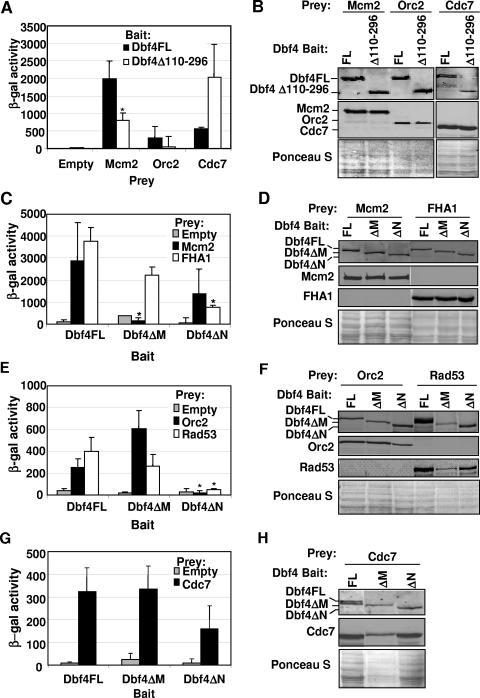
FIG. 2.
Two-hybrid analysis of Dbf4 variant interactions with replication and checkpoint factors. (A) Two-hybrid assays using bait constructs pEG-Dbf4-FL and pEG-Dbf4Δ110-296 along with pJG-Mcm2, pJG-Orc2, pJG-Cdc7, and empty pJG 4-6 as prey vectors were carried out as described in Materials and Methods. Relative β-galactosidase activity is shown and represents the average of at least three trials. Error bars represent standard deviations. The asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05; paired Student's t test) in the signal for Dbf4Δ110-296 relative to Dbf4FL. Insufficient trials were conducted to perform this analysis for the Cdc7 prey set. (B) To confirm that all baits and preys were properly expressed, culture aliquots were removed just prior to the measurement of β-galactosidase activity, and whole-cell extracts were prepared and subjected to immunoblot analysis. Bait proteins were detected with rabbit polyclonal anti-LexA antibody (Invitrogen), and prey proteins were detected with mouse monoclonal anti-HA antibody (Sigma). Ponceau S staining of the membrane to confirm equal loading of whole-cell extracts is shown. (C, E, and G) Two-hybrid assays were carried out as described above by using pEG-Dbf4FL, pEG-Dbf4ΔM, and pEG-Dbf4ΔN as bait, with pJG 4-6, -Mcm2, -FHA1, -Orc2, -Rad53, and -Cdc7 preys. Relative β-galactosidase activities are shown and in each case represent the average of three trials. Error bars represent standard deviations. Asterisks indicate those two-hybrid interactions with significant differences at a P level of <0.05. In each case the values obtained with Dbf4ΔM or Dbf4ΔN are compared to the equivalent interaction using Dbf4FL as bait. (D, F, and H) Confirmation of protein expression as described above.