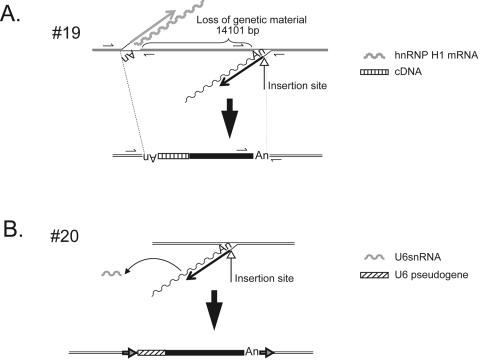
FIG. 2.
cDNA additions at the 5′ genomic DNA/L1 junction. A. A processed pseudogene/L1 chimera. Insertion 19 was accompanied by the addition of a 5′-truncated cDNA copy of hnRNP H1 mRNA, which is located in the opposite transcriptional orientation of the L1. The undulating and straight gray lines represent hnRNP H1 mRNA and hnRNP H1 minus-strand cDNA, respectively. The undulating and straight black lines represent L1 mRNA and minus-strand L1 cDNA, respectively. Recombination between the resultant cDNAs resulted in a genomic deletion of approximately 14.1 kb. The structure of the hnRNP H1/L1 chimera is shown at the bottom of the figure. The striped and black rectangles indicate the integrated hnRNP H1 and L1 cDNAs, respectively. Double black lines indicate flanking genomic DNA. “An” indicates the poly(A) tail at the ends of the hnRNP H1 and L1 cDNAs. Small arrows indicate the positions of PCR primers used to characterize the insertion. B. A U6/L1 chimera. Insertion 20 was accompanied by the addition of a full-length U6 cDNA copy in the same transcriptional orientation as the L1. The undulating and straight black lines represent L1 mRNA and minus-strand L1 cDNA, respectively. The gray undulating line indicates U6 snRNA. The structure of the resultant chimera is shown at the bottom of the figure. The striped and black rectangles indicate the integrated U6 and L1 cDNAs, respectively. Double black lines indicate flanking genomic DNA. “An” indicates the poly(A) tail at the end of the L1 cDNA. Horizontal arrows indicate TSDs that flank the chimera.