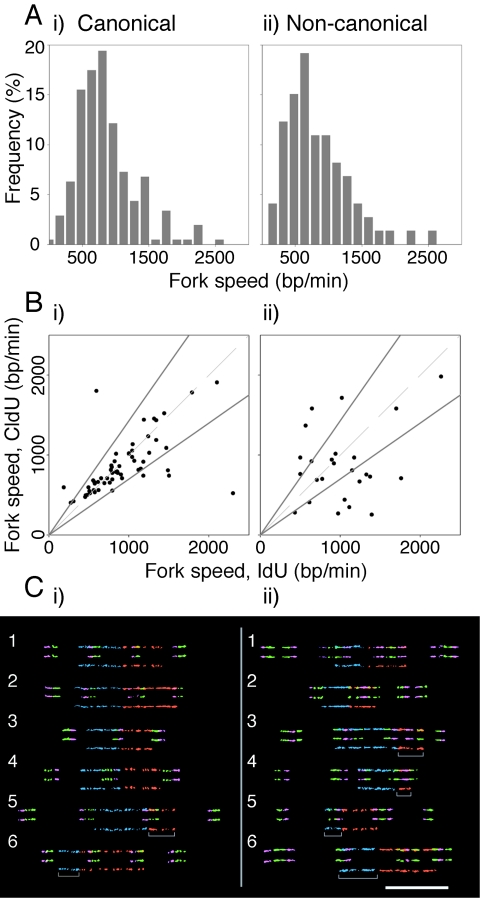
FIG. 4.
Effect of noncanonical rRNA genes on fork progression. (A) Histograms showing fork speed distributions for canonical (i) and noncanonical (ii) rRNA genes. (B) Fork speeds based on IdU and CldU tracts from single forks plotted against each other for canonical (i) and noncanonical (ii) rRNA genes. The dashed gray lines represent equal speeds calculated from IdU and CldU labels of the same length. The two solid lines represent thresholds that allow for a 30% difference in fork speed between the IdU and CldU pulses. (C) Forks with speed information available from both IdU and CldU labels. Molecules 1 to 4 for canonical rRNA genes (i) and molecules 1 and 2 for noncanonical rRNA genes (ii) contain IdU and CldU tracts of approximately the same length. Molecules 5 and 6 (i) and 3 to 6 (ii) are examples of data excluded by the thresholds established in panel B. They have IdU and CldU replication tracts from single forks that differ by >30%. The gray open rectangles indicate the regions of fork stalling.