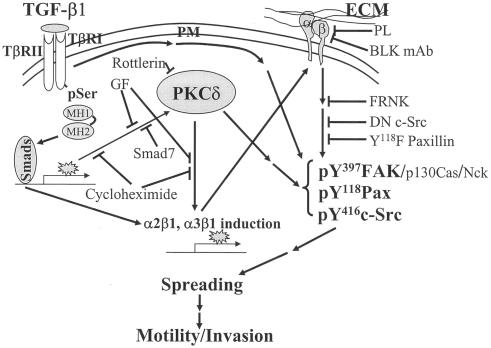
FIG. 9.
Schematic working model of the TGFβ1-, PKCδ-, and integrin-mediated cellular functions in gastric carcinoma cells. TGFβ1 treatments of cells on ECMs lead to increased expression and phosphorylation of PKCδ, cell surface levels of integrins α2 or α3, and activation of the focal adhesion molecules. This signaling network results in spreading, migration, and invasion of the SNU16mAd gastric carcinoma cell variant. In addition to a linear connection, presumably additional bypassing connections may contribute to the TGFβ1 effects.