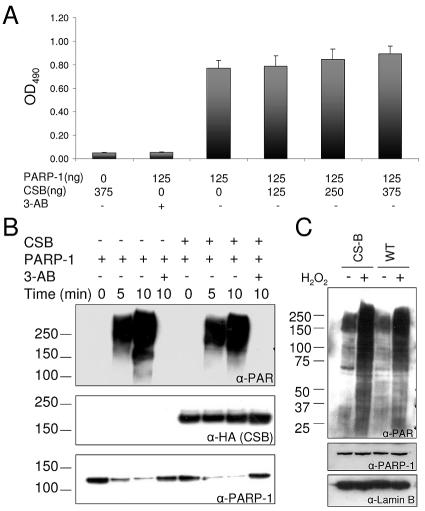
FIG. 6.
CSB does not regulate the PARP-1 poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation activity. (A) ELISA plates were coated with histone H1, and after blocking, CSB (125 to 375 ng) and PARP-1 (125 ng) were added to the indicated wells in 50 μl poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation reaction mix in either the presence or absence of 3-AB. The poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation reaction was stopped after 5 min, and the PAR polymer was detected with polyclonal PAR antibodies and colorimetric analysis. (B) Recombinant PARP-1 (20 ng/μl) and CSB (20 ng/μl) were mixed in ribosylation reaction mix, as indicated, in either the presence or absence of 10 mM 3-AB. After incubation for 5 or 10 min, the reactions were stopped and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blot. The same membrane was probed, stripped, and reprobed with the indicated antibodies. Top panel, monoclonal PAR antibodies. Middle panel, monoclonal HA antibodies (recognizes the N-terminal tag on CSB). Bottom panel, monoclonal PARP-1 antibodies. The migration of the molecular weight marker is illustrated on the left side. (C) CS1AN/CSBwt (WT) and CS1AN/vector (CS-B) cells were either mock treated or incubated with 250 μM H2O2 in PBS for 10 min to activate PARP poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation activity in vivo and subsequently analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blot. Top panel, PAR antibodies. Middle panel, monoclonal PARP-1 antibodies. Bottom panel, polyclonal goat lamin B antibodies. The same membrane was probed with the three different antibodies. The migration of the molecular weight marker is illustrated on the left side.