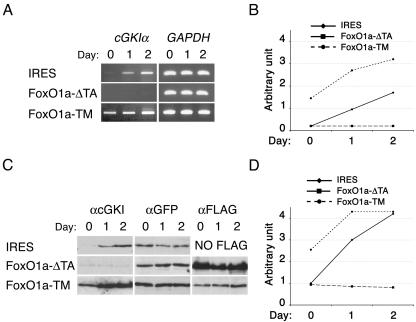
FIG. 2.
FoxO1a activation induces cGKIα transcription during primary myoblast differentiation. (A) RT-PCR analyses of cGKIα expression in primary myoblasts transduced with MSCV-IRES-GFP retrovirus vectors containing either no insert (IRES), FoxO1a-ΔTA (dominant negative), or FoxO1a-TM (dominant active). cGKIα was amplified using specific primers, and amplification of GAPDH mRNA was used to normalize mRNA levels. Following the induction of differentiation by transfer of the myoblasts to a low-serum medium (5, 30), cGKIα mRNA levels increased twofold in vector-transduced cells. Primary myoblasts expressing FoxO1a-ΔTA showed no increase in cGKIα expression, whereas myoblasts expressing FoxO1a-TM showed elevated expression of cGKIα. (B) Graph showing the induction of cGKIα transcripts in proliferating (day 0) and differentiating (days 1 and 2) myoblasts transduced with either the empty vector, FoxO1a-ΔTA, or FoxO1a-TM. Expression levels were normalized to GAPDH expression. (C) Western blot analysis of cGKI expression. Protein loading was controlled using an anti-GFP antibody. The expression of exogenous FoxO1a mutants was detected using an anti-FLAG antibody. (D) Graphic representation of the induction of cGKIα protein expression in the indicated myoblasts, normalized for expression of GFP.