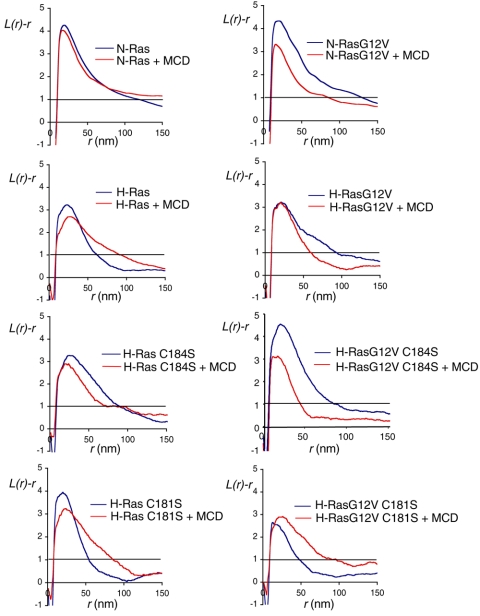
FIG. 3.
The plasma membrane microlocalization of monopalmitoylated H-rasG12V C184S emulates that of GFP-N-rasG12V. Apical plasma membrane sheets from BHK cells transiently expressing GFP-ras proteins were labeled with anti-GFP antibodies coupled directly to 4-nm gold. Where indicated, cells were incubated with 1% β-methyl-cyclodextrin for 30 min to deplete cell surface cholesterol. The immunogold point patterns were analyzed using Ripley's K-function. The graphs show weighted mean K-functions (n = 8 to 17 sheets) standardized on the 99% confidence interval (CI) for complete spatial randomness. The average number of gold particles per plasma membrane sheet evaluated was 939 μm−2. In this analysis a pattern is significantly clustered if the L(r) − r curve leaves the CI (i.e., is >1), whereas in a random pattern the L(r) − r approximates to 0 for all values of r (for examples see references 37 and 42). Differences between control and cholesterol-depleted membranes were evaluated for each construct using bootstrap tests. A statistically significant effect of cholesterol depletion is seen on the clustering of GFP-H-ras (P = 0.017), GFP-N-rasG12V (P = 0.039), and GFP-H-rasG12V C184S (P = 0.001).