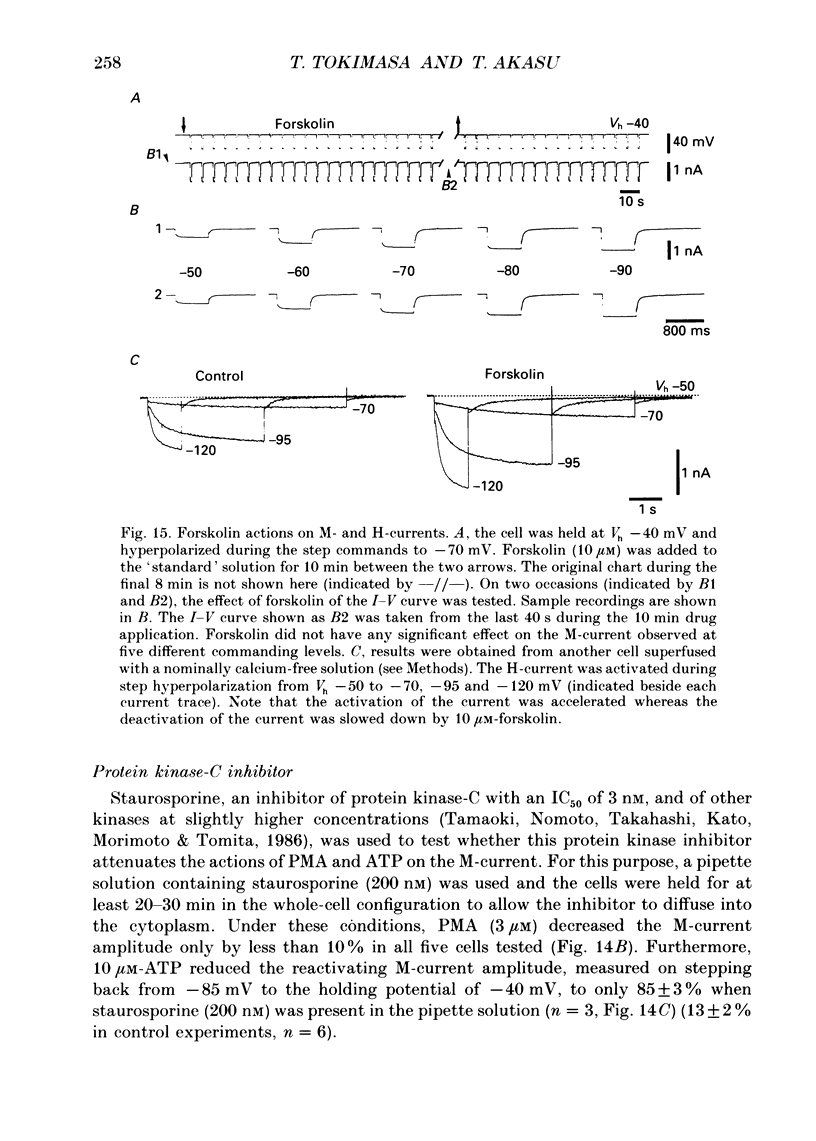
1. Bull-frog dorsal root ganglion cells in primary culture were voltage clamped in the whole-cell configuration. The pipette solution contained ATP (5 mM). 2. Step depolarizations (5-70 mV, 0.1-1 s) from a holding potential close to the resting potential (range, -64 to -79 mV) evoked a non-inactivating potassium current with properties indistinguishable from those which have been reported for the M-current of bull-frog sympathetic neurones. 3. An unhydrolysable ATP analogue APP(NH)P (5 mM), substitute with ATP in the pipette solution, did not support the M-current activation. 4. Bath application of ATP (30 nM-30 microM) reduced the amplitude of the M-current in a concentration-dependent manner, congruent to 50% inhibition of the current occurring with 1 microM-ATP. The main effect of ATP was to reduce the maximum M-conductance without changing the activation and deactivation kinetics of the M-current. 5. Essentially the same results were obtained with ADP (0.1-30 microM) and alpha, beta-methylene-ATP (10-30 microM). AMP (10-100 microM) and adenosine (10-30 microM) were without effect on the M-current. 6. The ATP-induced inhibition of the M-current was irreversible when an unhydrolysable GTP analogue GTP-gamma-S (10-30 microM) was present in the pipette solution. ATP (3 microM) reduced the amplitude of the M-current only by about 10% when GDP-beta-S (100 microM) was present in the pipette solution. Pre-treatment of the cells with pertussis toxin (IAP; 500 ng ml-1) for 24 h at 24 degrees C did not prevent the ATP-induced M-current inhibition. 7. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA; 1-3 microM) reduced the amplitude of the M-current to about 50%. A reduction in the M-current amplitude by PMA (3 microM) and ATP (10 microM) was attenuated when staurosporine (200 nM) was present in the pipette solution. Forskolin (10 microM) was without effect on the M-current. 8. It is concluded that ATP acting at P2 receptors, associated with an IAP-insensitive GTP-binding protein, inhibits the M-current in amphibian primary afferent neurones.
Full text
PDF




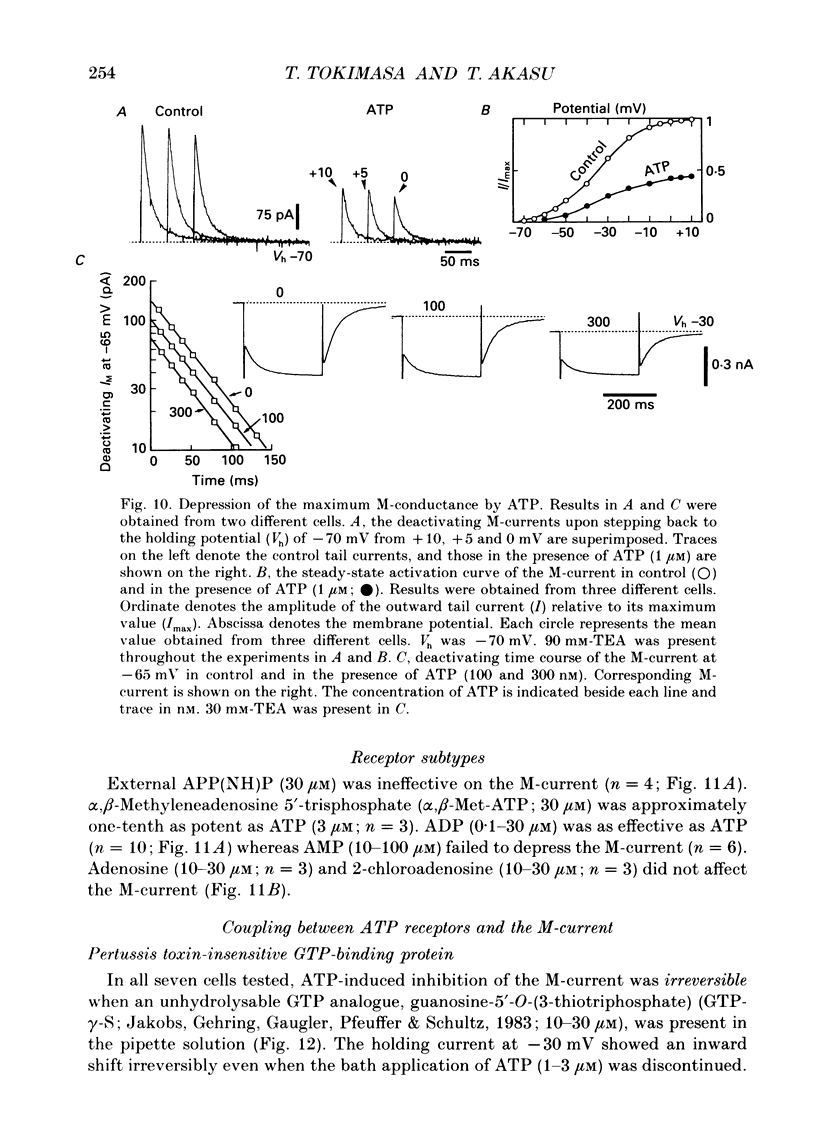






Selected References
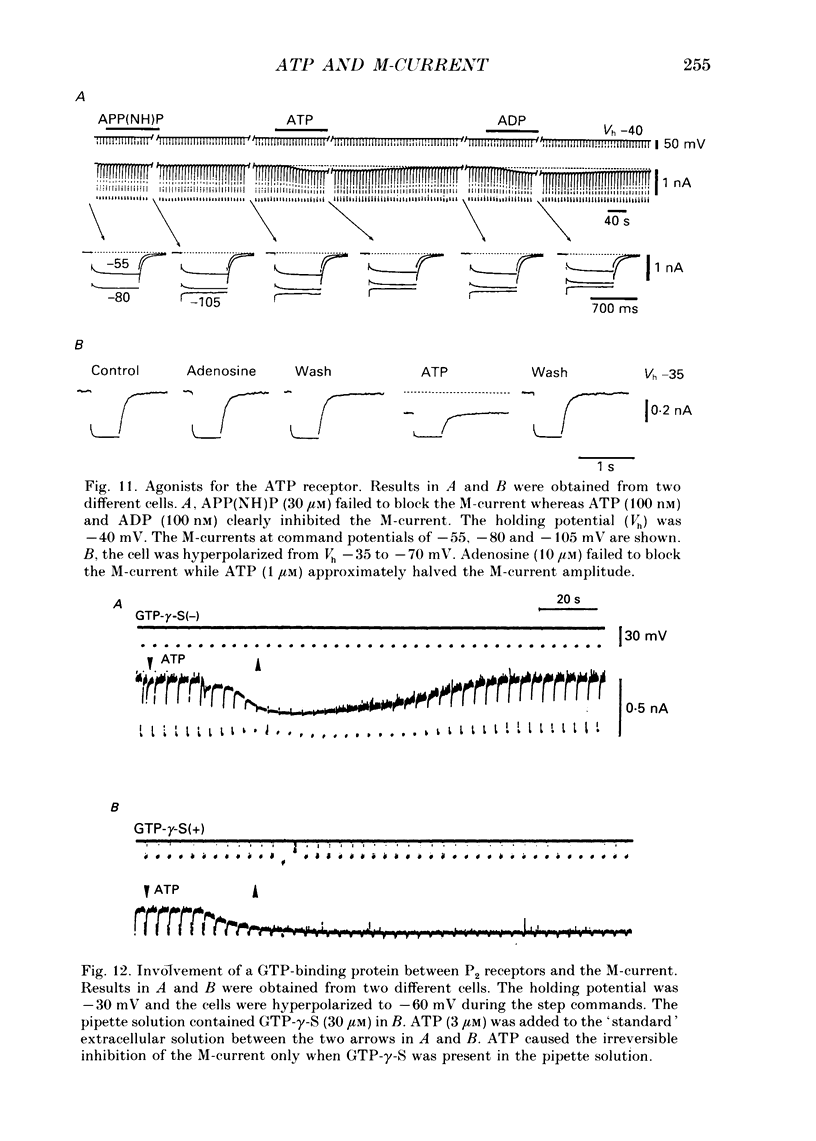
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
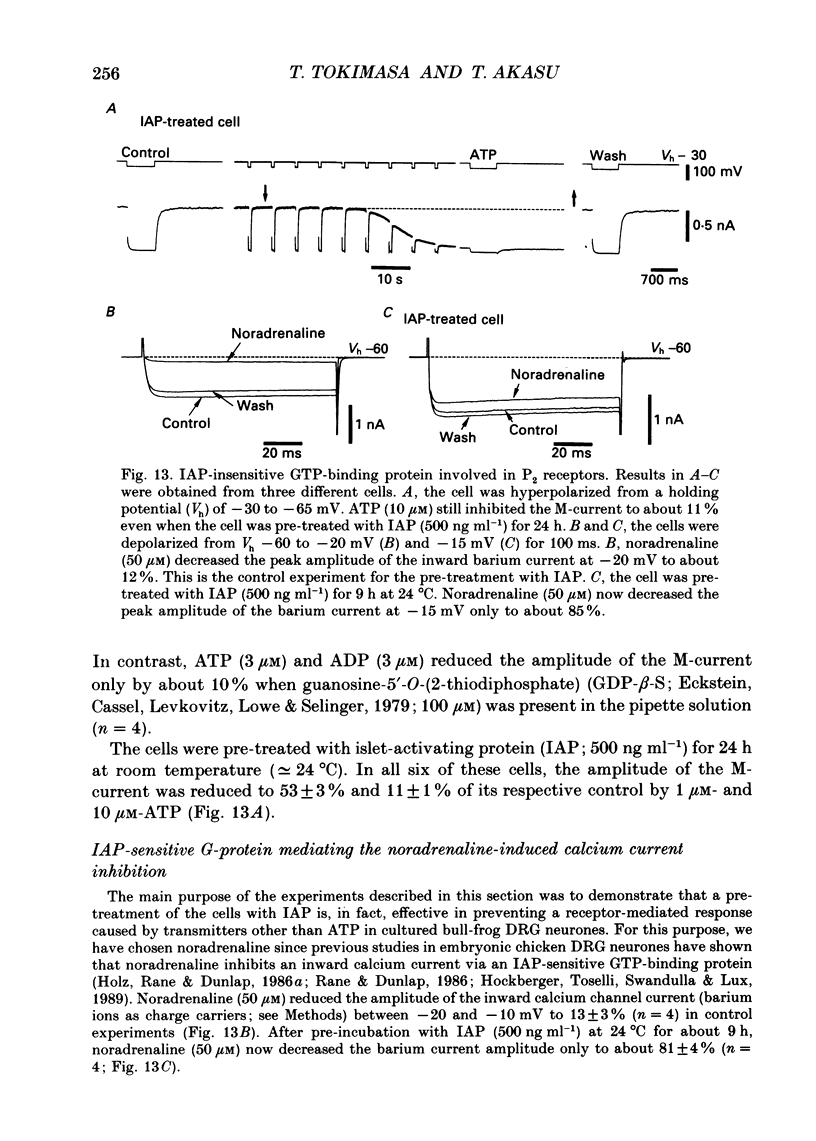
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. M-currents and other potassium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Sep;330:537–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
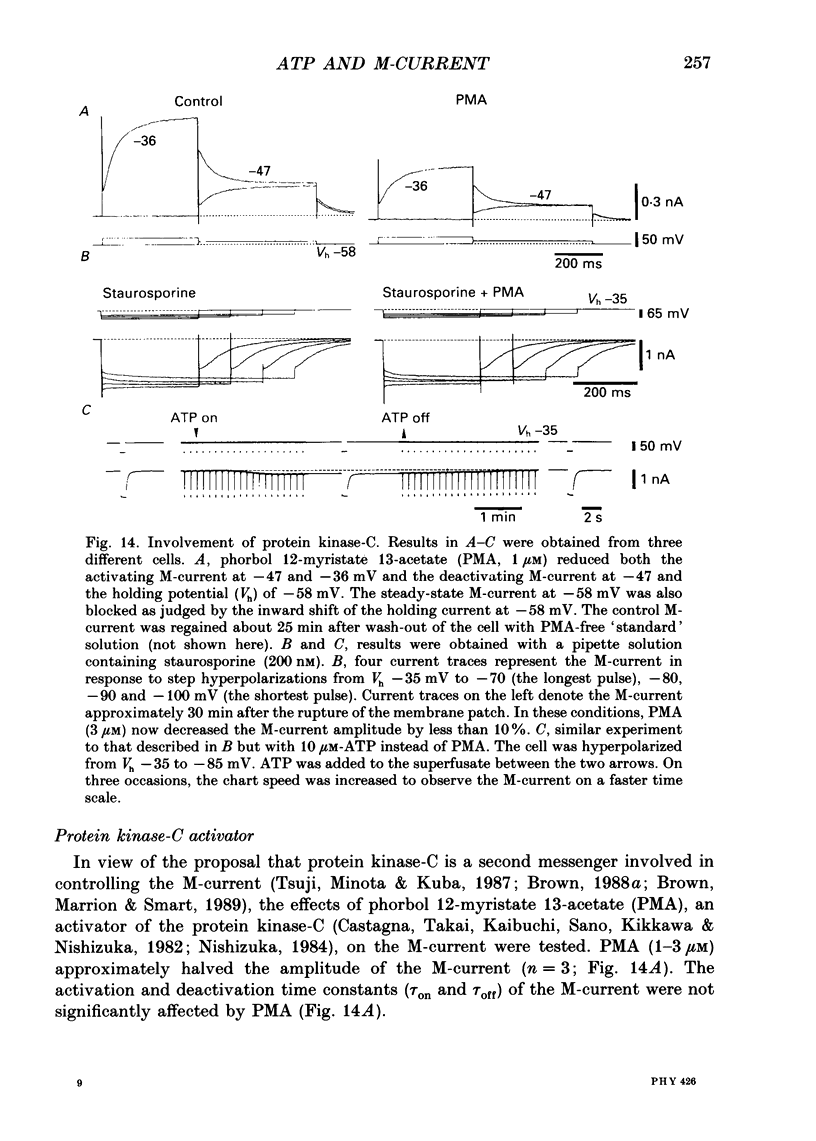
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. Pharmacological inhibition of the M-current. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:223–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akasu T., Hirai K., Koketsu K. Modulatory actions of ATP on membrane potentials of bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Brain Res. 1983 Jan 10;258(2):313–317. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma M. M., Hille B. Protein kinase C is not necessary for peptide-induced suppression of M current or for desensitization of the peptide receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2943–2947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Adams P. R. Muscarinic suppression of a novel voltage-sensitive K+ current in a vertebrate neurone. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):673–676. doi: 10.1038/283673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A. M currents. Ion Channels. 1988;1:55–94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-7302-9_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Marrion N. V., Smart T. G. On the transduction mechanism for muscarine-induced inhibition of M-current in cultured rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1989 Jun;413:469–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W. Adenosine receptors: targets for future drugs. J Med Chem. 1982 Mar;25(3):197–207. doi: 10.1021/jm00345a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F., Cassel D., Levkovitz H., Lowe M., Selinger Z. Guanosine 5'-O-(2-thiodiphosphate). An inhibitor of adenylate cyclase stimulation by guanine nucleotides and fluoride ions. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9829–9834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:149–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):449–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLTON F. A., HOLTON P. The capillary dilator substances in dry powders of spinal roots; a possible role of adenosine triphosphate in chemical transmission from nerve endings. J Physiol. 1954 Oct 28;126(1):124–140. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi H. Pharmacological aspects of visceral sensory receptors. Prog Brain Res. 1986;67:149–162. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62761-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockberger P., Toselli M., Swandulla D., Lux H. D. A diacylglycerol analogue reduces neuronal calcium currents independently of protein kinase C activation. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):340–342. doi: 10.1038/338340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Rane S. G., Dunlap K. GTP-binding proteins mediate transmitter inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):670–672. doi: 10.1038/319670a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Shefner S. A., Anderson E. G. Serotonin decreases the duration of action potentials recorded from tetraethylammonium-treated bullfrog dorsal root ganglion cells. J Neurosci. 1986 Mar;6(3):620–626. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-03-00620.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Shefner S. A., Anderson E. G. Serotonin depolarizes type A and C primary afferents: an intracellular study in bullfrog dorsal root ganglion. Brain Res. 1985 Feb 18;327(1-2):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91500-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S. R., Schofield G. G., Weight F. F. Na+ and Ca2+ currents of acutely isolated adult rat nodose ganglion cells. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Mar;55(3):527–539. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.3.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka S., Hattori K., Akaike N. Separation of ionic currents in the somatic membrane of frog sensory neurons. J Membr Biol. 1984;78(1):19–28. doi: 10.1007/BF01872528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito I., Maeno T. Catechol: a potent and specific inhibitor of the fast potassium channel in frog primary afferent neurones. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:115–127. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Jessell T. M. ATP excites a subpopulation of rat dorsal horn neurones. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):730–733. doi: 10.1038/304730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobs K. H., Gehring U., Gaugler B., Pfeuffer T., Schultz G. Occurrence of an inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of the adenylate cyclase system in cyc- variants of S49 lymphoma cells. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;130(3):605–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S., Fedulova S. A., Tsyndrenko A. Y. Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons-III. Potassium currents. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2439–2444. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S., Tsyndrenko A. Y. Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons-I. Sodium currents. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2423–2430. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishtal O. A., Marchenko S. M., Pidoplichko V. I. Receptor for ATP in the membrane of mammalian sensory neurones. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Jan 31;35(1):41–45. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90524-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L. Selective block of inward but not outward rectification in rat sensory neurones infected with herpes simplex virus. J Physiol. 1986 Jun;375:327–338. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Sugiyama K. A modulatory action of divalent cations on transient outward current in cultured rat sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:417–433. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. A voltage-clamp analysis of inward (anomalous) rectification in mouse spinal sensory ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:19–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister R. E., Noble D. The time and voltage dependence of the slow outward current in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1966 Oct;186(3):632–662. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., Katayama Y. 5-Hydroxytryptamine effects on the somata of bullfrog primary afferent neurons. Neuroscience. 1987 Jun;21(3):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., Katayama Y. Bullfrog dorsal root ganglion cells having tetrodotoxin-resistant spikes are endowed with nicotinic receptors. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Sep;62(3):657–664. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.62.3.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., Katayama Y. Calcium-dependent slow outward current in visceral primary afferent neurones of the rabbit. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Jun;414(2):171–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00580960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., Katayama Y., Koketsu K., Akasu T. Actions of ATP on the soma of bullfrog primary afferent neurons and its modulating action on the GABA-induced response. Brain Res. 1984 Feb 20;293(2):360–363. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., Katayama Y. Two types of acetylcholine receptors on the soma of primary afferent neurons. Brain Res. 1984 Jan 9;290(2):348–352. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90954-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOBLE D. A modification of the Hodgkin--Huxley equations applicable to Purkinje fibre action and pace-maker potentials. J Physiol. 1962 Feb;160:317–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Petersen M., Pierau F. K., Dreyer F. Dendrotoxin: a selective blocker of a non-inactivating potassium current in guinea-pig dorsal root ganglion neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Oct;407(4):365–369. doi: 10.1007/BF00652619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Leibowitz M. D., Subers E. M., Nathanson N. M., Almers W., Hille B. Agonists that suppress M-current elicit phosphoinositide turnover and Ca2+ transients, but these events do not explain M-current suppression. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):477–484. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. Muscarine and t-LHRH suppress M-current by activating an IAP-insensitive G-protein. J Neurosci. 1988 Sep;8(9):3343–3353. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-09-03343.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Wu P. H. The role of adenosine and its nucleotides in central synaptic transmission. Prog Neurobiol. 1981;16(3-4):187–239. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(81)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rane S. G., Dunlap K. Kinase C activator 1,2-oleoylacetylglycerol attenuates voltage-dependent calcium current in sensory neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):184–188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Daly J. W. Forskolin: a unique diterpene activator of cyclic AMP-generating systems. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;7(4):201–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims S. M., Singer J. J., Walsh J. V., Jr Antagonistic adrenergic-muscarinic regulation of M current in smooth muscle cells. Science. 1988 Jan 8;239(4836):190–193. doi: 10.1126/science.2827305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansfeld C. E., Marsh S. J., Parcej D. N., Dolly J. O., Brown D. A. Mast cell degranulating peptide and dendrotoxin selectively inhibit a fast-activating potassium current and bind to common neuronal proteins. Neuroscience. 1987 Dec;23(3):893–902. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90166-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Physiological roles for adenosine and adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the nervous system. Neuroscience. 1981;6(4):523–555. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokimasa T., Akasu T. Cyclic AMP regulates an inward rectifying sodium-potassium current in dissociated bull-frog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Jan;420:409–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokimasa T., Akasu T. Extracellular calcium ions are required for muscarine-sensitive potassium current in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1990 Feb;29(2):163–174. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(90)90182-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji S., Minota S., Kuba K. Regulation of two ion channels by a common muscarinic receptor-transduction system in a vertebrate neuron. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Oct 16;81(1-2):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90354-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Calker D., Müller M., Hamprecht B. Adenosine regulates via two different types of receptors, the accumulation of cyclic AMP in cultured brain cells. J Neurochem. 1979 Nov;33(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


