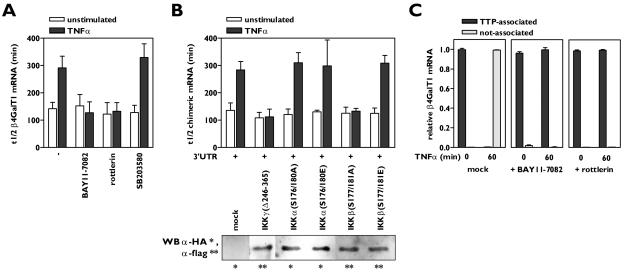
FIG. 2.
Activation of both IKKβ and PKCδ by TNF-α is required for β4GalT1 mRNA stabilization. (A) Inhibitors of IKK (BAY11-7082) and PKCδ (rottlerin) antagonize TNF-α-induced β4GalT1 mRNA stabilization, while the p38 inhibitor SB203580 has no effect. HUVECs were treated with various inhibitors as indicated, before the half-life of β4GalT1 mRNA was determined as described in the legend to Fig. 1B. The graphs (relative β4GalT1 mRNA expression versus time after the addition of ActD) for the determination of the half-lives are available in Fig. S2A in the supplemental material. (B) IKK activity is required but not sufficient to reduce the β4GalT1 mRNA turnover. Dominant-interfering [IKKγ(Δ246-365), IKKα(S176/180A), and IKKβ(S177/181A)], and kinase-active [IKKα(S176/180E), IKKβ(S177/181E)] mutants of IKK components were overexpressed in HeLa TO cells expressing chimeric mRNA containing the wt β4GalT1 3′UTR. Its half-life was determined as in the results shown in Fig. 1C. The graphs (relative chimeric mRNA expression versus time after addition of DOX) for the determination of the half-lives are available in Fig. S2B in the supplemental material. The overexpression of flag- or HA-tagged IKK mutants was checked by Western blotting with anti-flag and anti-HA antibodies as described in Materials and Methods. (C) Inhibitors of either IKK or PKCδ (BAY11-7082 and rottlerin, respectively) block the TNF-α-induced release of binding of TTP from β4GalT1 mRNA. RNA/immunoprecipitation assays were performed on HUVECs in either the absence or presence of inhibitors as described in the legend to Fig. 1D.