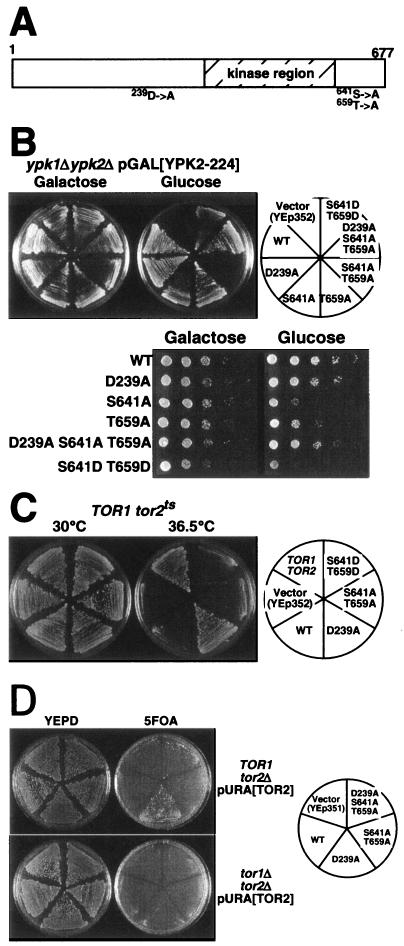
FIG. 4.
YPK2D239A overcomes mutation in cis, Tor2-dependent phosphorylation sites. A. Mutation sites of Ypk2. D239 is in a “TOS-like” conserved region, and S641 and T659 are in the turn motif and the hydrophobic motif (sites phosphorylated by Tor2), respectively. B. (Top) YPK2 genes (cloned into YEp352) harboring mutation at D239 or/and Tor2-phosphorylation sites as indicated (right) were transformed into YYK373 (ypksΔ p415GAL1[YPK2-224]). The transformants were grown on YEP galactose (Ypk2-224 expressed; left) or YEPD (Ypk2-224 not expressed; center) plates for 2 days at 30°C.(Bottom) Serial dilutions of the indicated transformants were spotted on SCgalactose-URA (left) and SCglucose-URA (right) and grown for 2 days at 30°C. C. A temperature-sensitive tor2-21 (SH121 [TOR1 tor2-21]) mutant was transformed with YEp352-based YPK2 plasmids as indicated (right) and grown on YEPD for 2 days at 30°C (left) or 36.5°C (center). Wild-type control cells (SH100 [TOR1 TOR2]) are also shown. D. YPK2 mutant genes were transformed into YYK353 (TOR1 tor2Δ pRS316[TOR2]) (top panel) and YYK357 (tor1Δ tor2Δ pRS316[TOR2]) (bottom panel) as indicated in the right panel, and the resultant transformants were grown on YEPD (left) and 5-fluoro-orotic acid (5FOA) plate (center) for 2 days at 30°C. On 5FOA plates, cells must lose the pRS316[TOR2] (harboring URA3 marker) plasmid to grow (19).