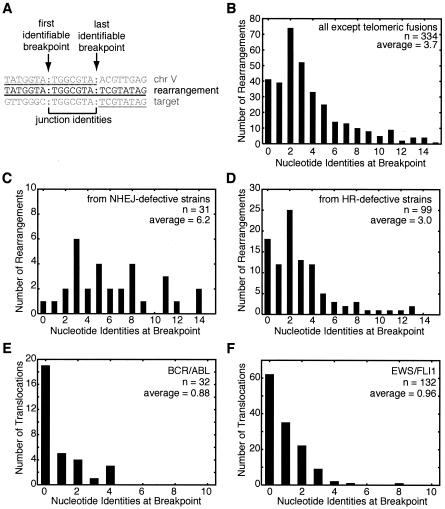
FIG. 2.
Rearrangement structure and distribution of identities at the junctions. (A) The rearrangement breakpoint positions can be ambiguous if there are regions of identity between chromosome V and the target sequence. The example rearrangement sequence (middle) is aligned with the chromosome V (top) and target (bottom) sequences. Contiguous matches to the rearrangement are underlined. Colons indicate breakpoint positions defined by two systematic methods. The last identifiable chromosome V breakpoint is the last nucleotide that matches the chromosome V sequence from the database; this method forces the nucleotide after the last identifiable breakpoint to never match the chromosome V sequence. The first identifiable target breakpoint is at the first nucleotide which could have come from the target; hence, there is no identity of the target with the nucleotide before the first identifiable breakpoint. (B) Distribution of breakpoints by the number of nucleotide identities between chromosome V and the target chromosome for the 334 rearrangements not involving fusions to the heterogeneous telomeric sequences. (C) Distribution of identity lengths for breakpoints from strains with mutations in genes involved in NHEJ (lig4 or yku70). (D) Distribution of identity lengths for breakpoints from strains with mutations in genes involved in HR (rad51, rad52, rad54, rad55, rad59, or rdh54). (E) Analysis of breakpoint identities at the genomic junctions of BCR/ABL fusions from leukemias suggesting that these translocations are formed by NHEJ. Breakpoints for both products of the reciprocal translocations, the der(9) and der(22) chromosomes, were combined from previous published studies (20, 21, 25, 41, 57, 98, 108, 113). (F) Analysis of EWS fusions to FLI1 (n = 113) and other targets, including ERG (n = 3), E1AF (n = 2), ZSG (n = 1), and CHOP (n = 1), from Ewing's sarcomas and other cancers suggesting that these translocations were formed by NHEJ. Breakpoints from both derivative chromosomes were included when available. Breakpoint sequence data were taken from previous reports (7, 30, 46, 66, 75, 77, 81, 114).