FIG. 2.
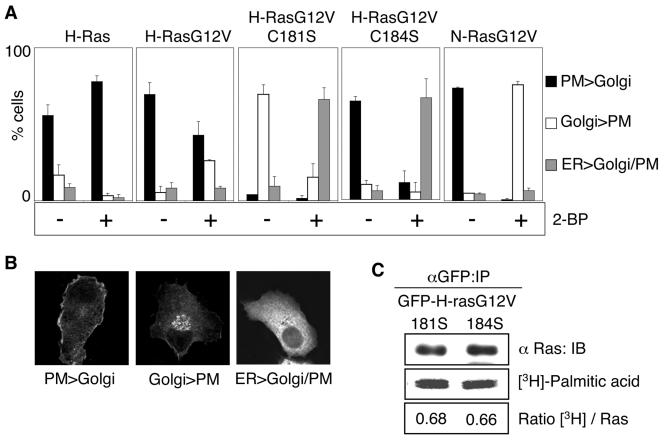
Inhibiting palmitoylation causes redistribution of H-ras monopalmitoylated mutants to the ER. A. BHK cells stably transfected with GFP-ras proteins were pretreated for 2 h with cycloheximide to inhibit de novo protein synthesis. Cells were then incubated for 3 h in cycloheximide with or without 2-BP. The cells were visualized in a confocal microscope and scored for predominant plasma membrane (PM), Golgi, or endoplasmic reticulum (ER) localization. Examples of typical cells scored in these three categories are shown in panel B. At least 300 cells were evaluated from three independent experiments for each Ras protein. C. BHK cells transiently expressing GFP-H-rasG12V C181S or GFP-H-rasG12V C184S were labeled with [3H]palmitic acid in the presence of cycloheximide. Duplicate anti-GFP immunoprecipitates prepared from whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted for Ras input and fluorographed for [3H]palmitic acid. Blots and scans were quantified, and the ratio of [3H]palmitic acid units per Ras unit was calculated. Representative blots and 3H scans are shown. The ratios of [3H]palmitic acid/Ras (in arbitrary units) for H-rasG12V C181S and H-rasG12V C184S, respectively, were 0.68 ± 0.01 and 0.66 ± 0.04 (means ± standard errors of the means, n = 3). IP, immunoprecipitation. IB, immunoblot.