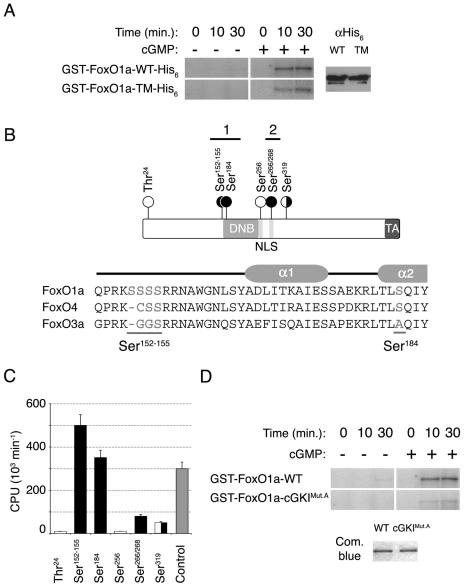
FIG. 5.
cGKIα phosphorylates FoxO1a in vitro. (A) Full-length GST/His6 double-tagged wild-type (WT) FoxO1a and FoxO1a-TM show similar levels of in vitro phosphorylation by cGKIα. Equal amounts of protein were used in the kinase assays, as assessed by anti-His6 immunoblotting. cGKIα did not phosphorylate GST alone (data not shown). (B) Schematic of the FoxO1a transcription factor shows the locations of the residues phosphorylated by cGKIα (black circles) and Akt (white circles). The Forkhead DNA binding domain (DNB), NLS, and transactivation domain (TA) are also indicated (not drawn to scale). A sequence alignment of the N-terminal portions of the DNA binding domains of the three FoxO transcription factors is also shown. Residues phosphorylated by cGKIα are underlined. A schematic of helices α1 and α2 of the Forkhead DNA binding domain is shown above the sequences. (C) Quantification of in vitro phosphorylation of FoxO1a peptides. The bar graph shows the identified cGKIα sites (black) as well as Akt sites (white), in comparison with a positive-control peptide that is a substrate for cGKIα (gray). Means are given for at least three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate with each peptide. Error bars show the variance at each data point. (D) Equal amounts of full-length GST-tagged wild-type FoxO1a and FoxO1a-cGKIMut.A (Ser152-155/184Ala) were phosphorylated in vitro by cGKIα. Note the marked reduction in phosphorylation of FoxO1a-cGKIMut.A compared to that of wild-type FoxO1a, demonstrating that these serine residues are the major targets of cGKIα.