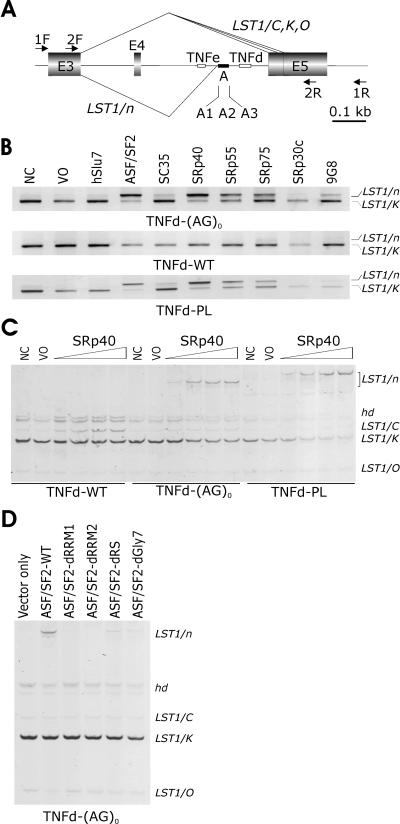
FIG. 1.
SR-dependent activation of a cryptic 3′ splice site in LST1. (A) Schematic representation of the LST1 minigene (to scale; scale units are kilobases). Exons are shown as shadowed boxes; introns are shown as lines. TNFe and TNFd are indicated by small open boxes; segment A is denoted by a closed rectangle. Arrows indicate primers. For a full genomic sequence of this region, see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material. Naturally occurring LST1 isoforms arising by alternative 3′ ss and designated LST1/C, LST1/K (53), and LST1/O (this study) are shown above the minigene, whereas cryptic 3′ ss activation generating LST1/n is shown below. The location of the alternative 3′ ss of intron 4 was as described in reference 53 (and see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). (B) Cryptic 3′ ss activation in cells overexpressing SR proteins in constructs lacking TNFd. LST1 reporters are shown below each panel, and LST1 RNA products are shown to the right. LST1/K is a predominant isoform in peripheral blood mononuclear cells generated by alternative 3′ ss of intron 4 (53). WT, wild-type; NC and VO; no-cotransfection and vector-only controls, respec-tively. No-template controls are not shown. (C) SR-dependent upregulation of LST1/n and LST1/C. We used 0.5 μg of each reporter plasmid together with 0.1, 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 μg of plasmids expressing SRp40. Hd, heteroduplexes. (D) Binding of ASF/SF2 to the pre-mRNA is essential for the LST1/n formation. d, deletion of ASF/SF2 domains RRM1, RRM2, and RS or a heptaglycine repeat (Gly7). LST1 isoforms described above are shown on the right side.