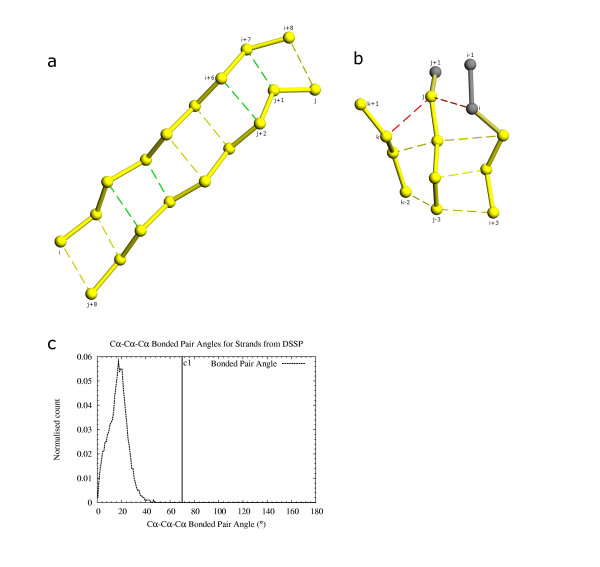
Figure 7.
Initiation and extension of ladders of paired residues using quadruplets. 7a: Ladders of paired residues are initiated and extended using quadruplets. The initiation quadruplets i+2, i+3, j+5, j+6 and i+6, i+7, j+1, j+2 are shown with green pairing. Quadruplets are attached on either side to extend the arms of the ladder. Addition of quadruplet i+4, i+5, j+3, j+4 joins the two ladders i, i+4, j+4, j+8 and i+5, i+8, j, j+3 to form the complete unit. Depending on the position of the best quadruplets any number of quadruplets might be responsible for seeding a ladder. Smaller ladder fragments get joined by worse scoring quadruplets. 7b: Residue pairing angle between residues on three β-strands (residue i+1, j-1, k-1 in fig. c) from DSSP output. Cutoff c1 (70°) is close to the largest angle observed. This was used to check new residue pairings formed while adding quadruplets. 7c: Checks performed during quadruplet addition and ladder extension. Quadruplet k, k-1, j-1, j and i, i+i, j-1, j share the common residues j-1 and j. Pairing and angle between pairs are checked for residues j-1 and j when worse scoring quadruplets are added. Quadruplet k, k-1, j-1, j scores better than i, i+1, j-1, j. While adding i, i+1, j-1, j it was found that the angle i, j, k fails the cutoff of 70° (fig. b). Quadruplet i, i+1, j-1, j is not added. Insertion of bulge residues is handled during joining of quadruplets. Quadruplets i+1, i+2, j-2, j-1 and i+2, i+3, j-3, j-2 share the common residues i+2, j-2. The quadruplets are simply added end to end. However, quadruplets j, j-1, k-1, k and j-2, j-3, k-2, k-1 (pairing between j-2, k-1 not shown) share only a single residue k-1. As j-2, j-3, k-2, k-1 scores worse than j, j-1, k-1, k, the pairing between j-1, k-1 is retained and residue j-2 becomes a bulge with respect to residue k-1.