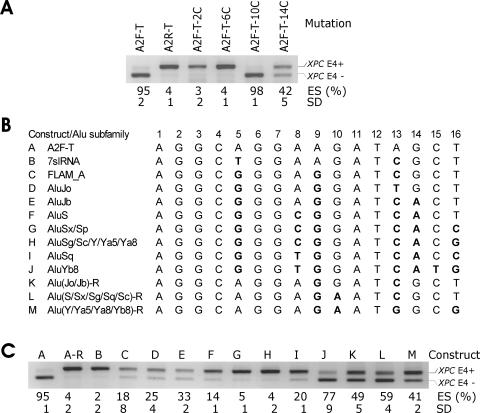
FIG. 4.
Characterization of splicing silencer A2. (A) The influence of A2 mutations in four AGs on exon inclusion. The splicing reporter constructs are shown at the top. Guanine-to-cytosine mutations are in positions shown in panel B. ES, exon skipping as a ratio of transcripts lacking exon 4 (E4−) to the sum of E4− and E4+ transcripts. SD, standard deviation of two transfection experiments. (B) Alignment of LST1 segment A2 with consensus sequences of Alu subfamilies. Mutations (in bold) that corresponded to sequence variations in the subfamilies were introduced in segment A2 inserted in the XPC-T construct in the sense orientation. The designation of Alu subfamilies was as described previously (2, 37). (C) Influence of A2 variants representing Alu subfamilies on inclusion of XPC exon 4 in mRNA. Constructs A to M shown at the top correspond to mutations listed in Fig. 4B. A-R, constructs with segment A2 inserted in the antisense orientation.