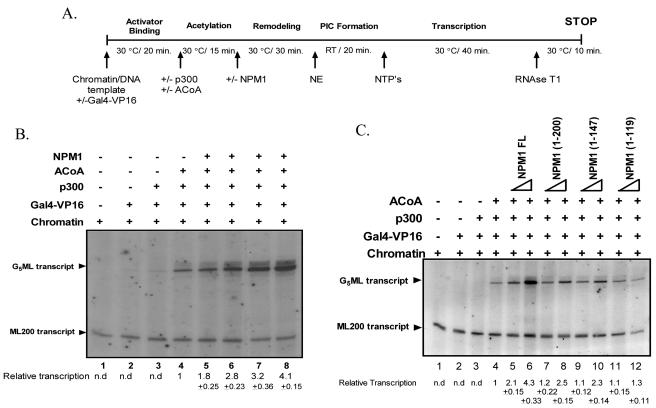
FIG. 3.
Nucleophosmin stimulates acetylation-dependent chromatin transcription. (A) Schematic representation of the in vitro transcription protocol. RT, room temperature; PIC, preinitiation complex. (B) Freshly assembled chromatin (28 ng) was subjected to the protocol described for panel A. NPM1 stimulates chromatin transcription in a dose-dependent manner. Lane 1, without activator; lanes 2 through 8, with Gal4-VP16 (50 ng); lanes 3 through 8, with p300 (25 ng); lanes 4 through 8, with acetyl-CoA (ACoA; 1.5 μM); lanes 5 through 8, 1, 10, 30, and 50 pmol of full-length NPM1, respectively. (C) Freshly assembled chromatin (28 ng) was subjected to the protocol described for panel A. Lane 1, without activator; lanes 2 through 12, with Gal4-VP16 (50 ng); lanes 3 through 12, with p300 (25 ng); lanes 4 through 12, with acetyl-CoA (1.5 μM). Lanes 5, 7, 9, and 11, have 5 pmol and lanes 6, 8, 10, and 12 have 30 pmol of full-length (FL) NPM1 or the respective deletion mutants added as indicated. The relative transcription per lane (in severalfold activation over the acetylation-dependent transcription lane [lane 4]) was determined by phosphorimage analysis (Fuji) and presented under each lane along with the standard deviation. n.d., not determined.